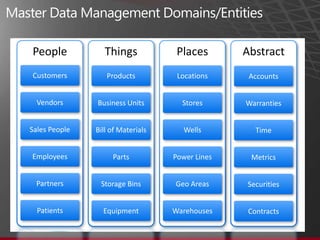
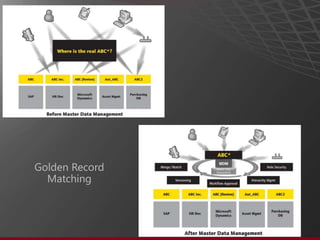
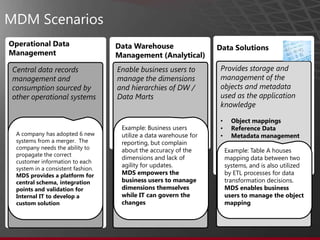
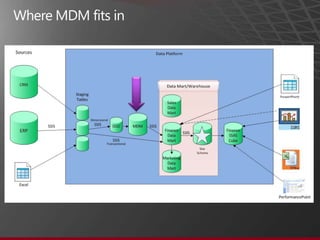
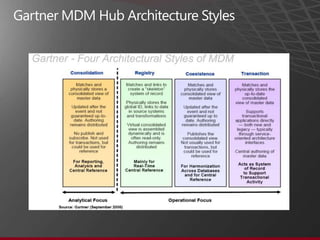
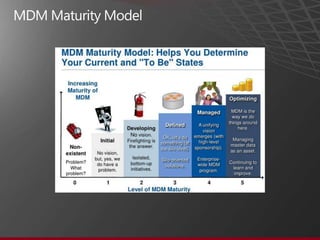
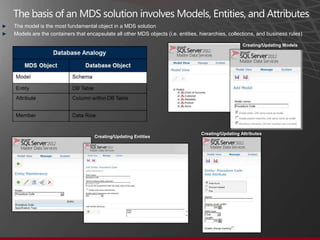
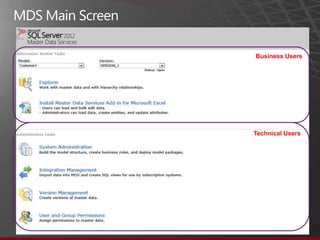
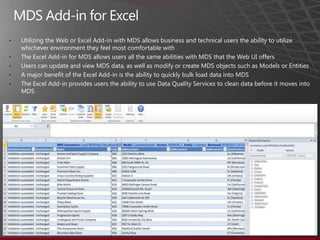
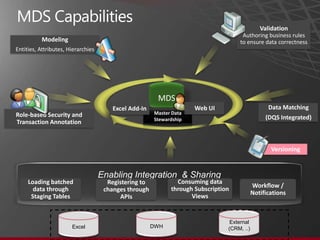
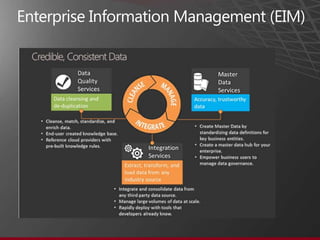
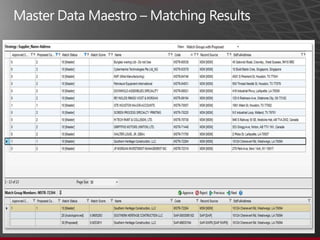
The document presents an overview of Master Data Management (MDM) highlighting its necessity, benefits, and various scenarios for implementation. It emphasizes the importance of MDM in reducing duplicate data, improving decision-making and compliance, and facilitating efficient data stewardship. Additionally, it discusses Microsoft Data Services (MDS) and the integration capabilities with business user needs through tools like Excel add-in.