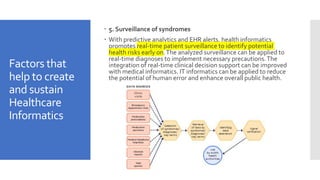
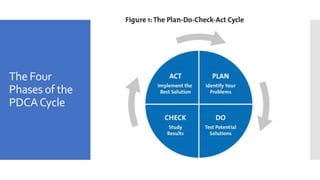
This document provides information on quality improvement strategies, protocols, and evidence-based healthcare. It discusses principles of designing information systems and strategies for evaluating them. It also covers quality improvement tools like the PDCA cycle and factors that help create and sustain healthcare informatics as a new field. The learning objectives are outlined on quality improvement tools, factors to create healthcare informatics, and understanding the PDCA cycle. The introduction defines quality and different approaches to defining it. Six criteria for right healthcare are also mentioned.