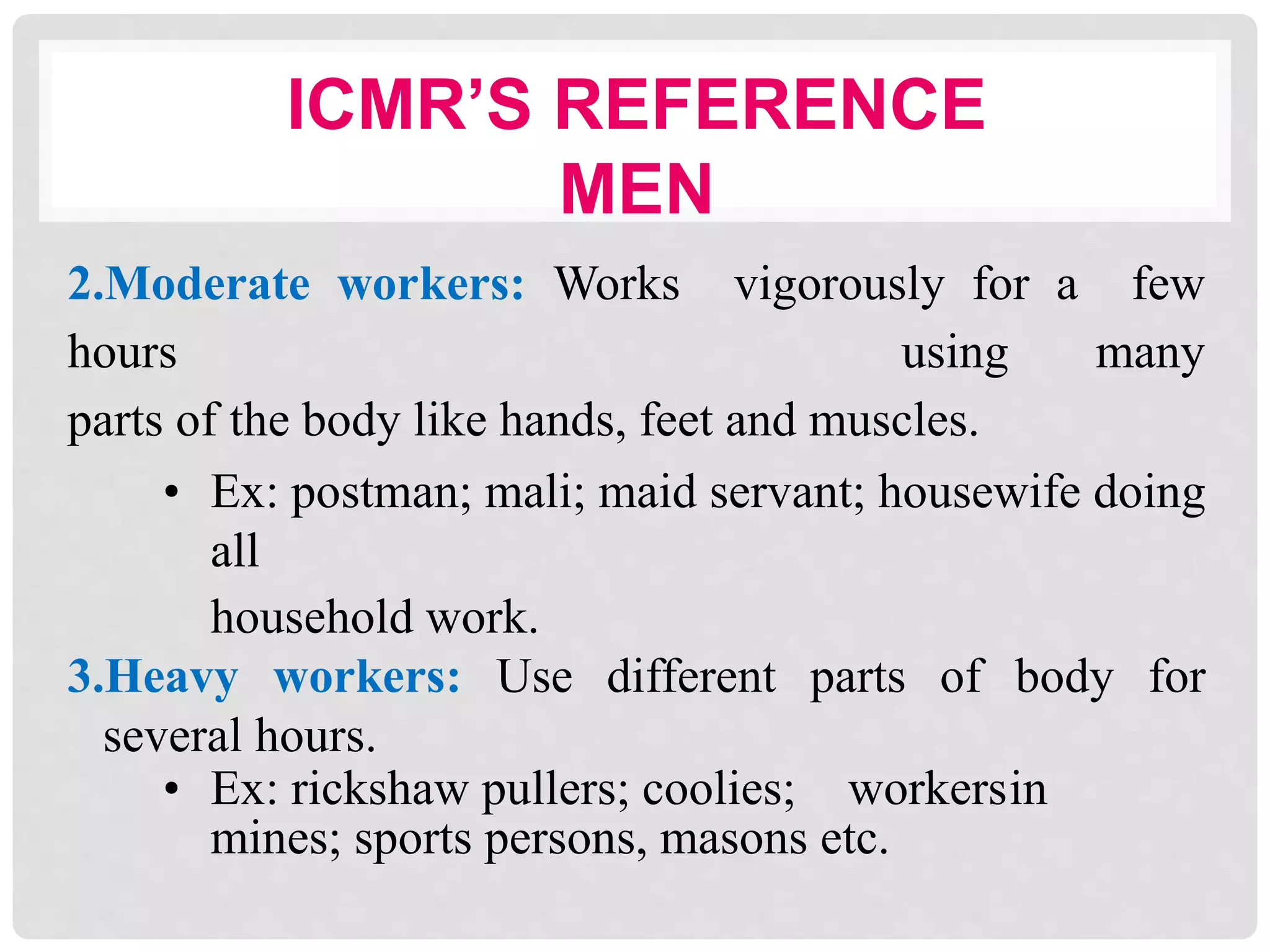
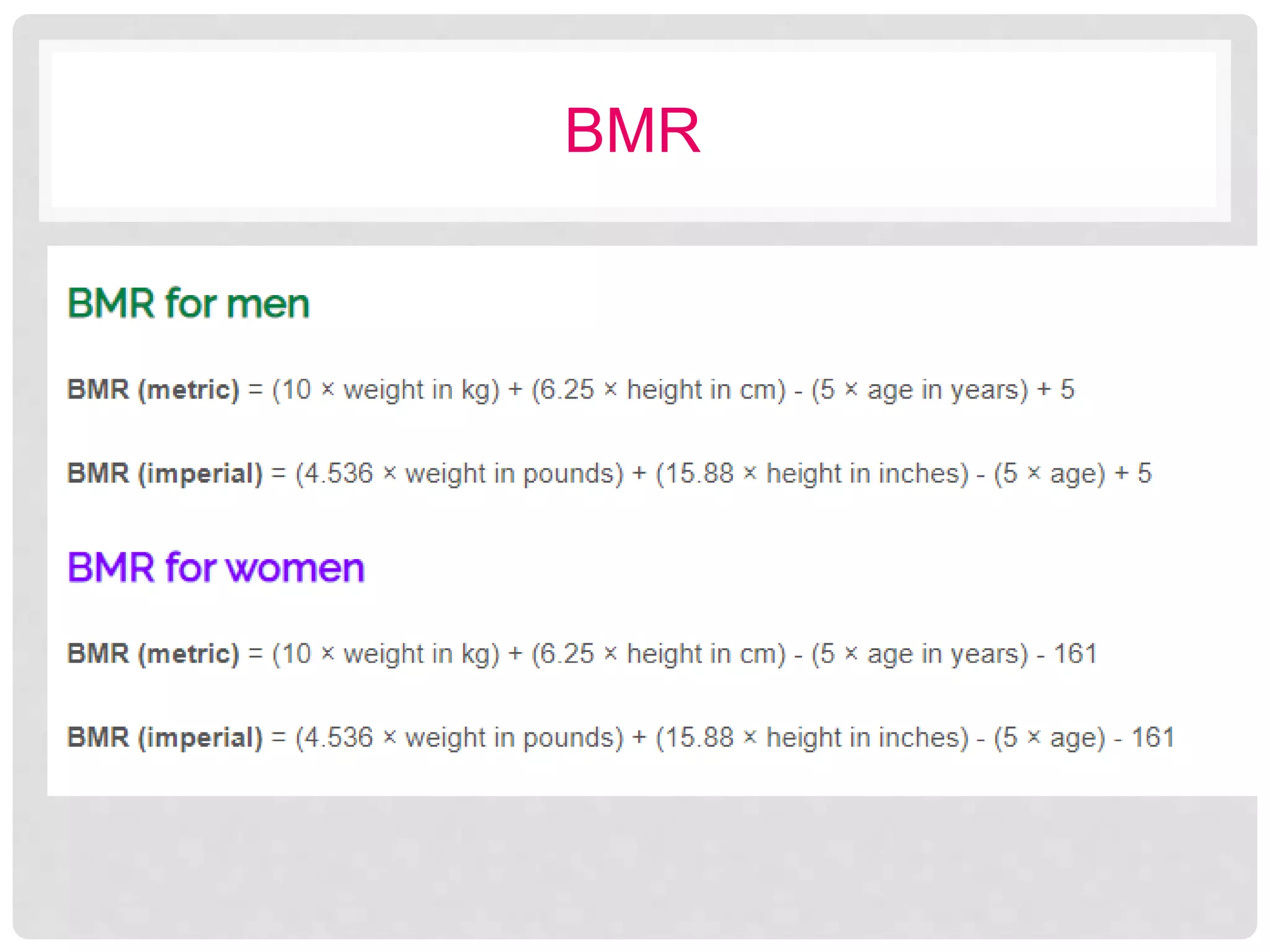
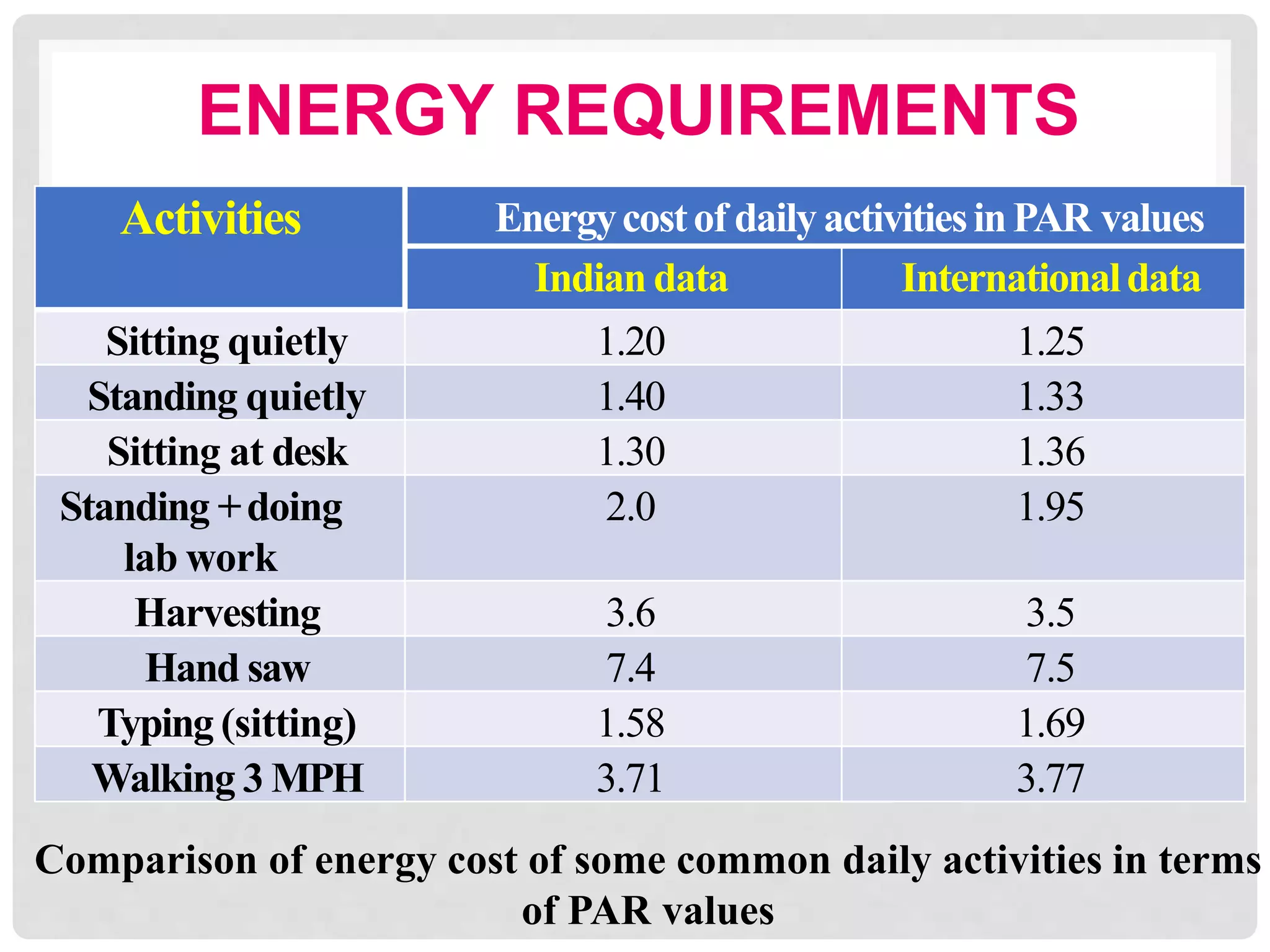
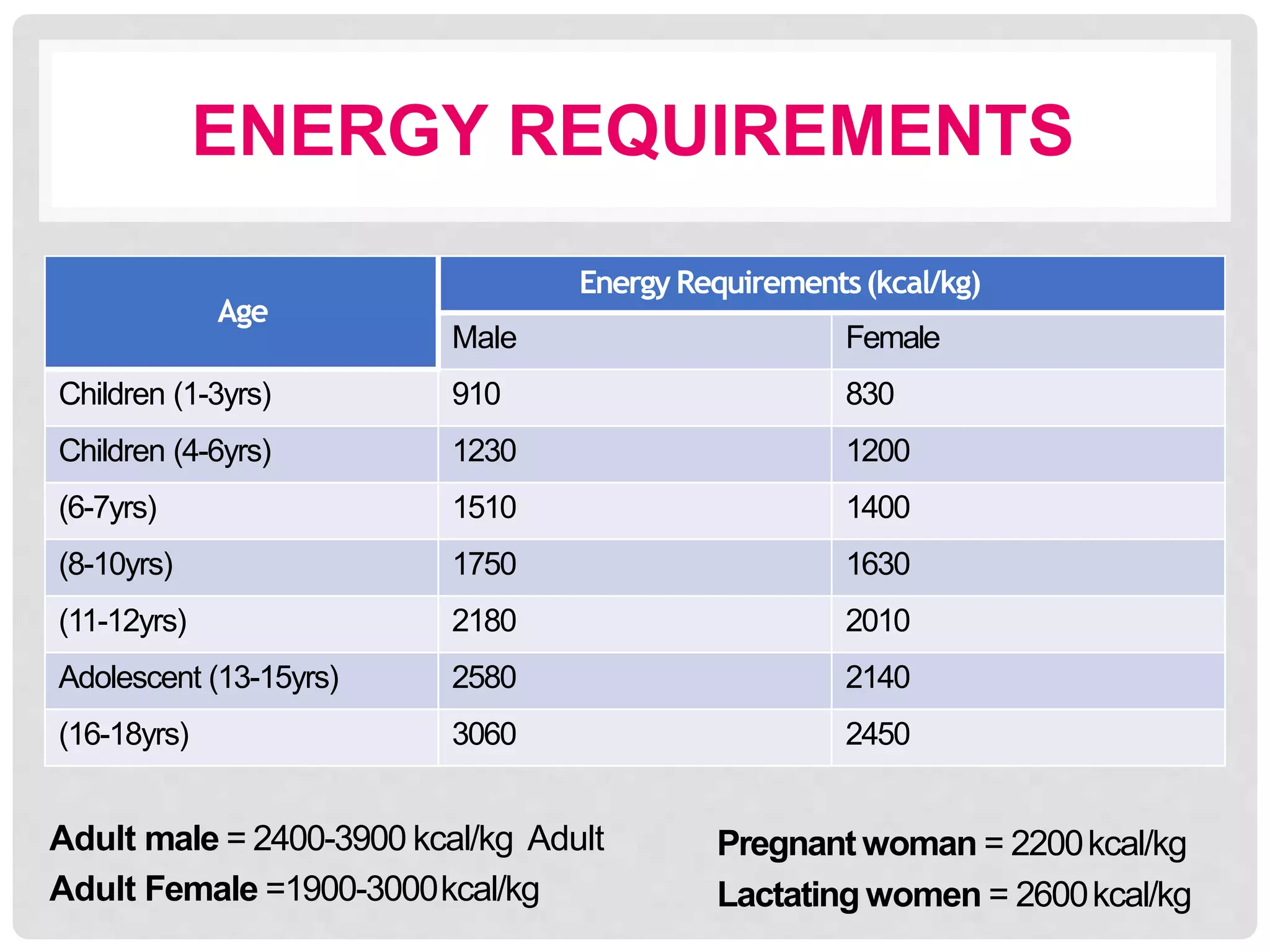
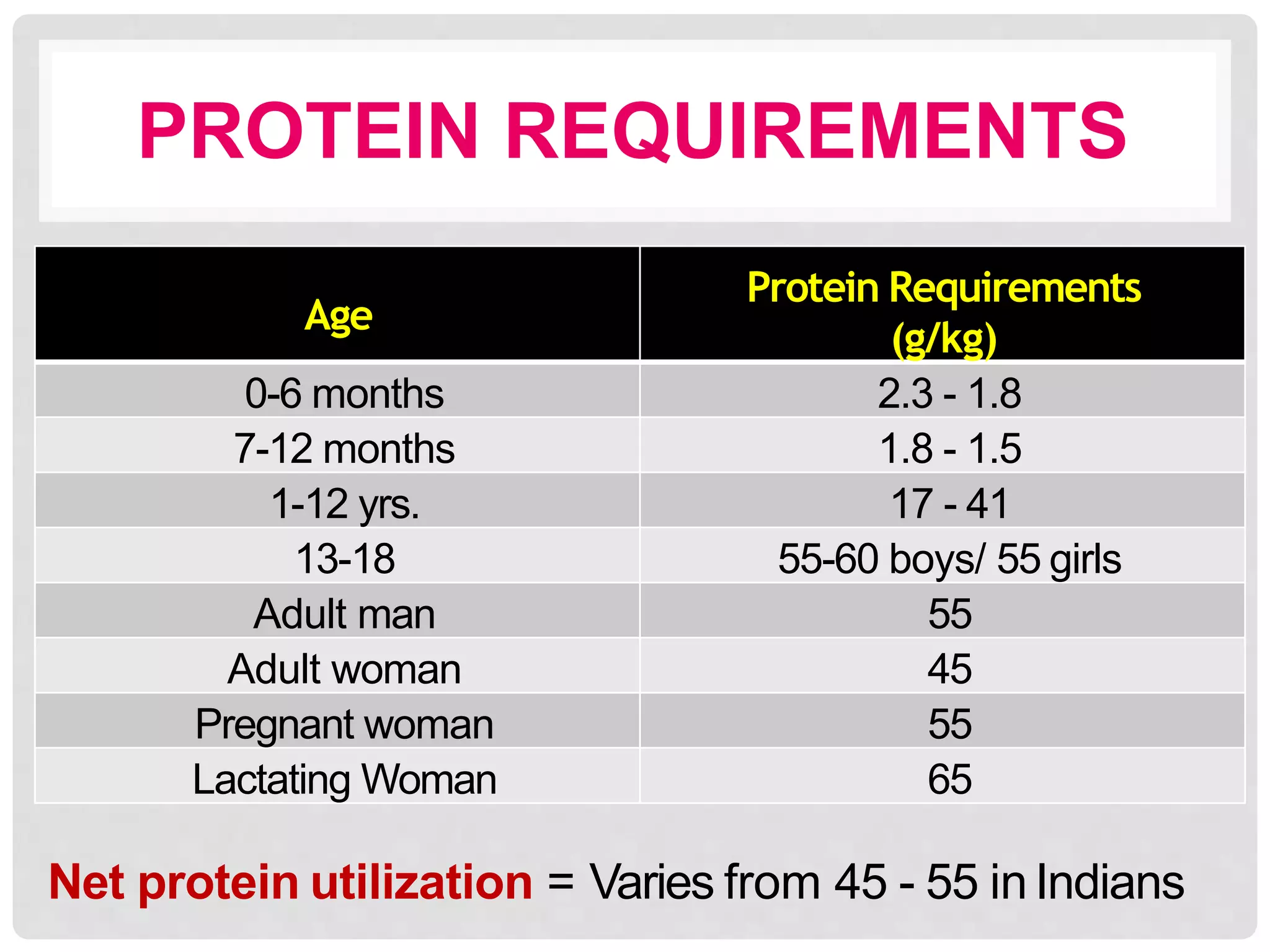
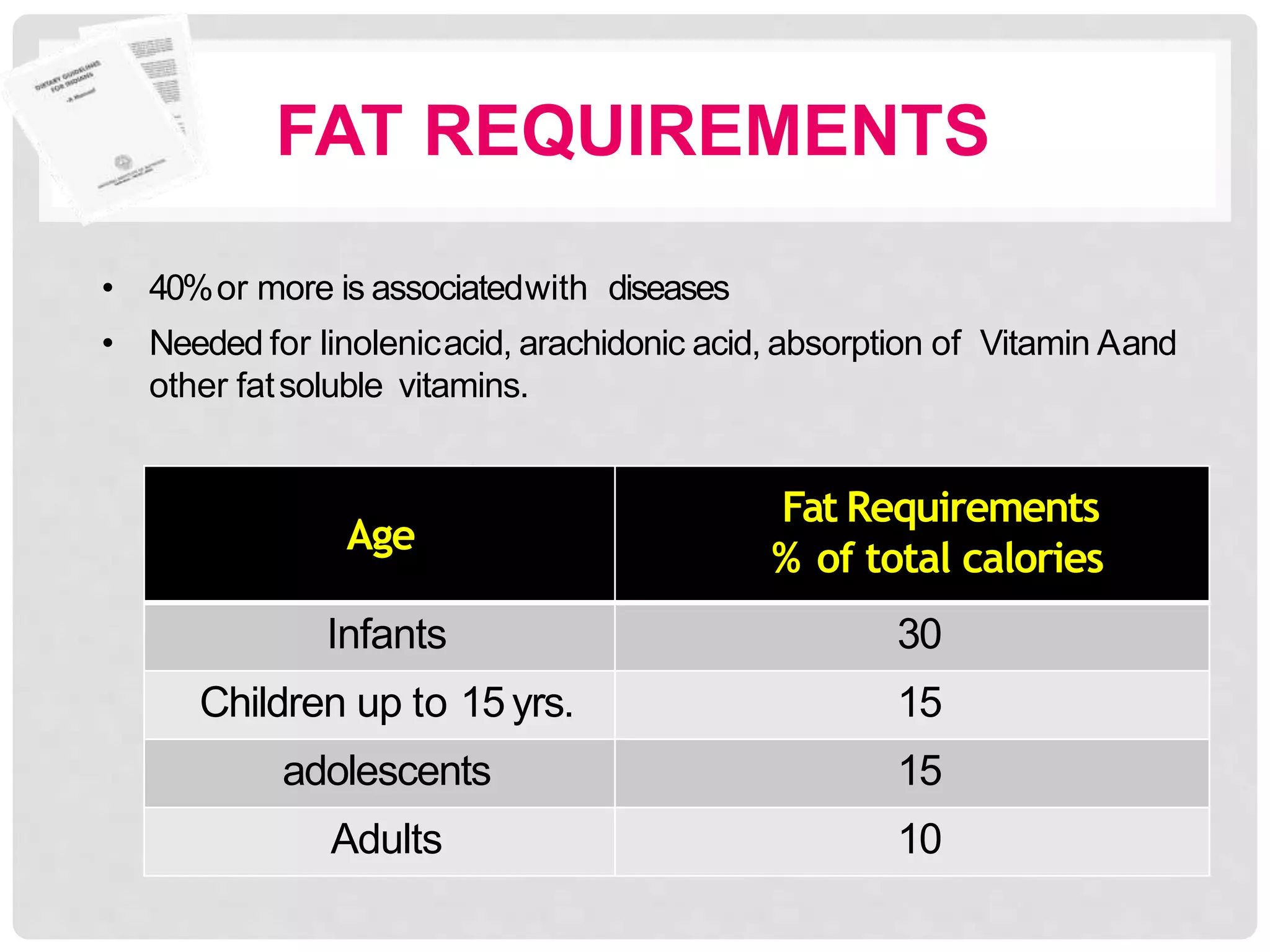
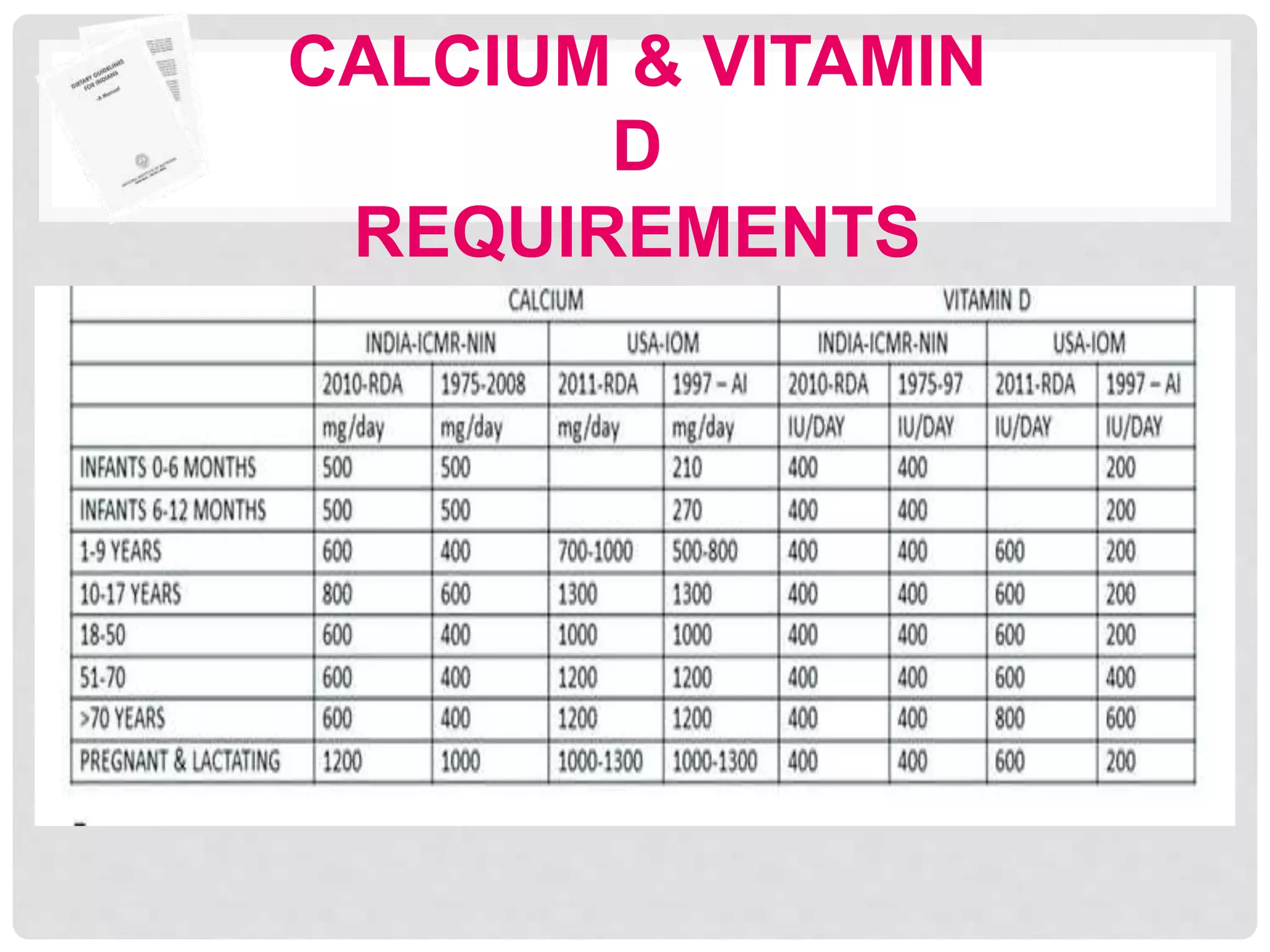
This document discusses recommended daily allowances (RDA) for nutrients in India. It defines RDA as the average daily intake of nutrients that is sufficient to meet the requirements of nearly all healthy individuals. The RDA is determined based on factors like age, gender, physiological state and physical activity level. It also discusses the Indian Council of Medical Research's reference man and woman which are used to determine RDA for Indian adults. Finally, it provides RDA values for key nutrients like energy, protein, fat, iron, calcium and vitamins A and B for different age groups.