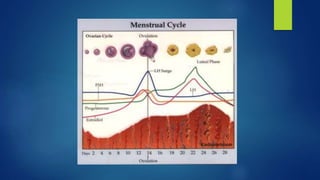
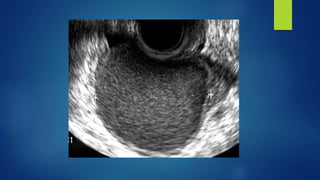
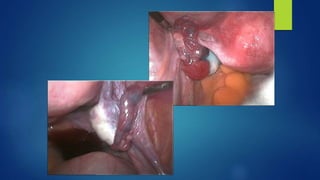
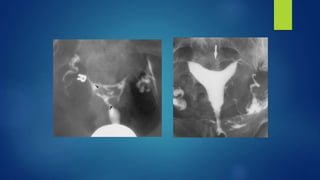
This document outlines an integrated approach to infertility workup. It discusses evaluating the male partner, ovarian function, tubal function, and the uterus. For the male partner, a history, examination, and semen analysis are recommended. Ovarian function is assessed through menstrual history, ultrasound, and hormone levels. Tubal function can be evaluated with HSG, laparoscopy, or hysteroscopy. The uterus is examined with imaging like HSG, ultrasound, or hysteroscopy and potentially endometrial biopsy. A complete workup considers factors from both the male and female partners.