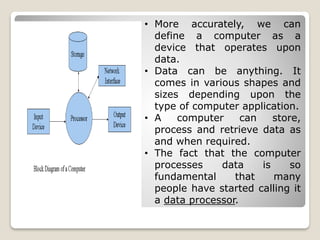
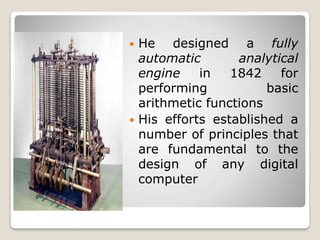
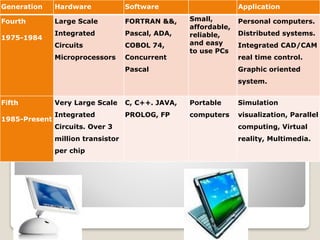
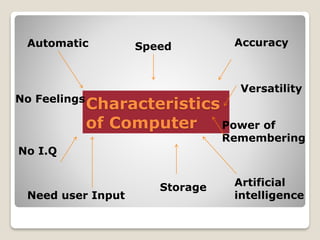
The document discusses the evolution of computers from early mechanical calculating devices like the abacus to modern electronic digital computers. It outlines the key developments from the 1800s to present, including Babbage's analytical engine, the first programmable computers like ENIAC and UNIVAC, and the five generations of computers defined by changes in hardware technology. It also describes the basic characteristics of computers such as their speed, accuracy, ability to store and process vast amounts of data, and capacity for artificial intelligence once programmed, while noting their limitations in lacking human qualities like feelings and independent decision making.