MongoDB is an open source, scalable, high-performance, document-oriented NoSQL database that uses a schema-less JSON-style document model, supports master-slave replication and horizontal sharding to scale out, and provides basic CRUD operations and rich queries on document collections. The document demonstrates MongoDB's data structures, basic CRUD operations, indexing, querying, optimization, architecture including replication and sharding, and use cases.


![CRUD Demo time
Ø
show dbs view existing databases
Ø
use test use database “test”
Ø
db.t.insert({name:’bob’,age:’30’}) insert 30 years bob
Ø
db. t.insert({name:’alice’,gender:’female’}) insert lady alice
Ø
db. t.find() list all documents in
collection t
Ø
db. t.find({name:’bob’},{age:1}) find 1 year old bob
Ø
db. t.find().limit(1).skip(1) find the second document
Ø
db. t.find().sort({name:1}) sort the results with ascend
name
Ø
db. t.find({$or:[{name:’bob’},{name:’tom’}]}) find bob or tom’s documents
Ø
db. t.update({name:’ bob’},{$set:{age:31}}, update all bob’s age to 31
Ø
false,true})
Ø
db.stats() database statistic
Ø
db.getCollectionNames() collections under this db
Ø
db.t.ensureIndex({name:1}) create index on name
Ø
db.people.find({name:“bob"}).explain() explain plan step](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongopresentationconf-130621053950-phpapp02/85/Mongo-presentation-conf-5-320.jpg)


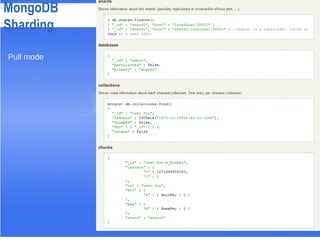
![MongoDB Sharding: Briefly
FROM:C TO:N
#Copy Index Definition from C
#Remove existing data in [min~max]
#Clone the data in[min~max] from C
#Ask C to replicate the changes
#Make sure my view is complete and lock
#Get the document’s DiskLoc for sharding
#Trigger the N to sharding in Pull mode
Sequence
#N commit
#Ask N to commit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mongopresentationconf-130621053950-phpapp02/85/Mongo-presentation-conf-10-320.jpg)