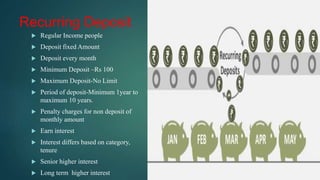
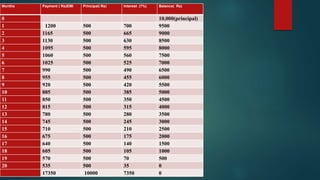
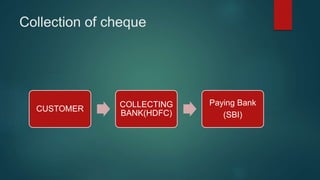
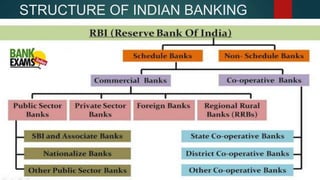
The document provides an introduction to banking, describing what banks do such as accepting deposits, lending money, and offering other services. It explains the primary functions of banks, which include accepting deposits like savings, fixed, and current accounts, and granting loans like overdrafts, cash credits, and term loans. Various types of deposits, loans, and other banking services are defined and described in detail.