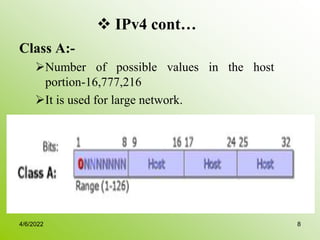
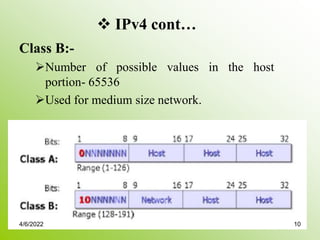
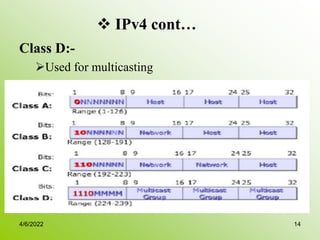
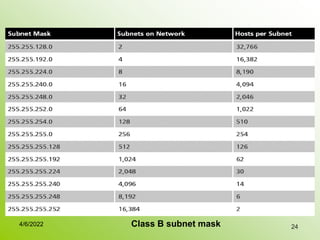
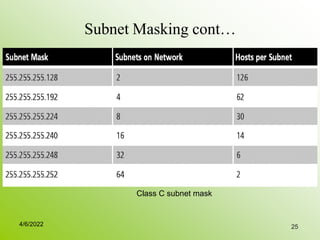
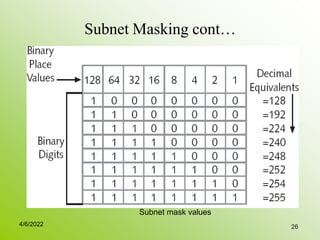
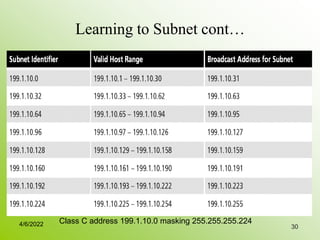
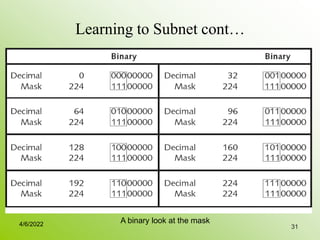
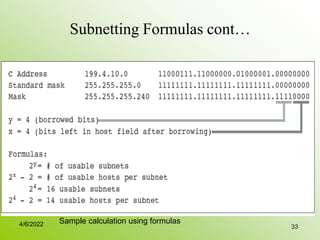
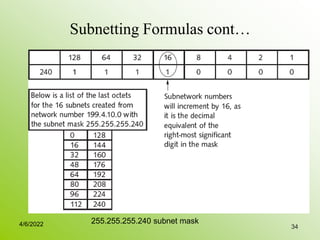
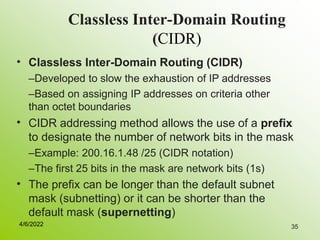
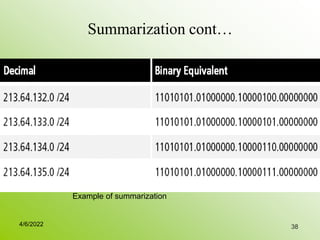
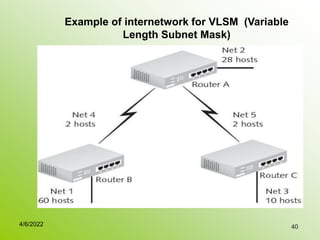
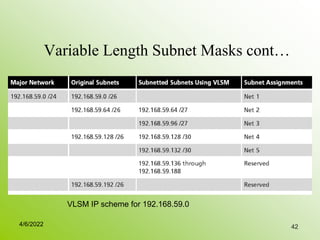
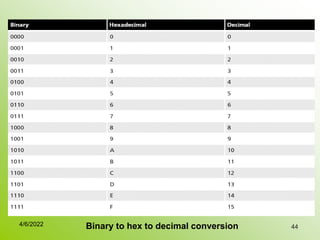
IPv4 addresses identify devices on the internet and consist of 32 bits represented by 4 octets separated by periods. Addresses include a network ID and host ID portion, with the division determined by the address class (A, B, C, etc). Class A uses 8 network bits and 24 host bits, Class B uses 16 network bits and 16 host bits, and Class C uses 24 network bits and 8 host bits. Subnetting and CIDR allow networks to be further subdivided to introduce subnets and supernetting.