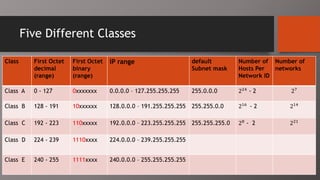
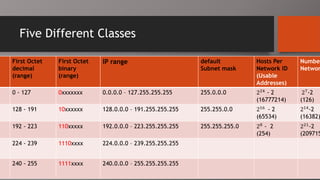
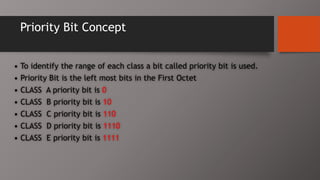
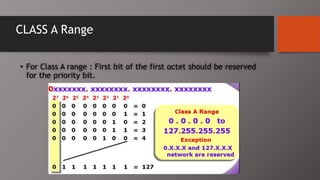
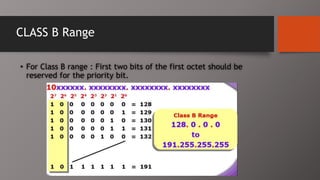
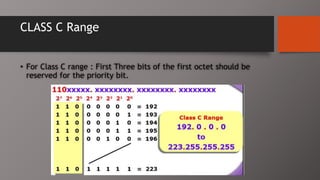
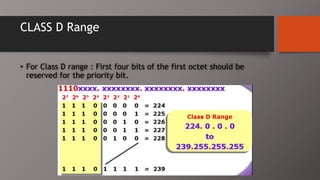
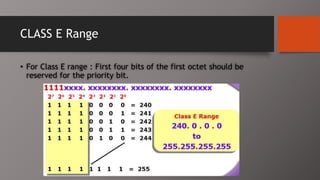
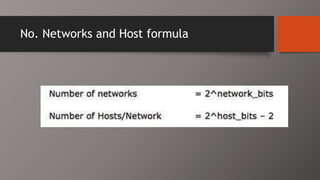
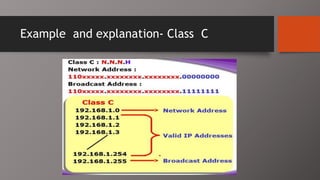
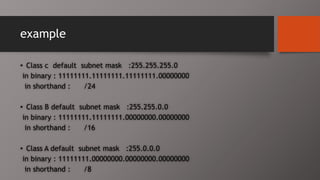
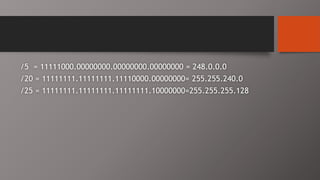
The document details the classification of IP addresses into five classes (A to E) based on their first octet, along with their corresponding ranges, subnet masks, and the number of hosts and networks per class. It explains key concepts including priority bits for each class and the significance of network and broadcast addresses. Additionally, the document covers private IP address ranges and the purpose of subnet masks in determining network connectivity.