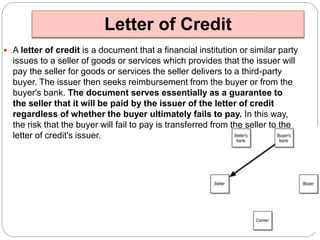
Bank products have evolved beyond traditional loans and deposits to include a wide variety of wholesale, retail, fee-based, and foreign products. Commercial credit includes both funded credit like cash credits and demand loans that involve funds flowing from the bank to borrowers, as well as non-funded credit like guarantees. Retail banking offers consumers credit products like credit cards, retail loans, and housing loans, as well as deposit products like savings and current accounts.