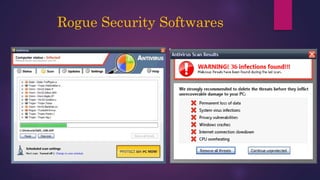
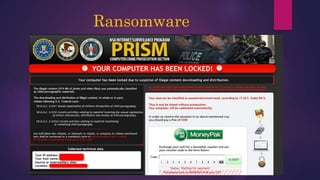
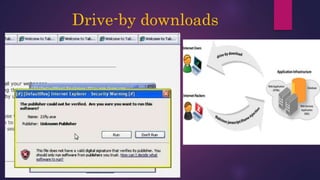
The document provides a thorough overview of malware, including its definition, various types such as viruses, trojans, and ransomware, and methods of infection and propagation. It highlights detection techniques and preventative measures while emphasizing the importance of understanding malware rather than fearing it. The conclusion encourages vigilance against unknown sources and keeping systems up to date to avoid infections.