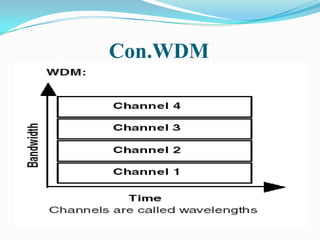
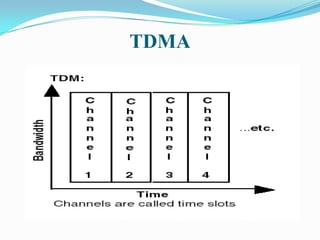
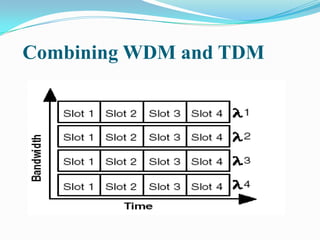
This document discusses wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) and how it can be combined with time-division multiplexing (TDM). It explains that WDM separates different channels by assigning each a unique optical wavelength, similar to how frequency-division multiplexing separates channels by frequency. When combining WDM with TDM, fixed time slots are assigned to each wavelength, allowing multiple users to share the bandwidth of a single wavelength. Most optical networks today use this combination of WDM and TDM technologies to efficiently transmit multiple signals simultaneously over one fiber.