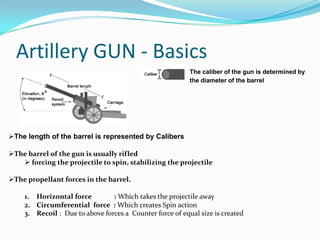
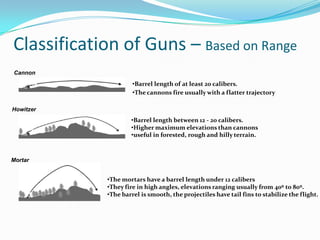
This document provides information about artillery guns and projectiles. It discusses that artillery guns are weapons that can project munitions over long distances. It then describes the basic components of artillery guns, including the barrel, propellant, and classification based on range. It also discusses the basic structure of anti-personnel guns. Finally, it covers the types of artillery projectiles and their effects, such as fragmentation and blast effects.












![Indian Army – Key Artillery
TOWED Artillery:
Indian Ordnance Factories 105 mm Light Field Gun
D-30 122 mm Towed Artillery Howitzer [2A18]
M-46 130 mm Towed Artillery Field Gun [M1954]
Haubits Bofors FH77B Towed Artillery Howitzer
Rocket Launchers:
BM-21 Grad 122mm Multi Barrel Rocket Launcher
BM-30 Smerch 9A52-2T 300mm Multi Barrel Rocket
Launcher
Pinaka 214mm Multi Barrel Rocket Launcher](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoguns-dange-120225104119-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-guns-Dange-15-320.jpg)
