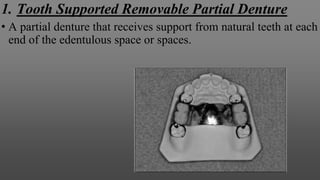
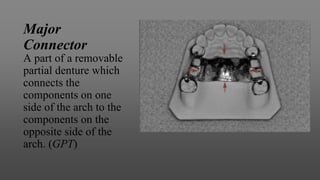
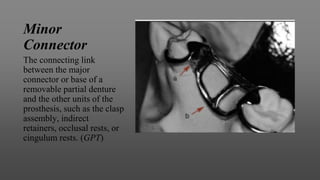
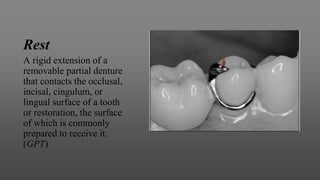
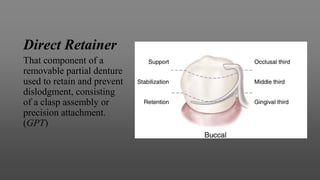
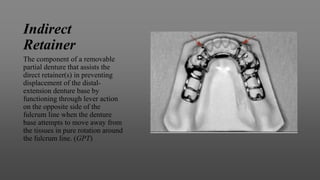
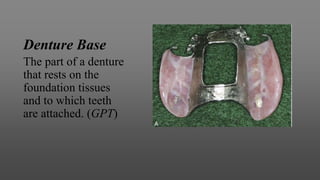
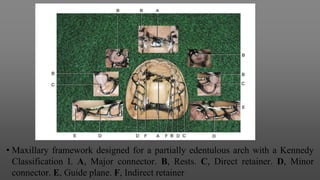
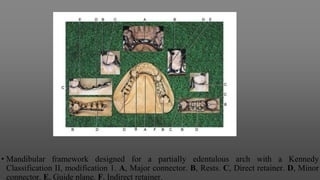
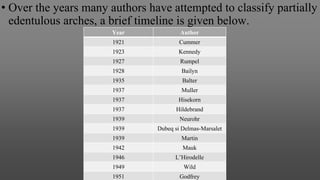
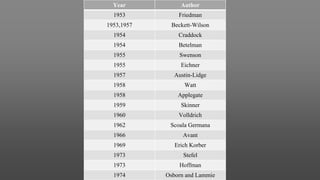
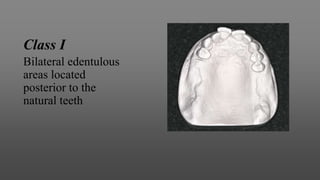
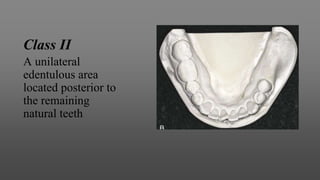
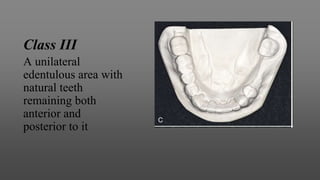
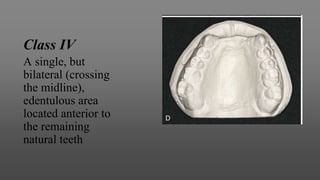
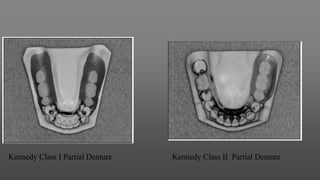
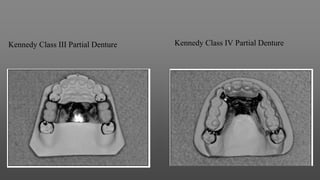
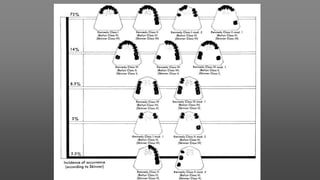
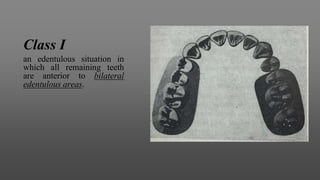
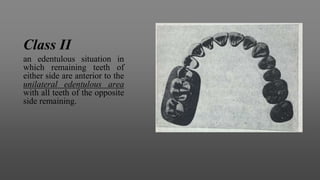
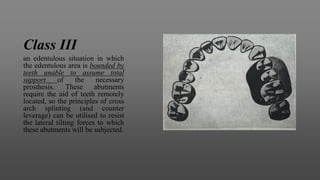
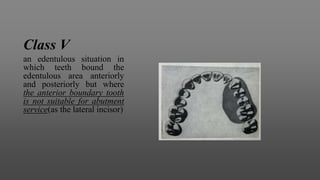
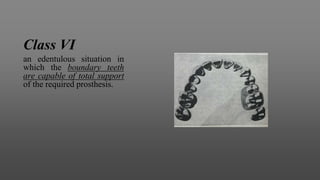
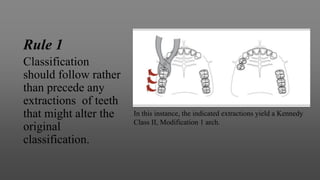
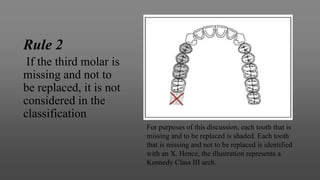
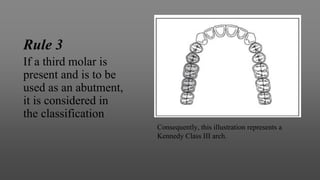
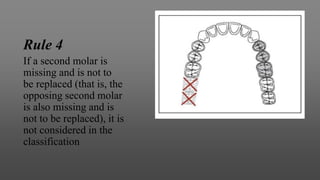
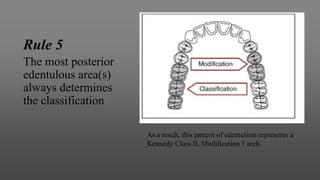
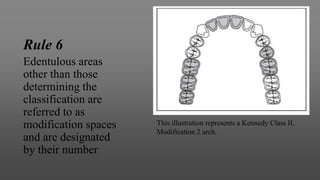
This document provides an introduction to removable partial dentures (RPDs). It defines RPDs and classifies them as either tooth-supported or tooth-tissue supported. The key parts of RPDs are identified, including the major connector, minor connector, rest, direct retainer, and indirect retainer. The Kennedy classification system for partially edentulous arches is described in detail, identifying its four main classes. The Applegate-Kennedy classification is also introduced as a modification of the original Kennedy system. Merits and demerits of the classifications are discussed.