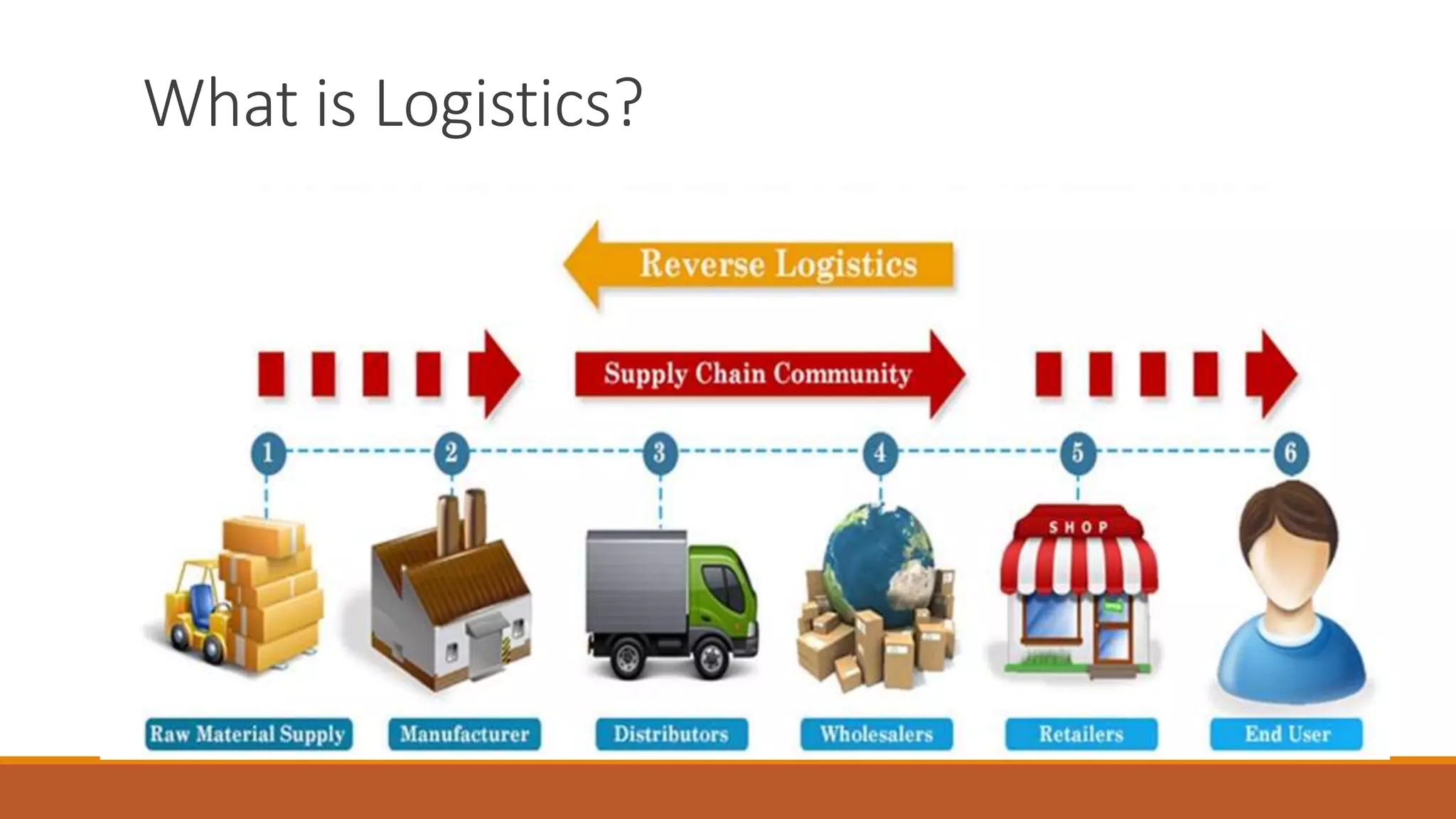
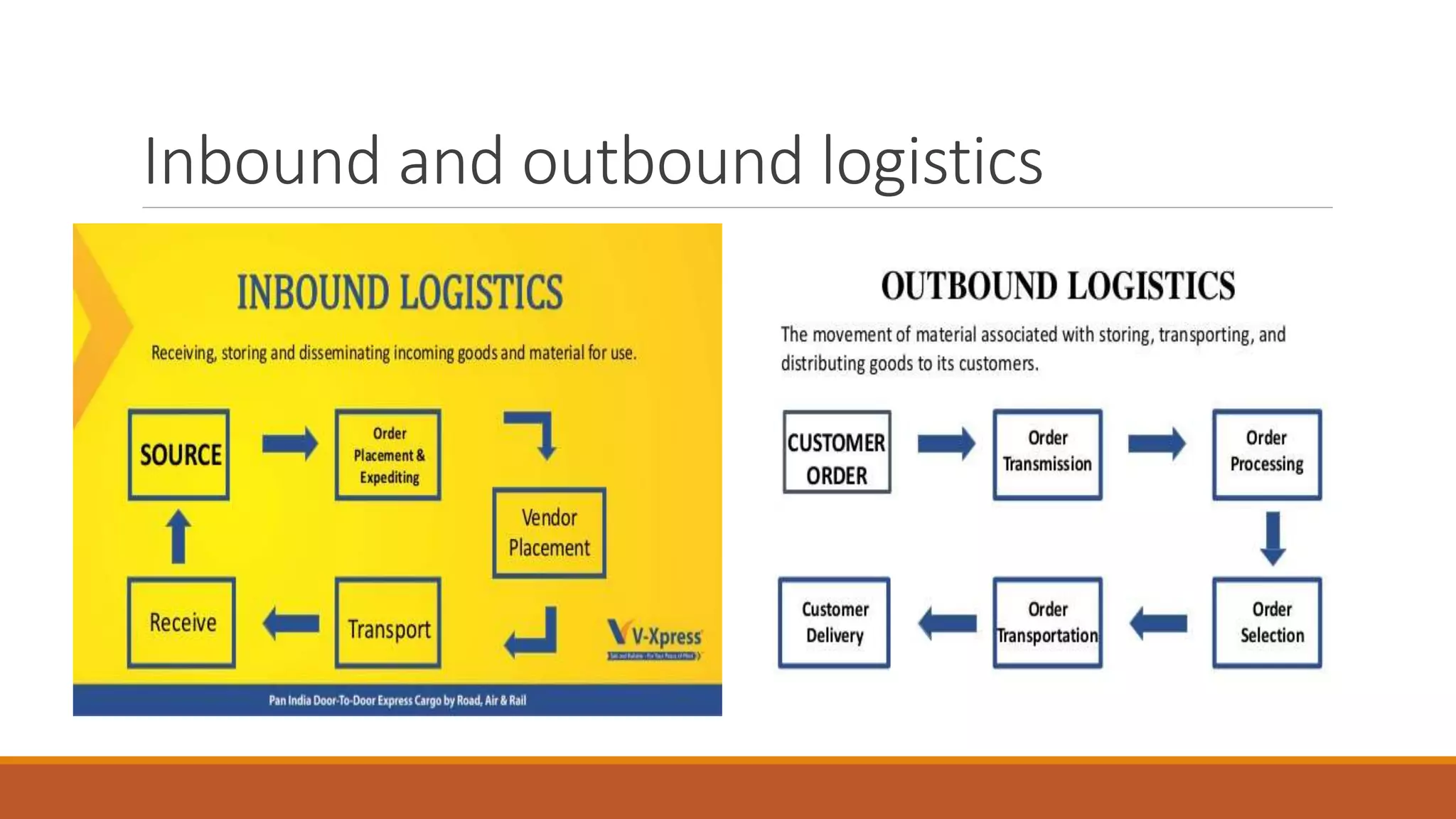
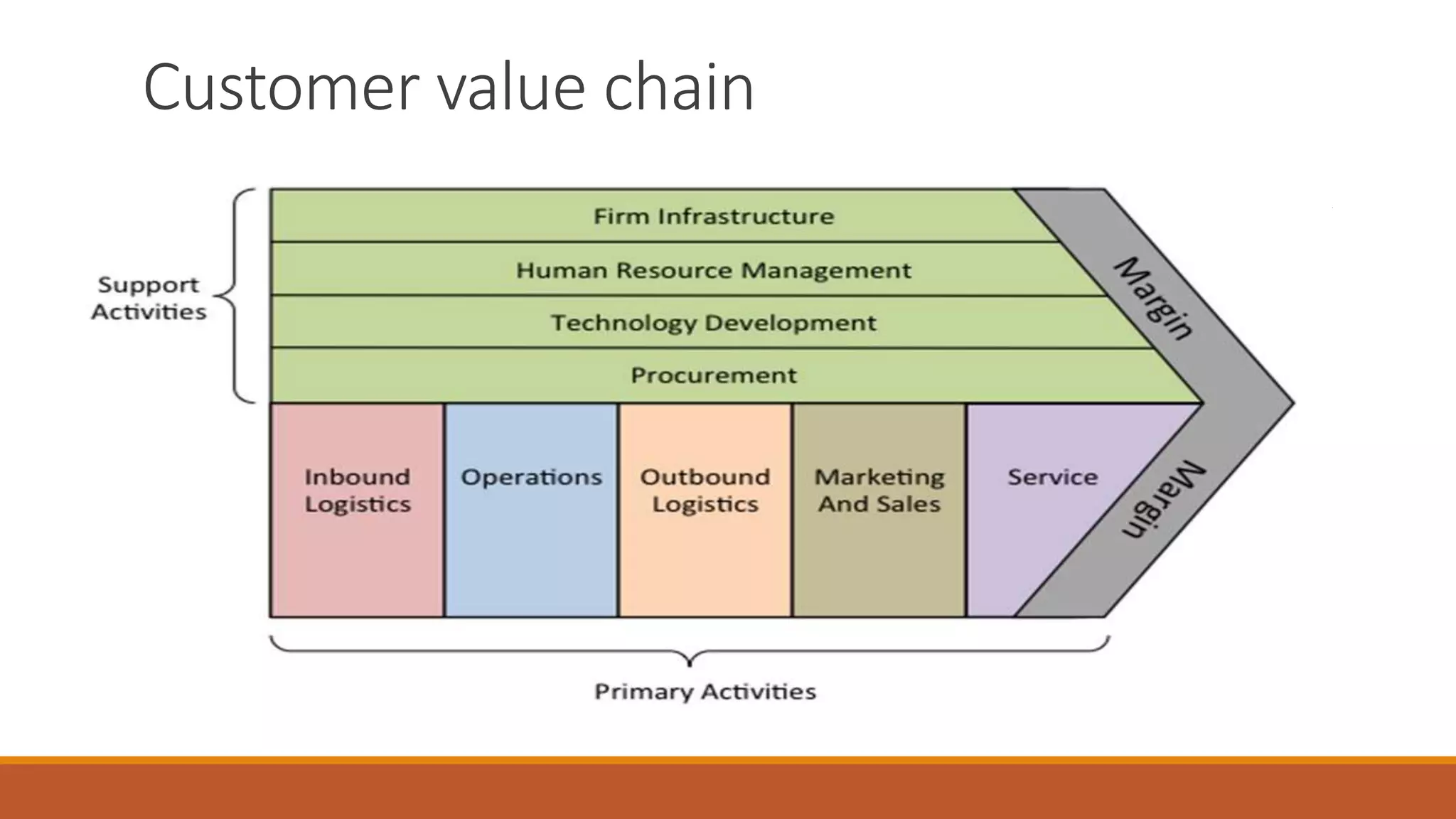
This document provides an introduction to logistics management, including definitions, functions, objectives, and the role it plays in competitive strategy. It defines logistics as planning and controlling the efficient flow of materials and goods from supplier to customer. Key points covered include: the scope of logistics includes value-adding processes and market penetration; functions involve order processing, inventory planning, and transportation; objectives are to reduce costs and inventory while ensuring reliable delivery; and logistics enables competitive strategies like cost leadership and differentiation. It also discusses customer service phases from pre-to-post transaction and how logistics provides value through services such as packaging, customs clearance, and doorstep delivery.