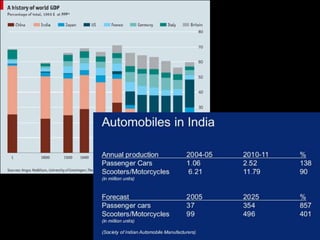
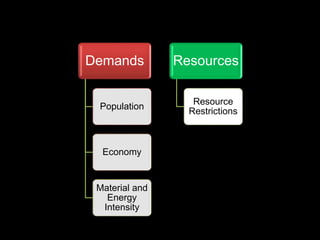
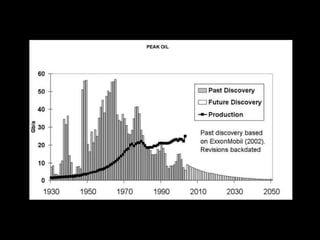
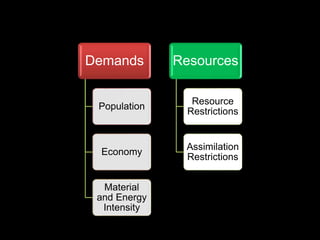
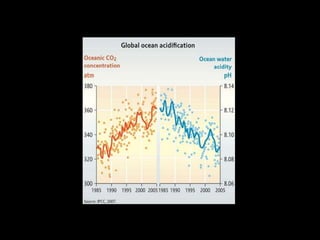
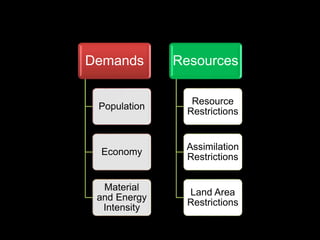
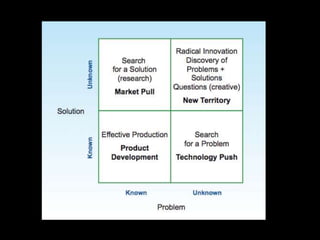
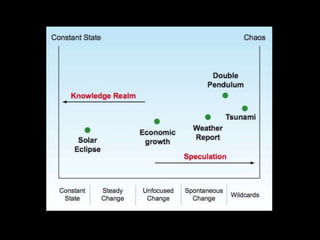
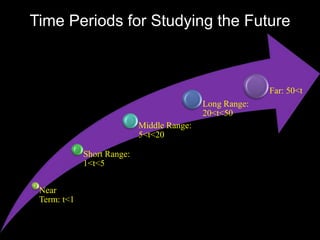
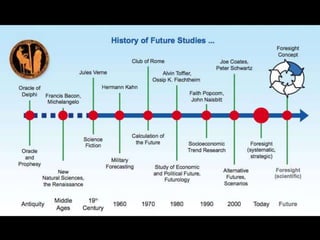
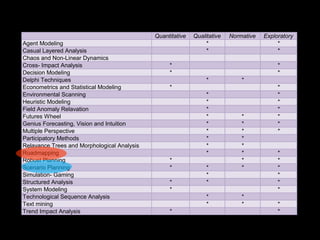
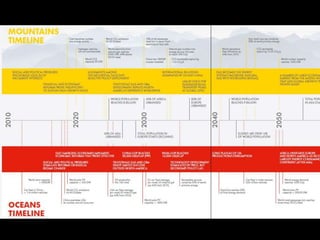
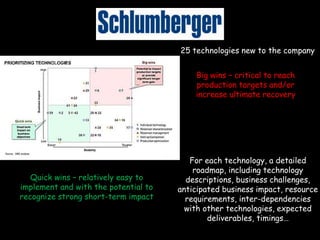
This document provides an introduction to the field of futures studies. It discusses how futures studies aims to systematically explore possible and desirable futures in order to improve decision making. Key methods discussed include scenario planning, roadmapping, and trend analysis. The document outlines various time horizons and subject areas studied by futurists, such as technology, environment, economy and society. It also discusses differences between prediction and forecasting, and compares various qualitative and quantitative futures studies methods. The overall purpose of futures studies is to help organizations and societies envision and plan for potential alternative futures.