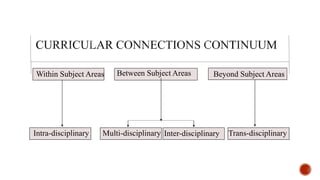
The document discusses intra-disciplinary approaches to teaching and learning. It defines intra-disciplinary as occurring within a single subject area or discipline. An intra-disciplinary approach fully integrates the knowledge and skills within a subject area from one grade to the next. It respects the conceptual structures and methods of inquiry of the subject. Teachers using this approach focus on big ideas and learning outcomes rather than isolated facts, helping students find personal meaning and relevance.