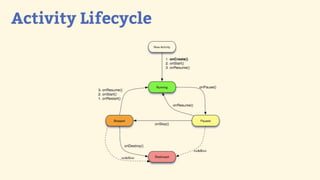
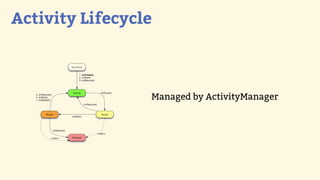
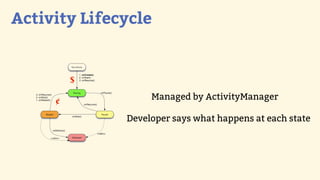
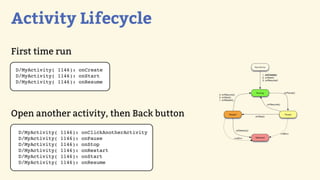
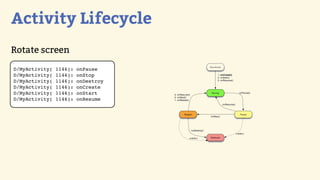
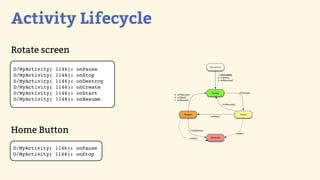
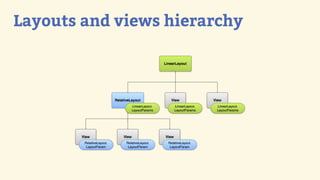
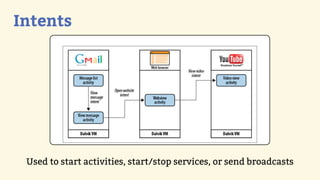
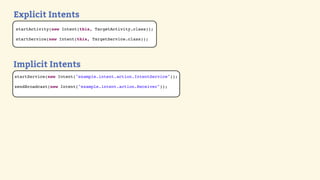
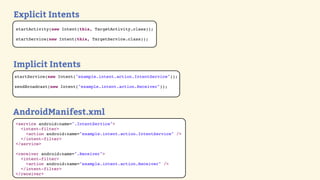
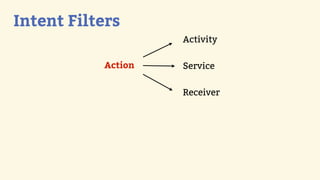
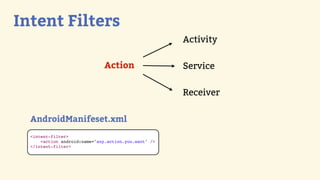
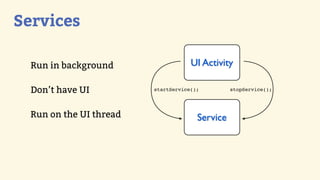
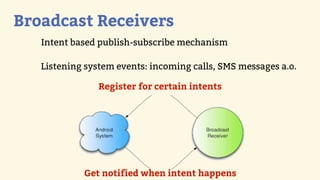
This document provides an introduction to Android development, covering key concepts like activities, intents, services, and broadcast receivers. It explains that activities represent screens in an app and make up the user interface. The activity lifecycle and how to declare activities are described. Intents are used to start activities, services, and send broadcasts. Services run in the background without a UI, and broadcast receivers allow apps to listen for system events and intents. Examples of implementing services and broadcast receivers are also provided.