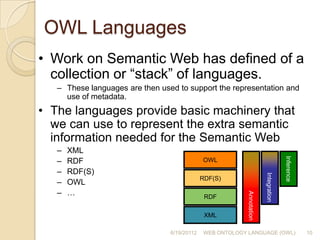
The document discusses the Web Ontology Language (OWL). It provides an overview of OWL, describing its three sublanguages - OWL Lite, OWL DL, and OWL Full - and their increasing expressiveness and reasoning complexity. The document also reviews the requirements for ontology languages and how OWL builds upon XML, RDF, and RDF Schema as the ontology language for the Semantic Web.