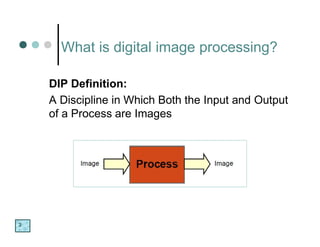
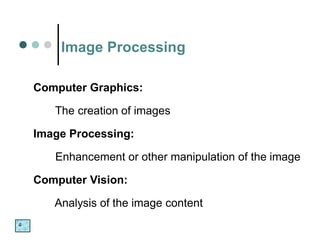
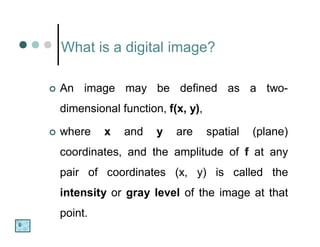
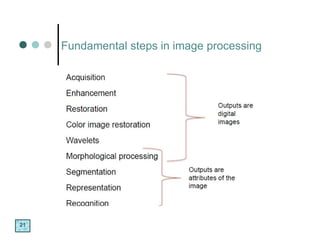
The document discusses what a digital image is, defining it as a spatial representation of a scene that is composed of pixels arranged in rows and columns. It also defines digital image processing as a discipline where both the input and output are images, and discusses some key applications of image processing such as document handling, biometrics, object identification, target recognition, and cancer detection. The fundamental steps in image processing are also briefly outlined.