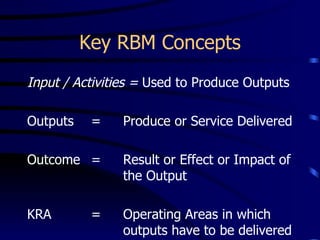
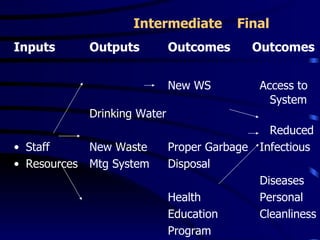
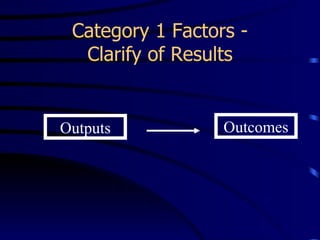
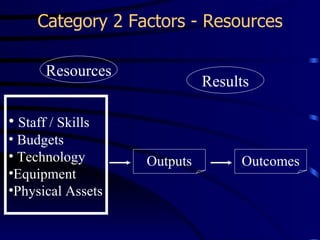
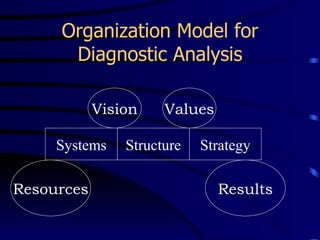
This document provides an introduction to Results Based Management (RBM). It began in the 1960s and was adopted by many countries in the 1980s and 1990s. RBM focuses on tangible results, resource allocation, and value. Key concepts include inputs, activities, outputs, and outcomes. Performance is measured by indicators like effectiveness, efficiency, equity, and sustainability. RBM is integral to capacity building by driving continuous improvement through performance information. The diagnostic approach begins with performance analysis to identify gaps and determine constraining variables to develop an organizational development plan.