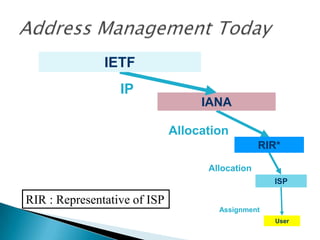
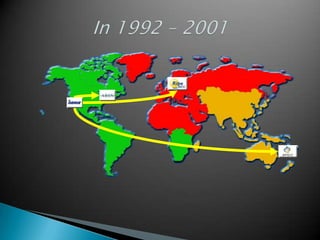
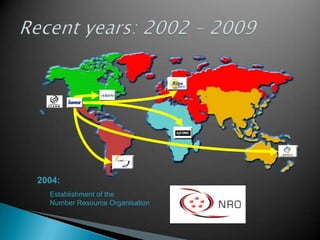
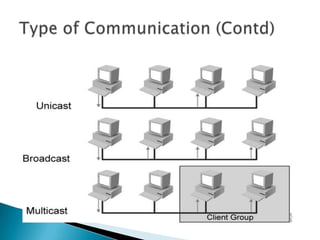
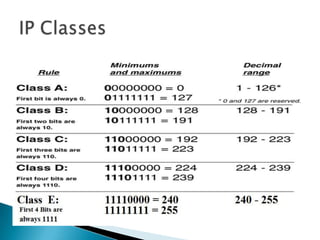
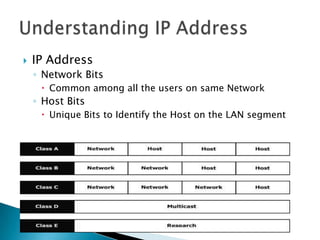
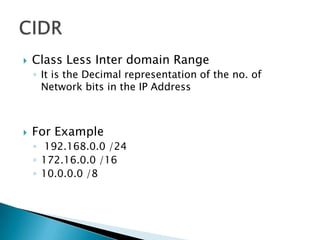
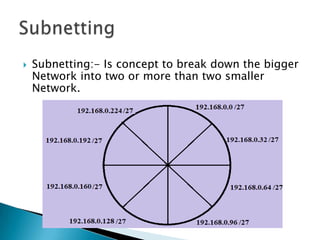
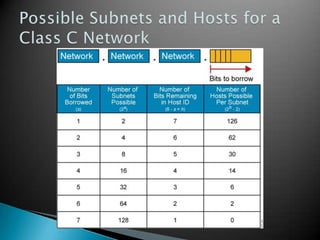
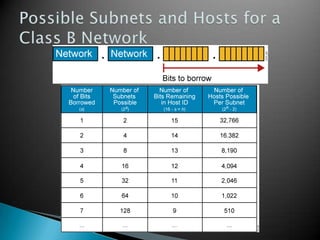
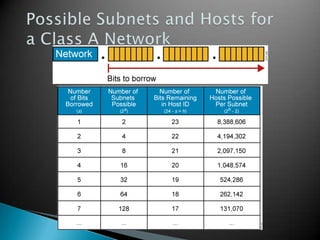
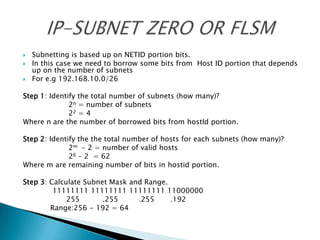
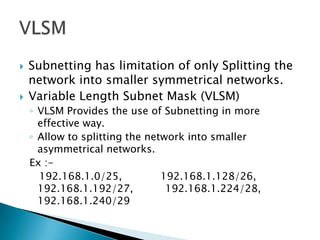
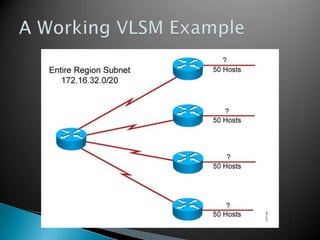
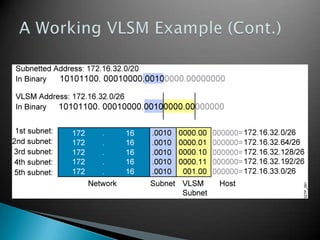
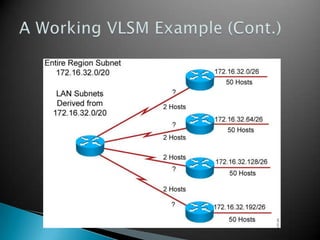
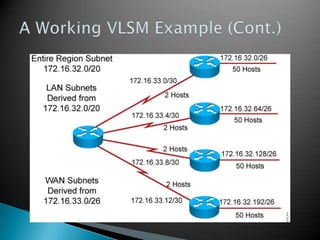
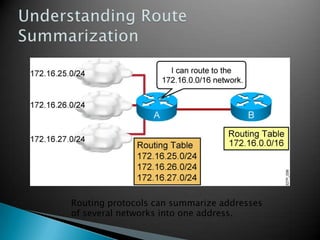
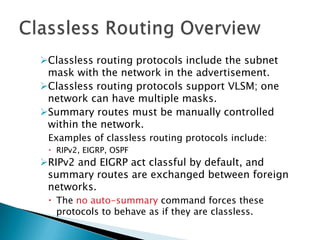
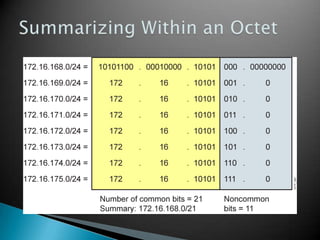
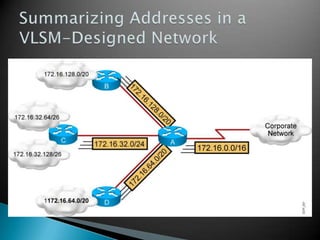
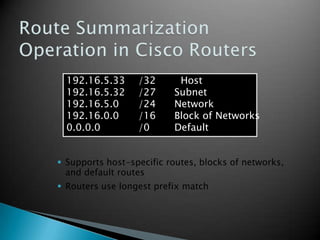
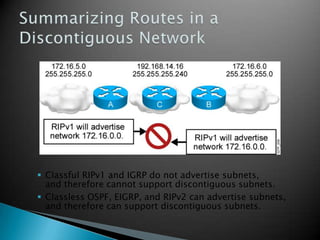
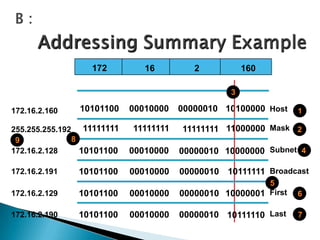
IP addresses are assigned to devices to identify them on a network. Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) manage and allocate IP addresses and resources regionally. There are currently five RIRs that oversee different global regions. IP addresses are represented as 32-bit numbers that are broken into network and host portions through the use of subnet masks. Subnetting and Variable Length Subnet Masking (VLSM) allow networks to be divided into smaller subnets in an efficient manner. Route summarization helps reduce routing table sizes.