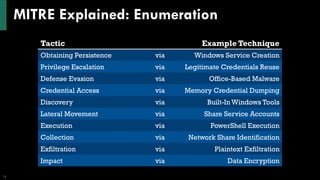
The document discusses the MITRE ATT&CK framework, highlighting its purpose as a knowledge base for understanding adversarial behaviors during cyber-attacks. It outlines various tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by threat actors and emphasizes the need for comprehensive threat intelligence and detection strategies. Additionally, it provides insights on improving detection capabilities and mapping adversary behaviors to enhance security measures.