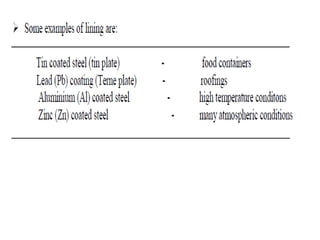
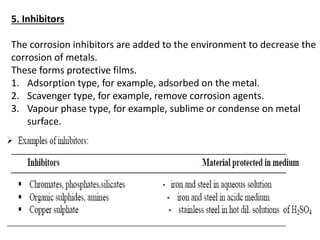
Corrosion is the reaction of a metal with its environment that can cause functional failure. It occurs through electrochemical processes and is influenced by factors like pH, temperature, velocity, and surface films. There are different types of corrosion including general corrosion that uniformly affects a surface, and localized corrosion that occurs at specific sites like pits, cracks, or grain boundaries. Localized corrosion can be influenced by stresses or chemical reactions and causes like galvanic corrosion or stress corrosion cracking. Understanding corrosion mechanisms and influencing factors is important for preventing problems in equipment like reactors, fermenters, and storage containers.






![FACTORS INFLUENCING CORROSION
A number processing factors affect rate of corrosion.
1. Solution pH
2. Oxidizing agents
3. Temperature
4. Velocity
5. Surface films
6. Other factors [concentration of corrosive chemicals ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corrosion-180817062355/85/Corrosion-7-320.jpg)