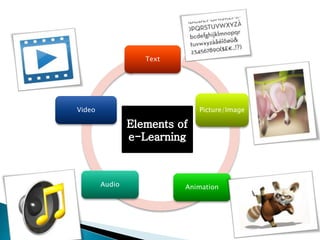
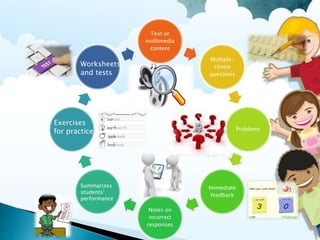
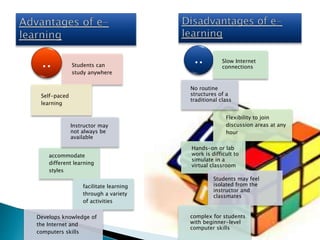
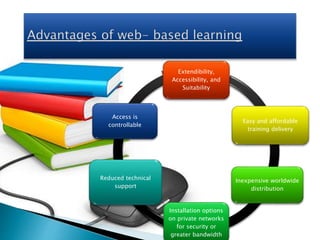
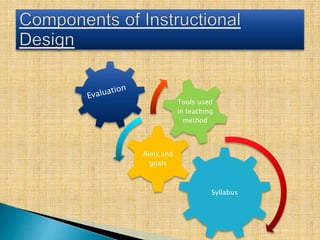
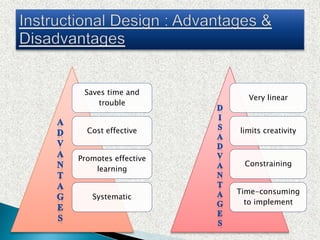
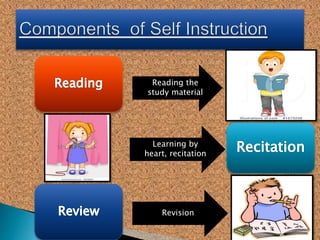
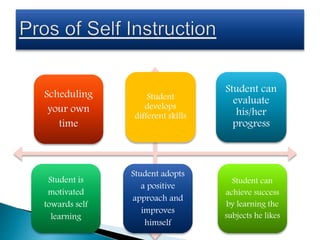
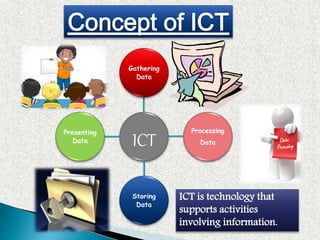
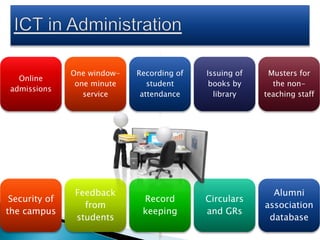
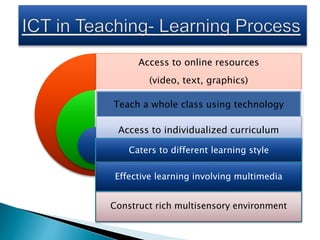
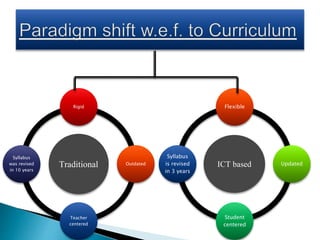
This document provides information on various aspects of using information and communication technology (ICT) in education. It discusses how ICT can be used to support activities involving information gathering, data processing, data storage, and data presentation. It also outlines several ways ICT can enhance teaching and learning, such as providing access to online resources, catering to different learning styles, and enabling new forms of instruction like video conferencing. Both benefits and challenges of ICT-based and traditional education methods are presented.





![Fixed space
Inside class wall
Traditional
Classroom
Multipurpose space
Inter-connected lab
(E-LAB)
Modern
Classroom
Learner’s participation
is less practical
Time constraint
learning
Isolated work
Learner’s participation
is more practical
Learning occurs
anywhere
Collaborative
work
Que by students:
1] how does it work?
Que by students:
1] How do I build it?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ict-conceptmapping-151123094131-lva1-app6892/85/ICT-concept-mapping-11-320.jpg)