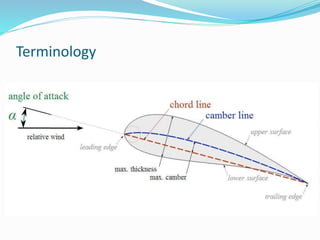
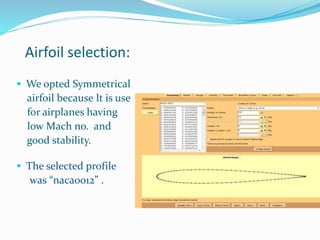
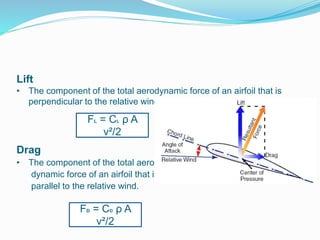
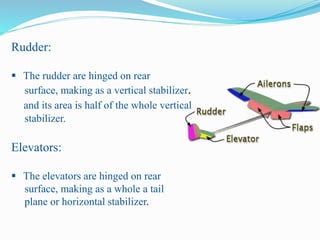
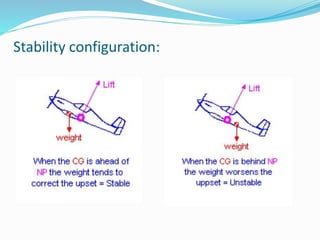
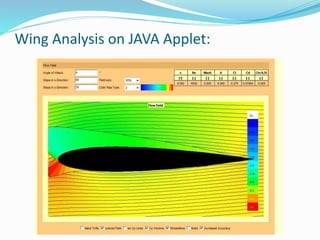
This document summarizes the design of a remote controlled aircraft. It discusses selecting a symmetrical airfoil with a NACA0012 profile for its low speed stability. It describes control surfaces like ailerons and elevators. Calculations are shown for wing area based on lift and drag coefficients. A CATIA model and flow simulation were also created. The design focuses on stability concepts like neutral point, center of pressure, and aerodynamic center. References include aerodynamics textbooks and software used like JAVA, Flow Design, and CATIA V5.