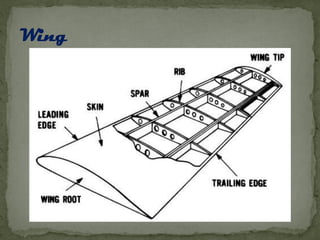
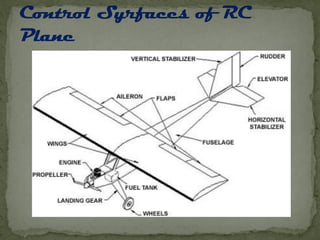
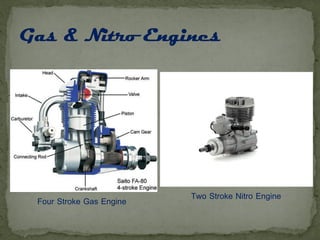
The document provides an overview of different types of radio-controlled (RC) planes including trainer, sport, aerobatic, 3D, gliders, jet planes, and helicopters, specifying their features and characteristics. It also discusses materials used in construction (such as balsa wood, foam, and fiberglass) and components needed for operation, including engines, servos, and batteries. Specifications vary among plane types, emphasizing factors like wing design, speed, and maneuverability.