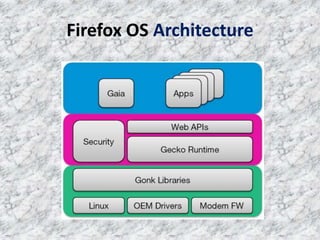
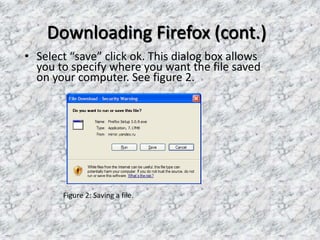
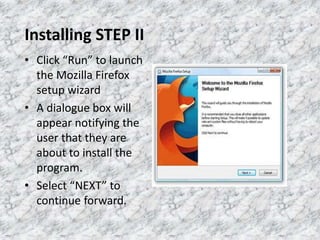
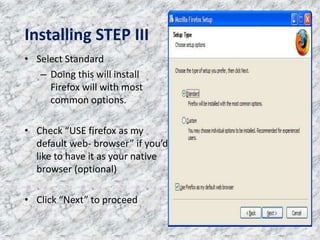
Firefox OS is an open-source operating system developed by Mozilla, based on boot-to-gecko (b2g) and implemented using web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. It features a user interface called Gaia and offers various applications, as well as a lower-level OS called Gonk that includes a Linux kernel and hardware abstraction layer. The document also highlights the advantages of using the Firefox web browser and provides instructions for downloading and installing it.