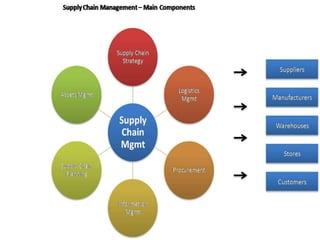
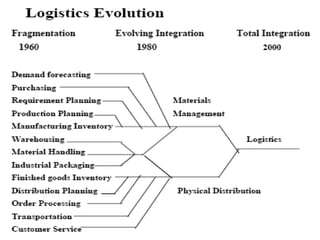
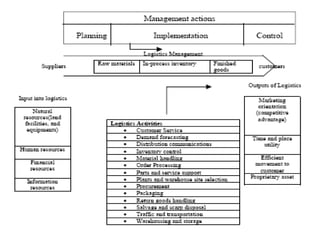
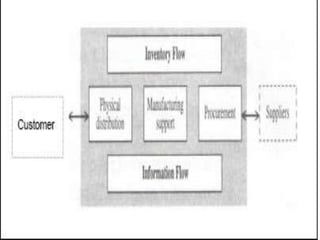
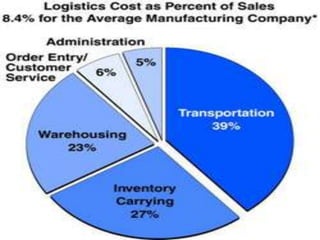
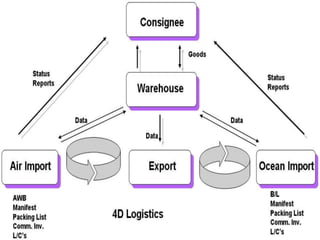
The document discusses the fundamentals of logistics and supply chain management, defining logistics as the process of managing the flow of goods and services efficiently and cost-effectively from origin to consumption. It outlines key principles, phases, objectives, and concepts of logistics, emphasizing the importance of logistics in the marketing process and highlighting the need for integration and coordination among various elements of the logistics system. Additionally, it provides insights into the impact of logistics costs and offers tips for reducing supply-chain expenses.