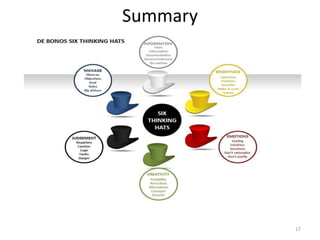
The document introduces Edward de Bono's method of parallel thinking using six colored thinking hats. Each hat represents a different perspective or thought process: white for objective facts, red for emotions, black for caution, yellow for benefits, green for creative ideas, and blue for organization and control. The six hats method structures group discussions to consider an issue from different angles in a set sequence, allowing for a more comprehensive analysis that incorporates logic, creativity, and feelings. Applying the hats helps remove ego and confrontation from problem solving so groups can effectively generate, evaluate, and implement solutions.