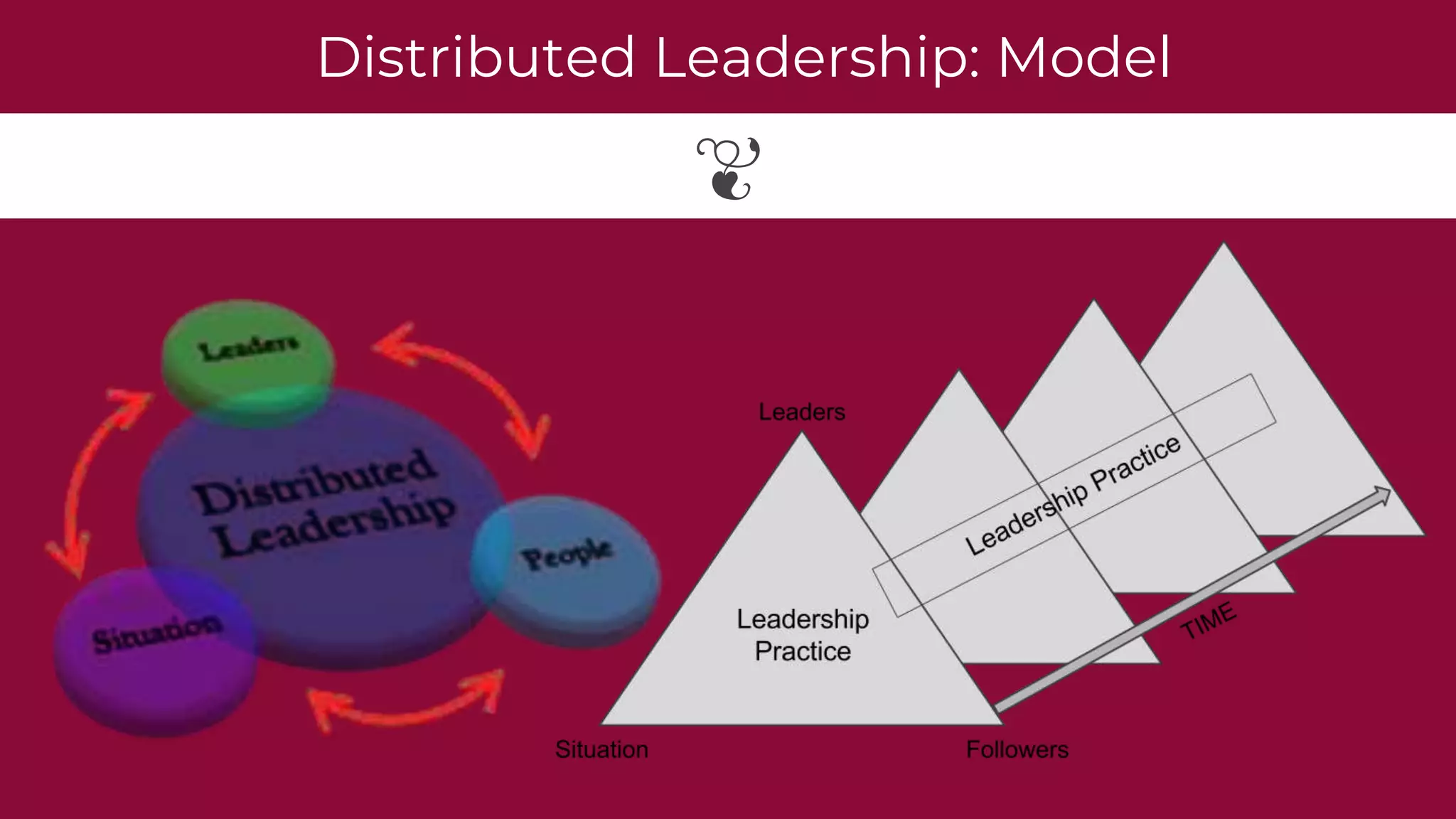
The document discusses distributed leadership, emphasizing its role in increasing leadership capacity within organizations, particularly in education. It outlines various leadership types and theories, highlighting the advantages and disadvantages of distributed leadership, such as enhanced ownership and accountability challenges. Examples illustrate its application in different contexts, showcasing its effectiveness and complexities.