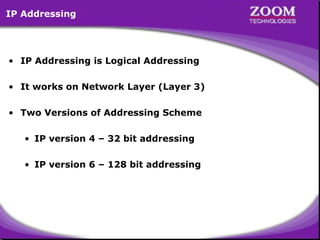
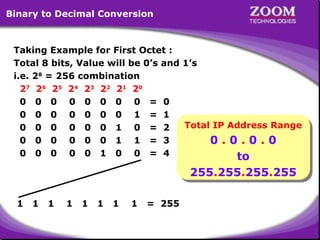
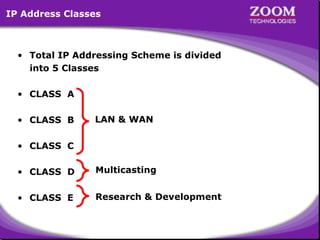
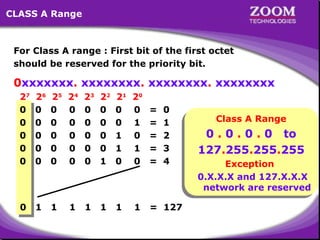
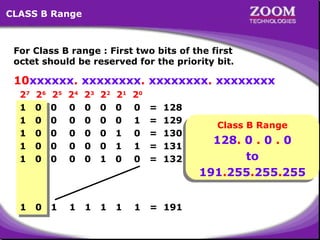
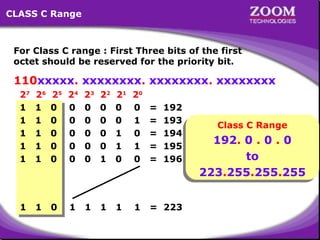
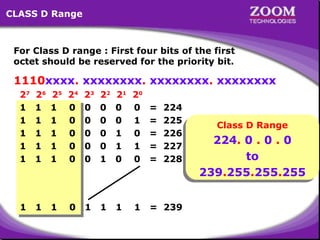
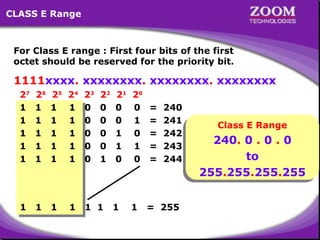
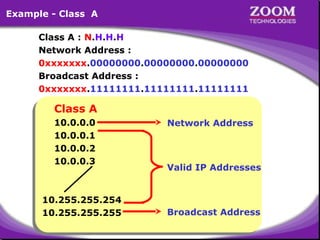
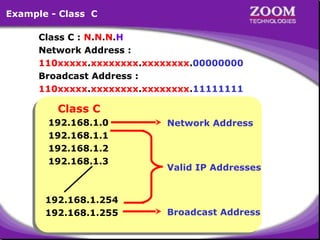
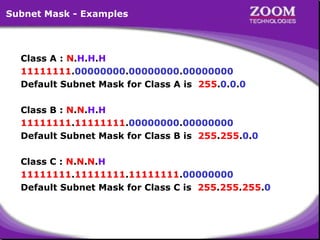
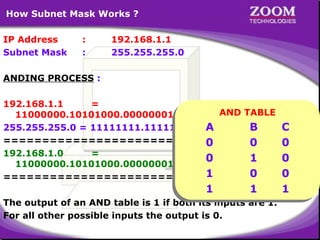
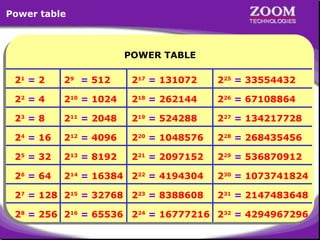
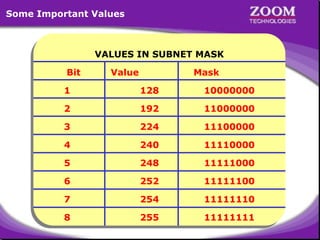
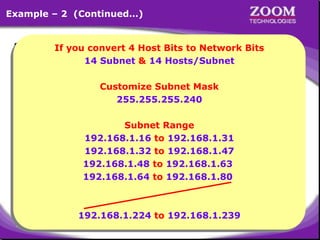
The document outlines IP addressing, covering versions IPv4 and IPv6, including their structures, classes (A, B, C, D, E), and ranges. It explains the concept of subnetting, subnet masks, network and broadcast addresses, and provides detailed classifications for private IP addresses. Additionally, it discusses how to manage network segmentation and host allocation effectively.