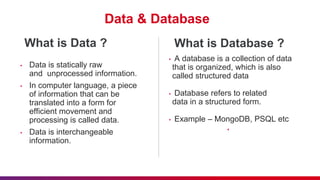
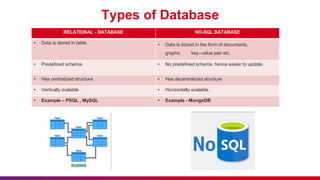
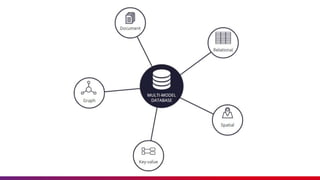
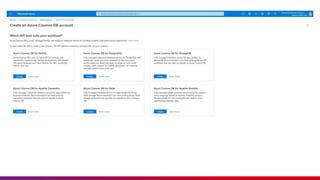
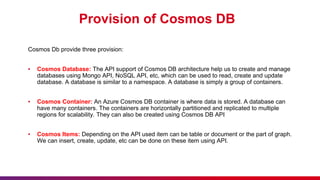
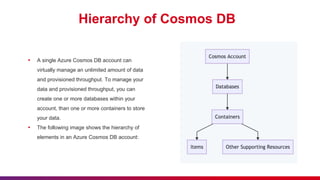
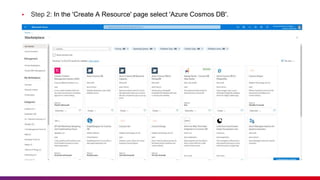
The document presents an introduction to Azure Cosmos DB, detailing its features as a cloud-based multi-model database service offered by Microsoft Azure. It discusses database types, API options within Cosmos DB, and the hierarchy of data organization, along with instructions for setting up an Azure Cosmos DB account. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of session etiquettes for effective participation in related presentations.