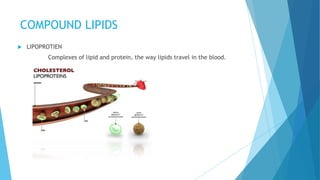
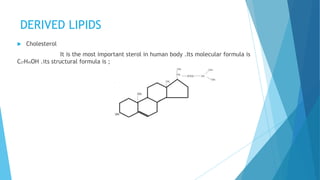
The document defines lipids as organic compounds that are fatty acids or their derivatives that are insoluble in water but soluble in non-polar solvents. It classifies lipids into three main categories: simple lipids, compound lipids, and derived lipids. Simple lipids include oils, fats, and waxes and contain only carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen. Compound lipids also contain phosphorus, nitrogen, or sulfur. Derived lipids are substances derived from simple and compound lipids through hydrolysis, such as fatty acids, alcohols, and steroids. The document provides examples and descriptions of lipid subclasses within each main category.