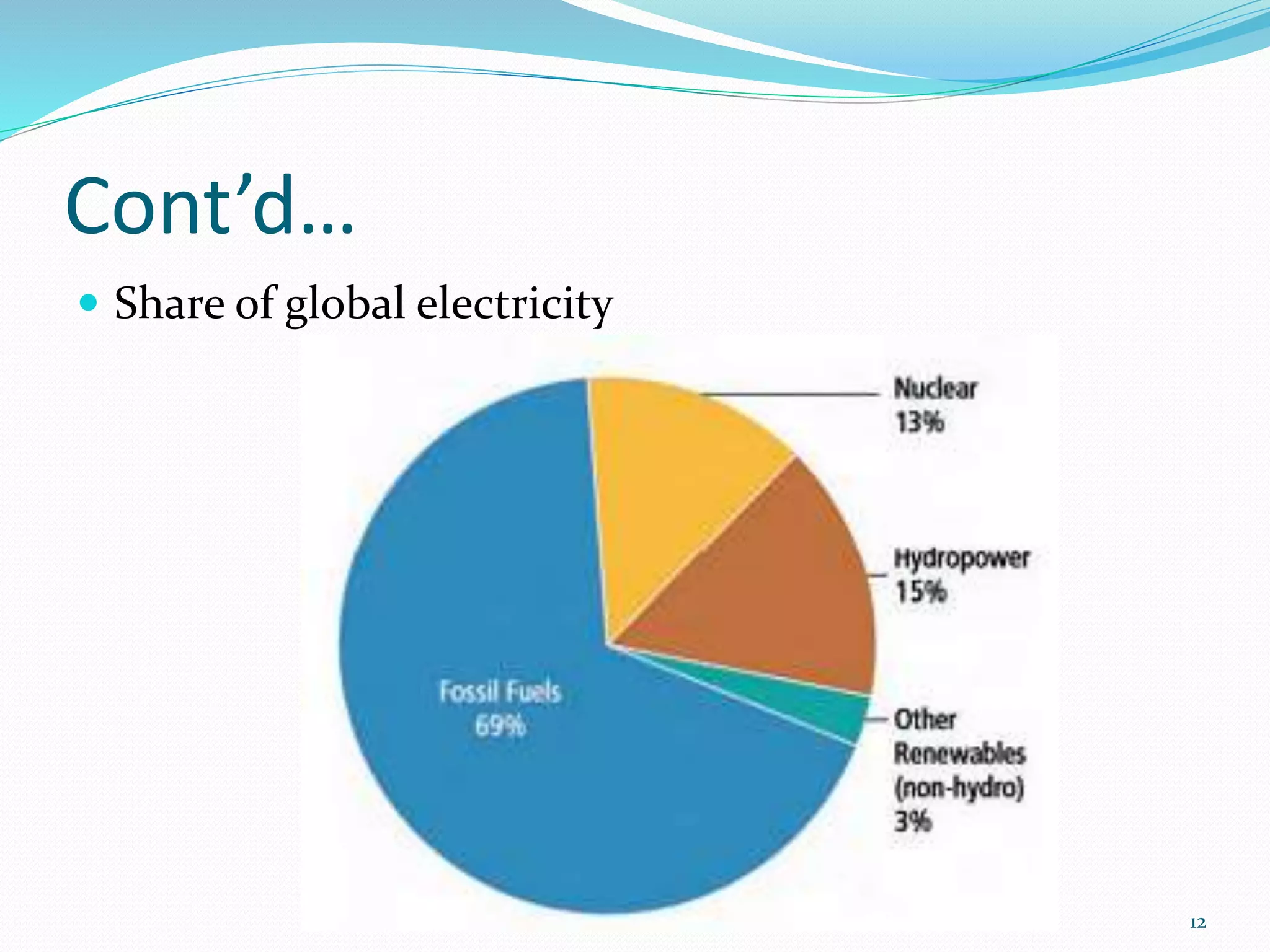
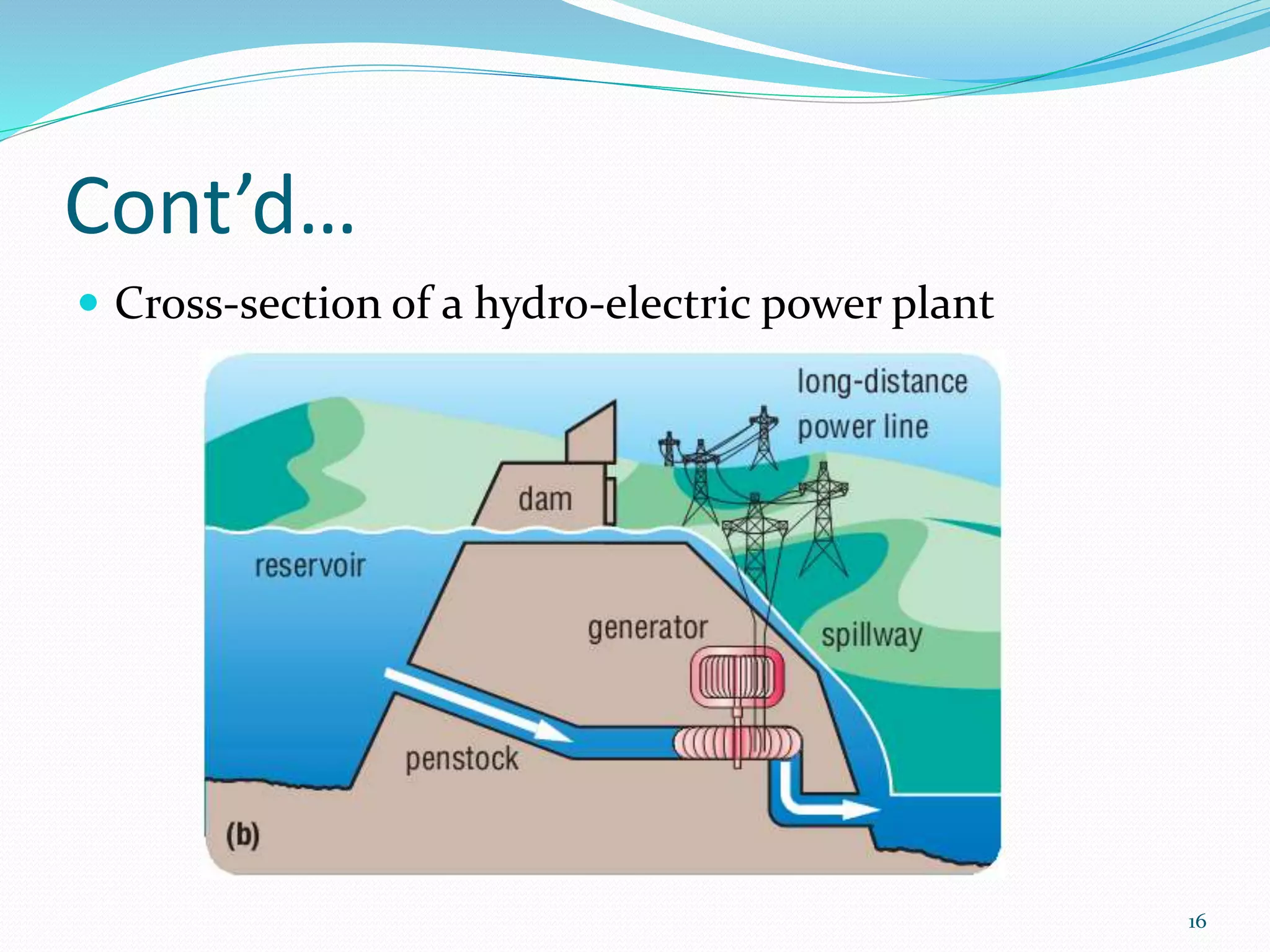
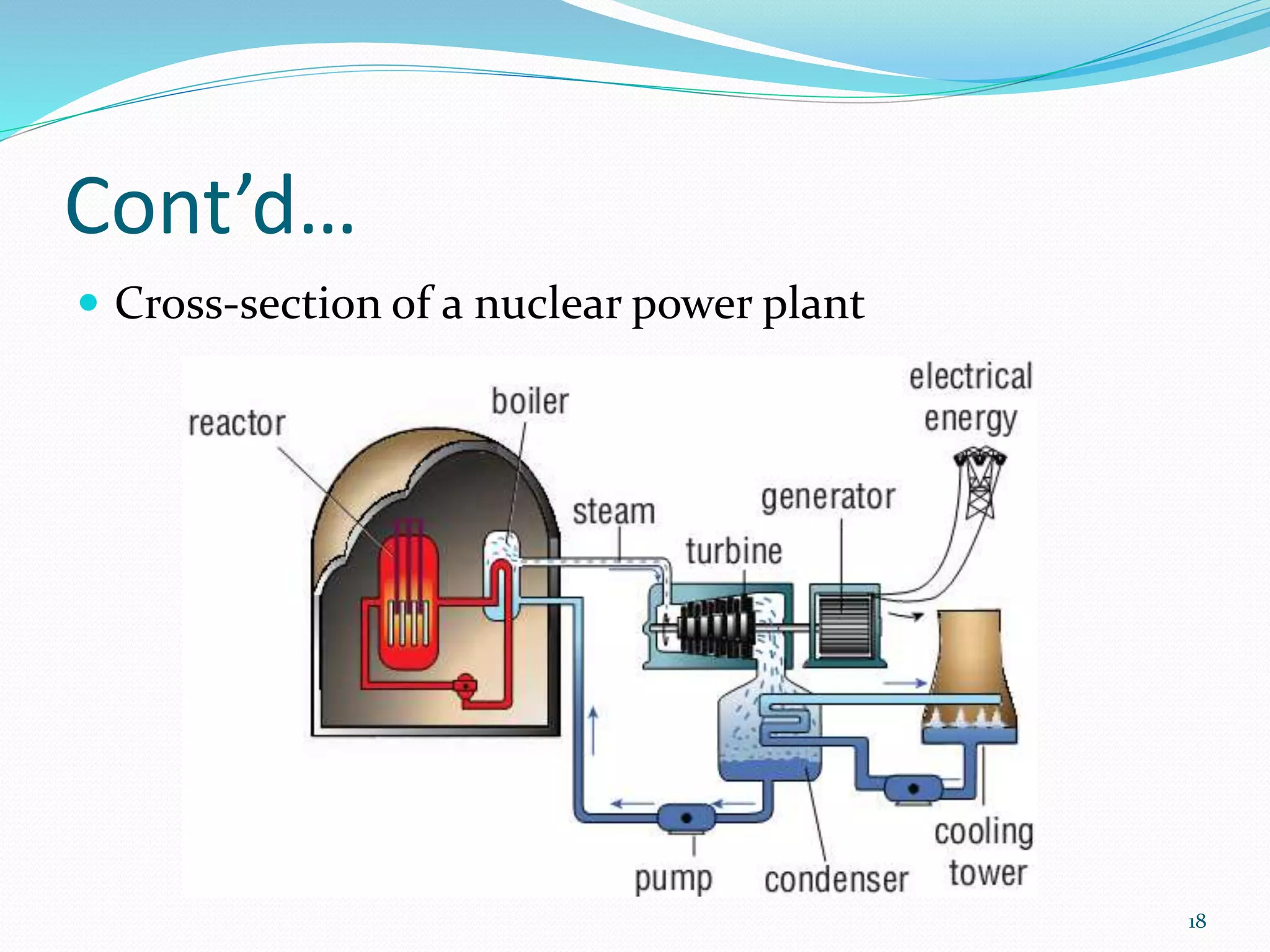
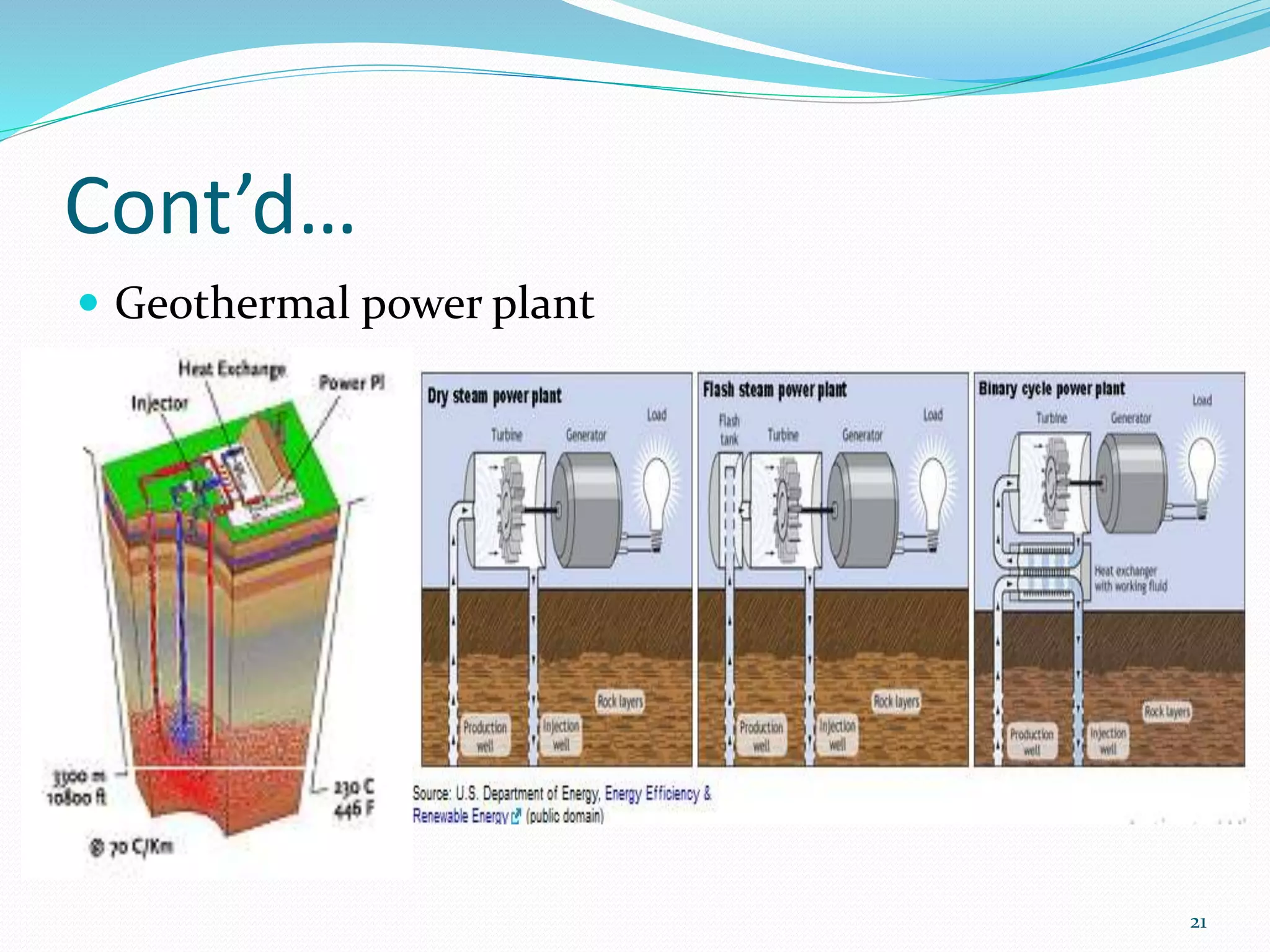
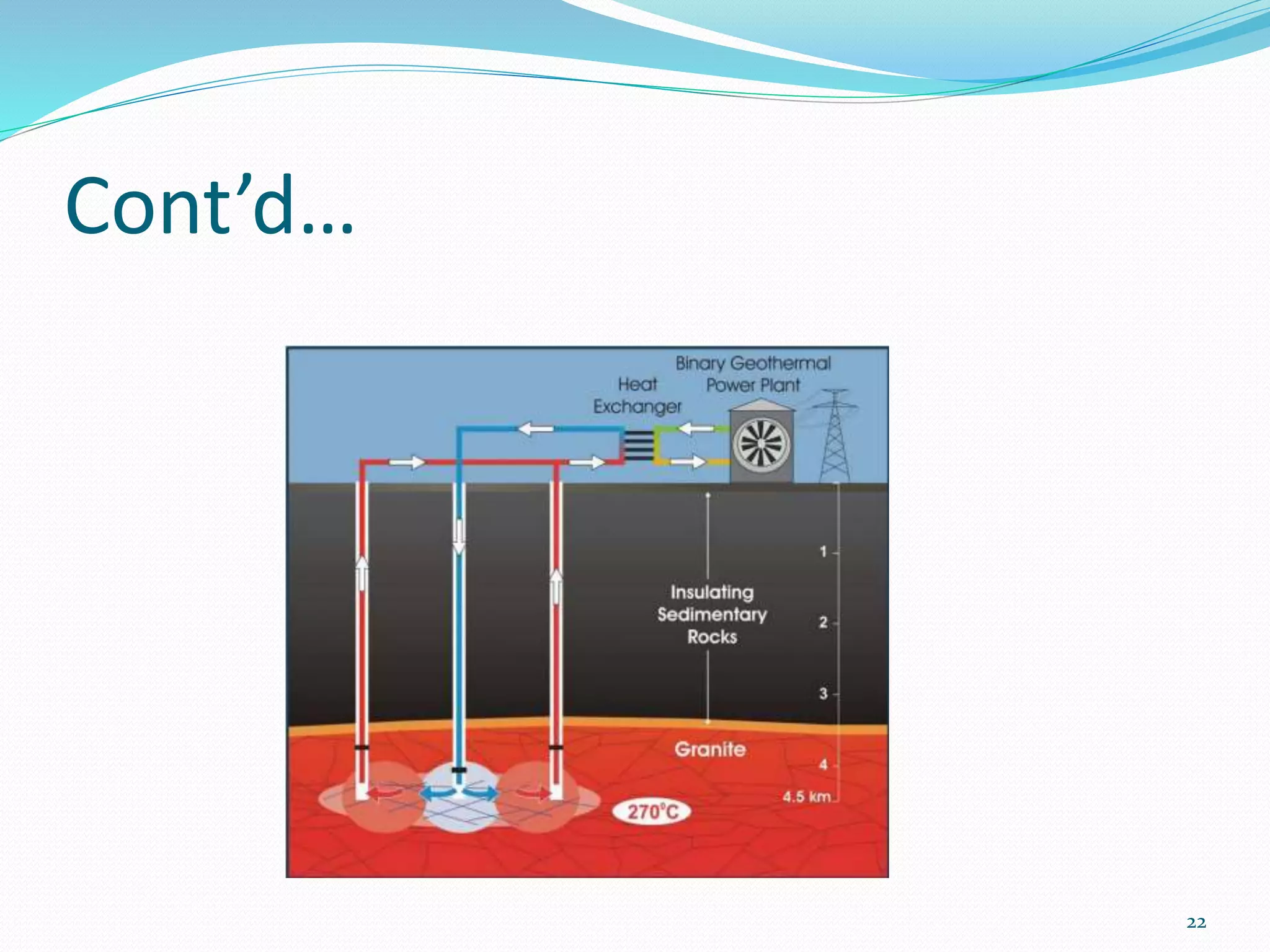
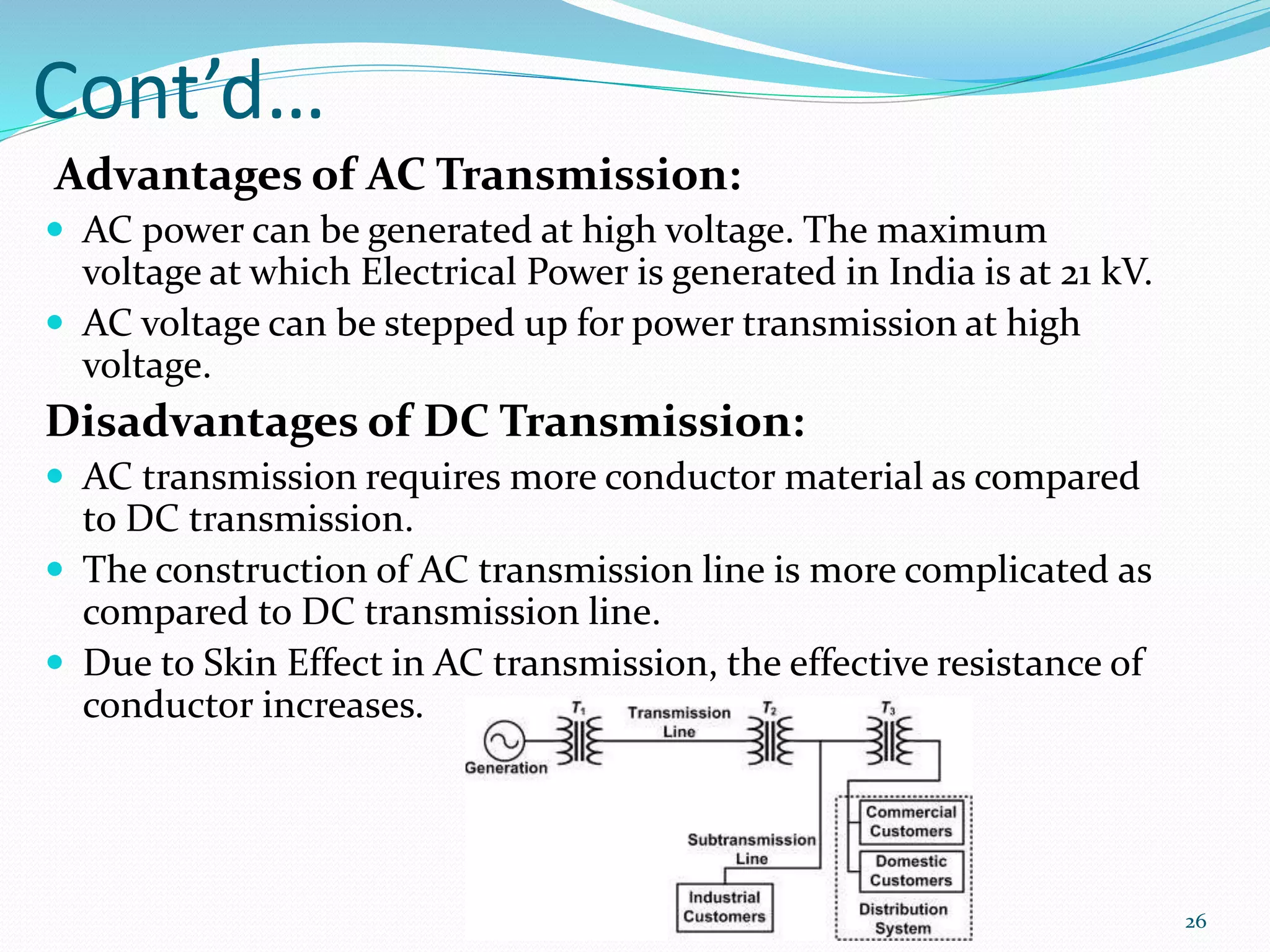
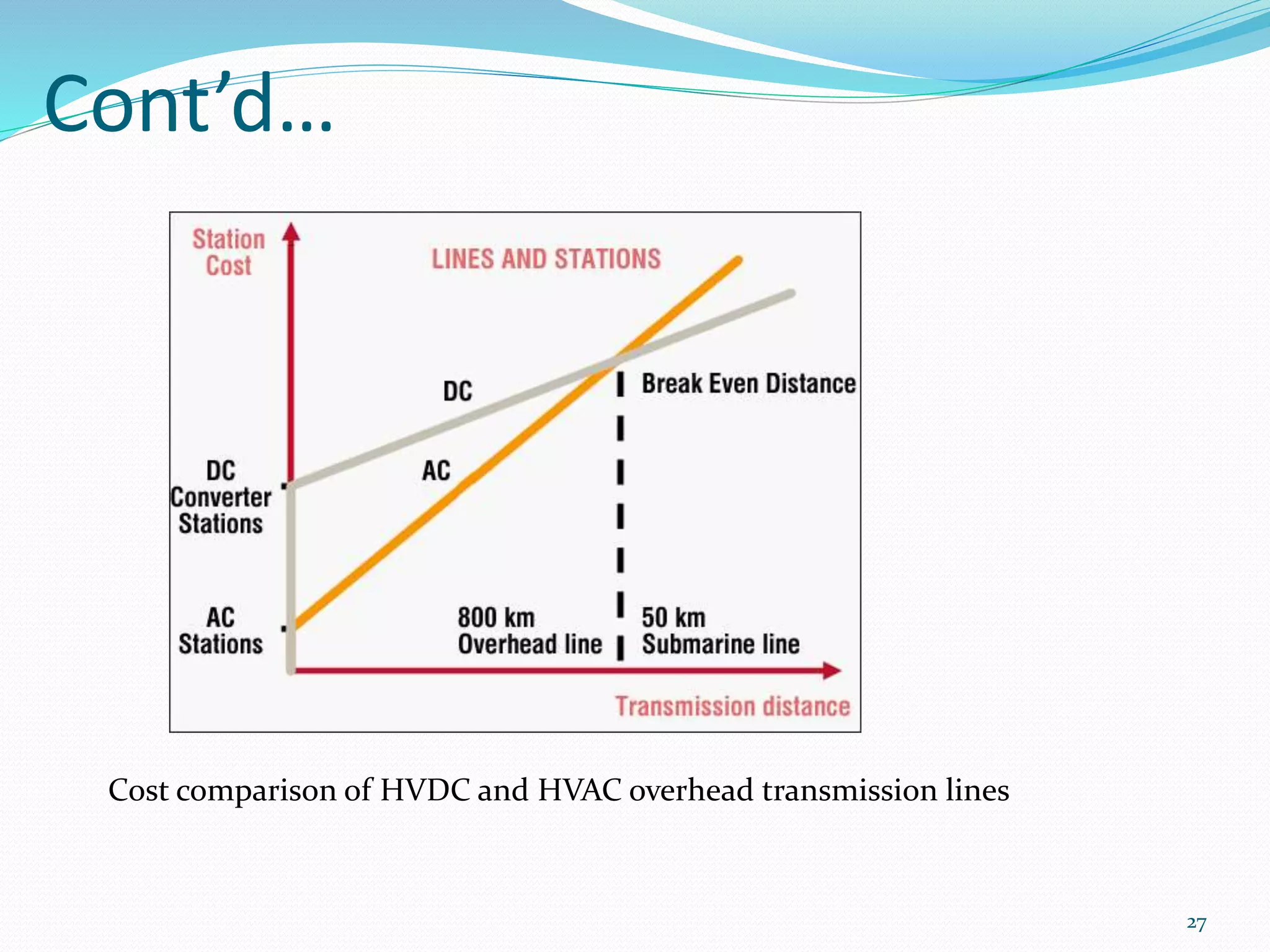
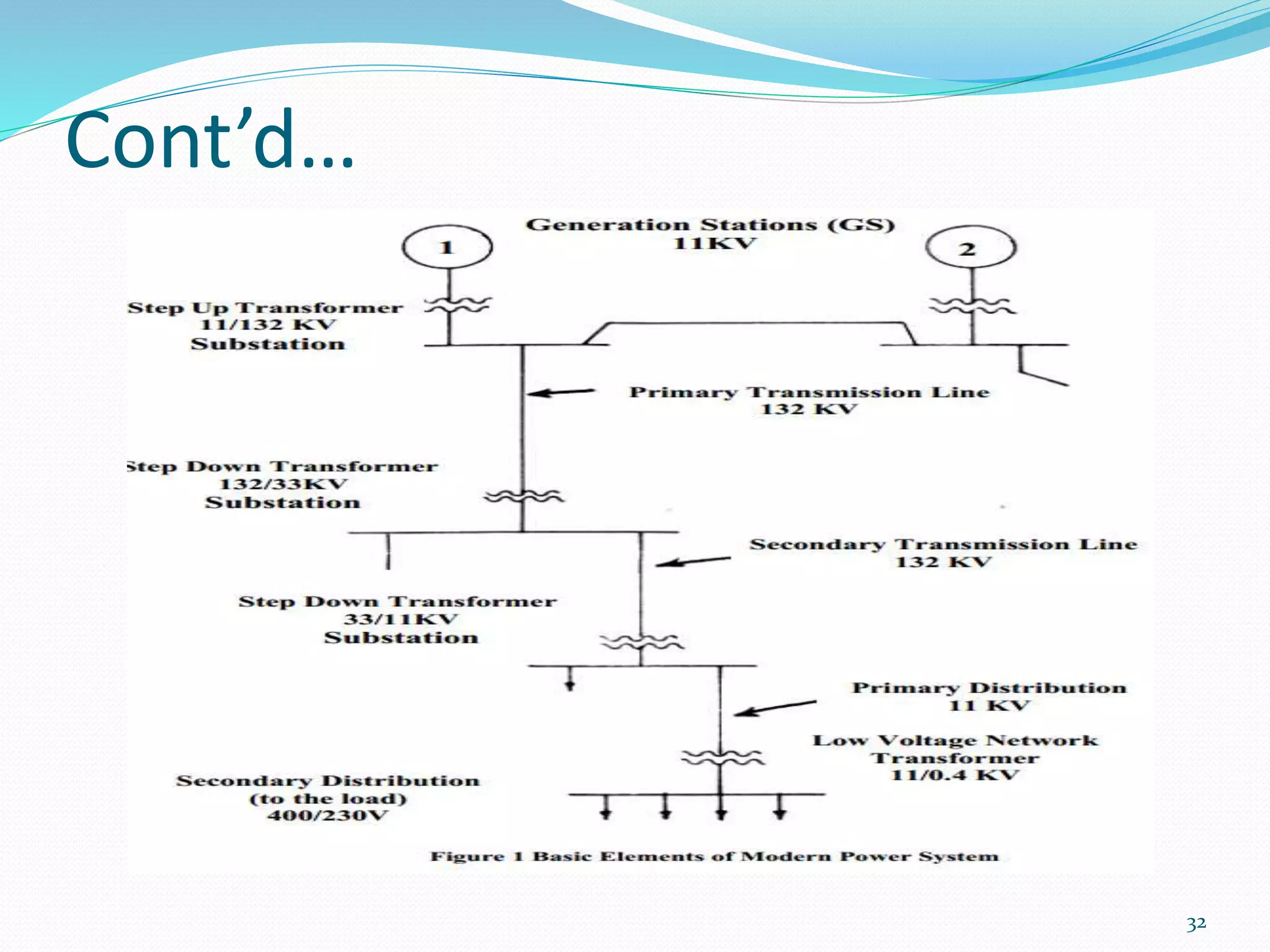
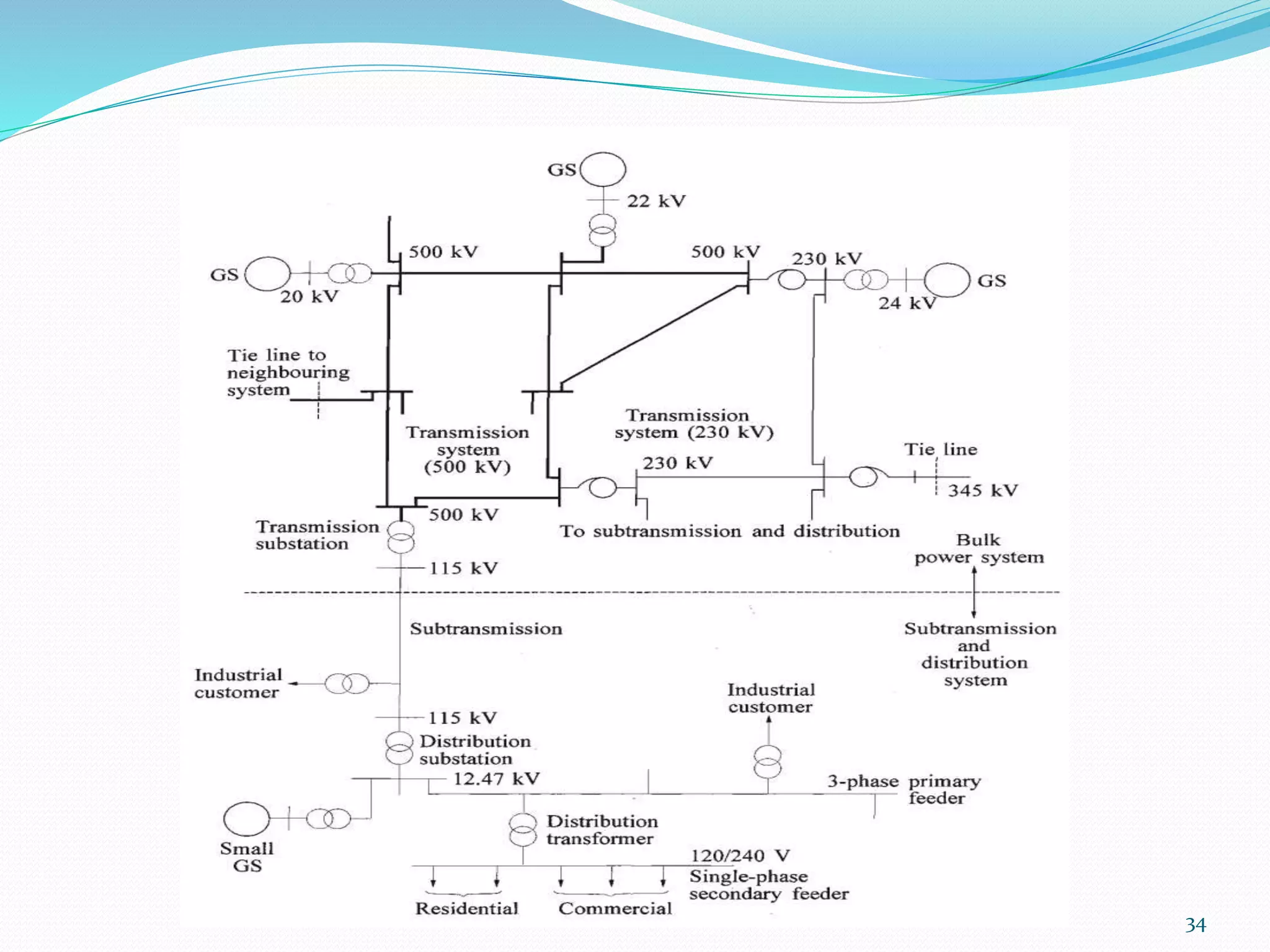
The document traces the evolution of electric power systems from Thomas Edison's first system in 1882 to modern systems. Key developments include the introduction of AC power which allowed transmission over longer distances, standardization of frequencies and voltages, increasing use of higher voltages for transmission, and integration of different energy sources like fossil fuels, nuclear, and renewables. Modern power systems have generation, transmission, sub-transmission and distribution components to supply, transfer and deliver electricity reliably.