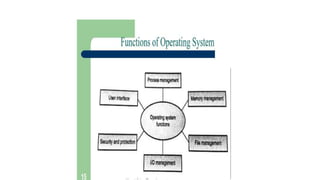
This document provides an introduction to operating systems. It discusses that an operating system acts as an interface between the user and computer hardware, with key functions like executing programs and managing resources efficiently. It describes the popular types of operating systems like Windows, Linux, and Android. It also gives a brief history of operating systems from the earliest generation with no OS to later developments like multiprocessing and distributed systems.