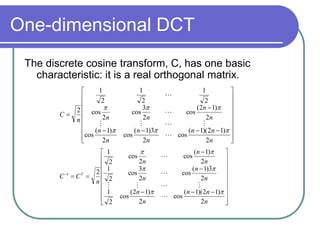
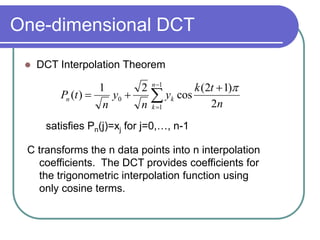
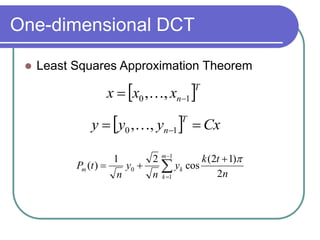
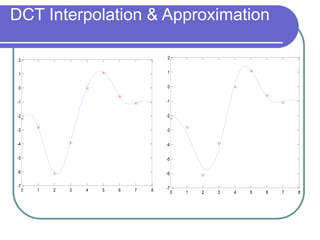
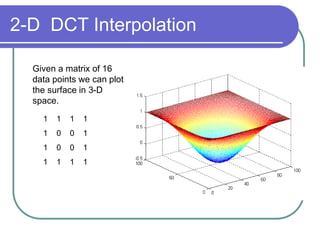
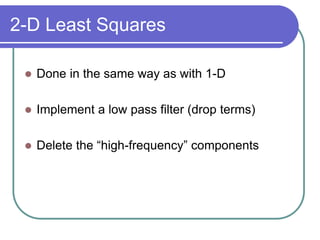
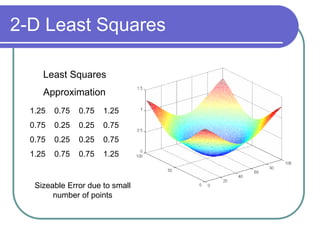
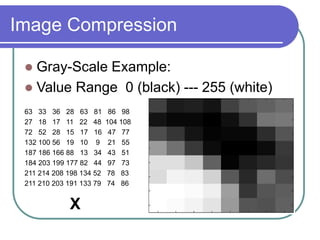
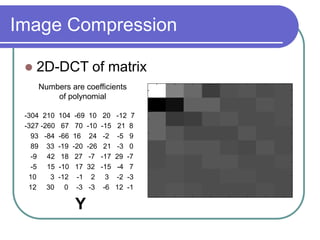
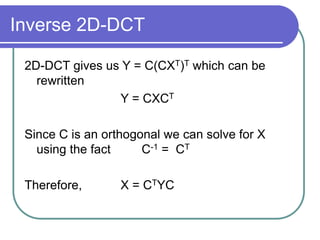
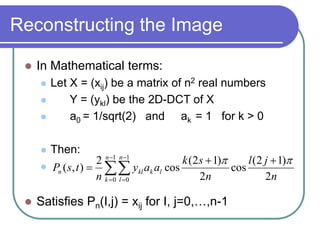
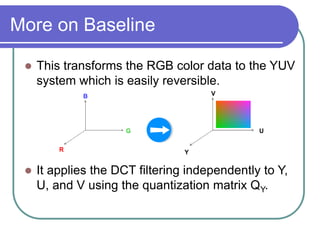
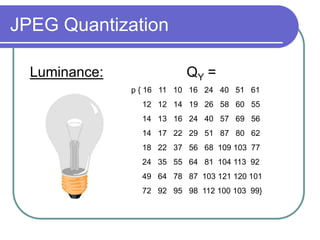
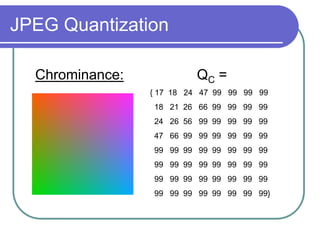
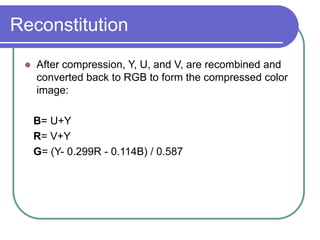
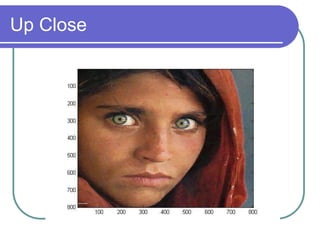
The document discusses the discrete cosine transform (DCT) and its applications in image compression. DCT transforms a signal or image into a combination of cosine functions arranged by frequency. This property allows for efficient compression by discarding high-frequency components with little visual impact. Specifically:
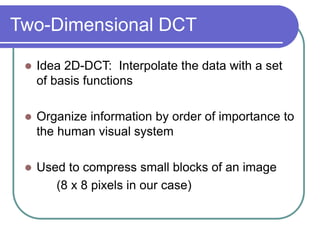
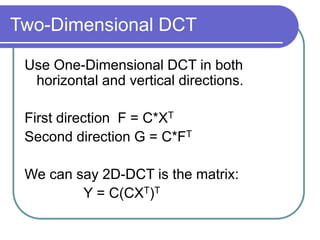
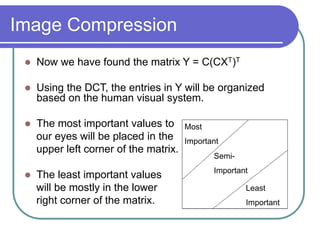
- DCT provides a basis to represent an image as a sum of cosine functions, with low frequencies more important visually.
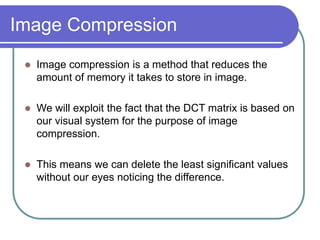
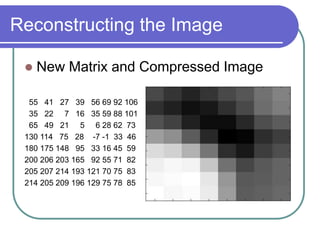
- Applying DCT to blocks of an image separates information by importance, allowing lossy compression by discarding high frequencies.
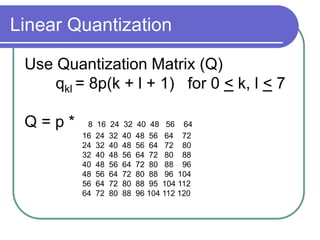
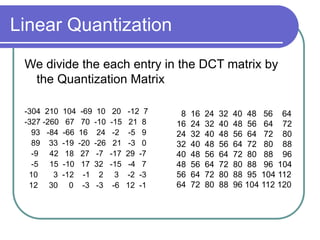
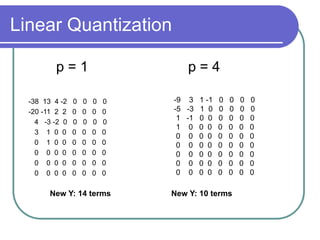
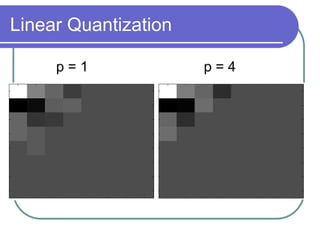
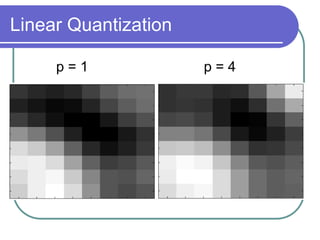
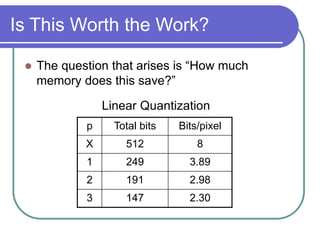
- Quantization further compresses data by allocating fewer bits to store high-frequency DCT coefficients.
- Together DCT and quantization provide significant data compression with minimal visual