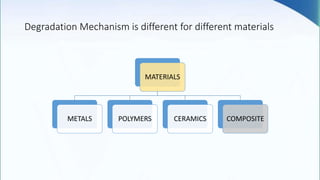
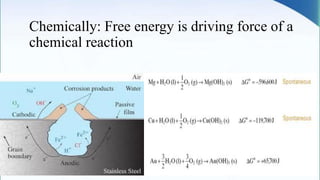
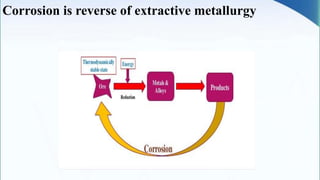
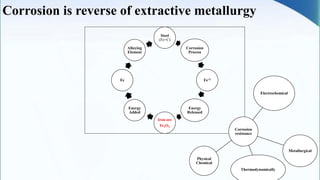
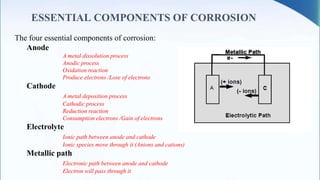
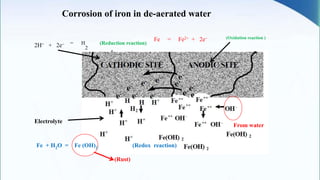
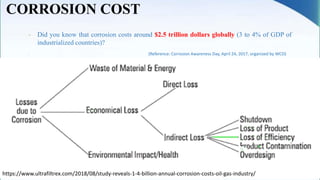
Corrosion is the degradation of a material due to interaction with its environment. It is the reverse process of extractive metallurgy. Corrosion can be broadly classified based on the electrolyte, environment, or temperature. The four essential components required for corrosion to occur are the anode, cathode, electrolyte, and metallic path. Globally, corrosion costs an estimated $2.5 trillion dollars annually, which amounts to 3-4% of GDP for industrialized countries. Prevention and maintenance efforts aim to reduce both economic losses and safety hazards resulting from corrosion-induced structural failures.