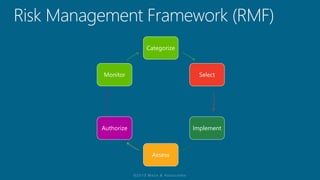
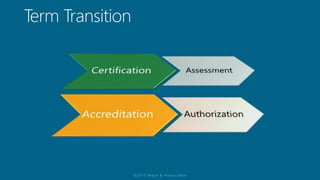
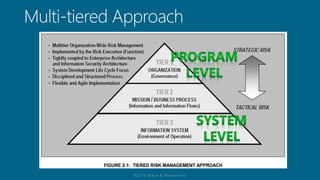
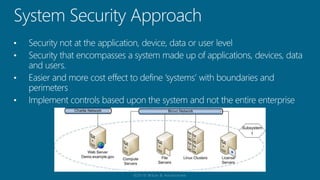
The document discusses the methodology of certification and accreditation aimed at ensuring security controls for information systems, highlighting their importance in protecting information system integrity, confidentiality, and availability. It defines the management decision to authorize system operation while accepting associated risks and proposes the need for robust security measures. The content reflects on the vulnerabilities agencies face against cyber threats, emphasizing the significance of implementing agreed-upon security controls.