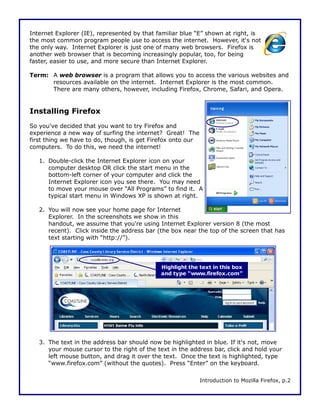
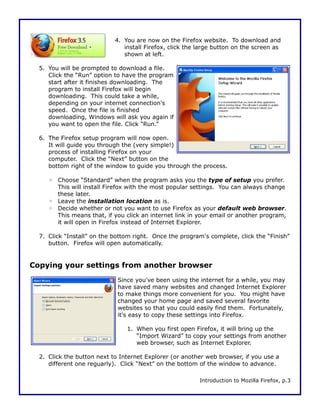
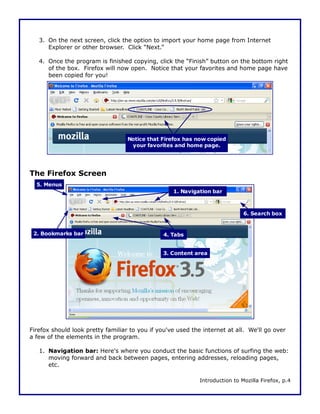
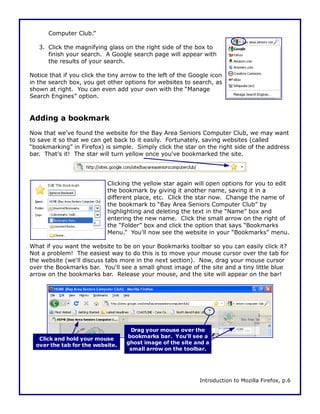
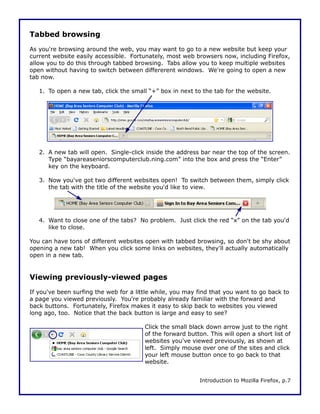
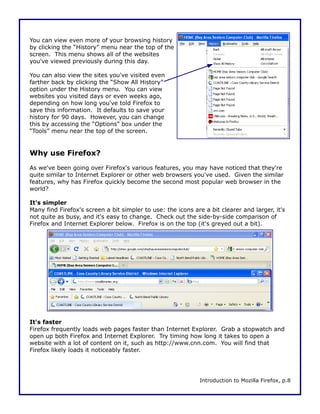
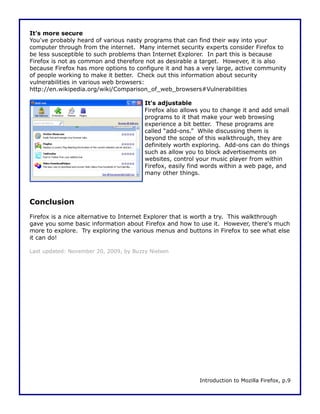
This document is a walkthrough for Mozilla Firefox, highlighting its features such as installing the browser, copying settings from other browsers, and utilizing its tools like tabbed browsing and bookmarking. It compares Firefox to Internet Explorer, emphasizing its speed, security, and user-friendly interface. The guide is designed for users transitioning from Internet Explorer, specifically version 8 on Windows XP.