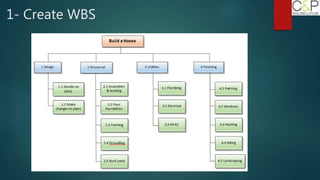
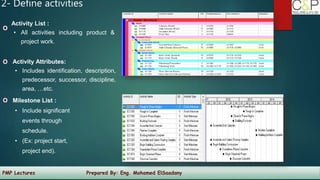
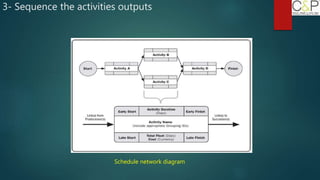
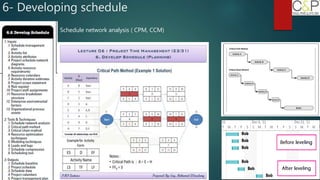
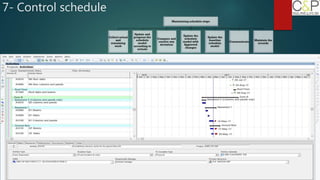
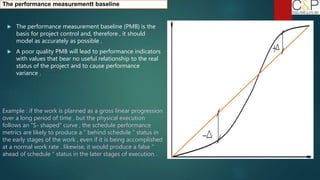
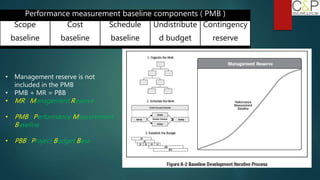
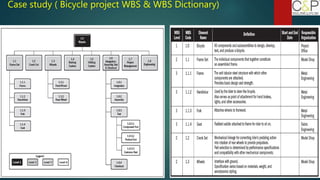
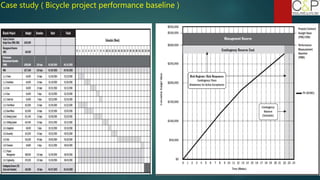
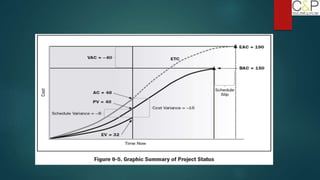
The document provides an introduction to project management, detailing methodologies such as PMBOK, Six Sigma, and Agile. It outlines the project scheduling process, including activity definition, resource allocation, and performance measurement using a performance measurement baseline (PMB). Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of accurate baseline modeling to prevent discrepancies in project status reporting.