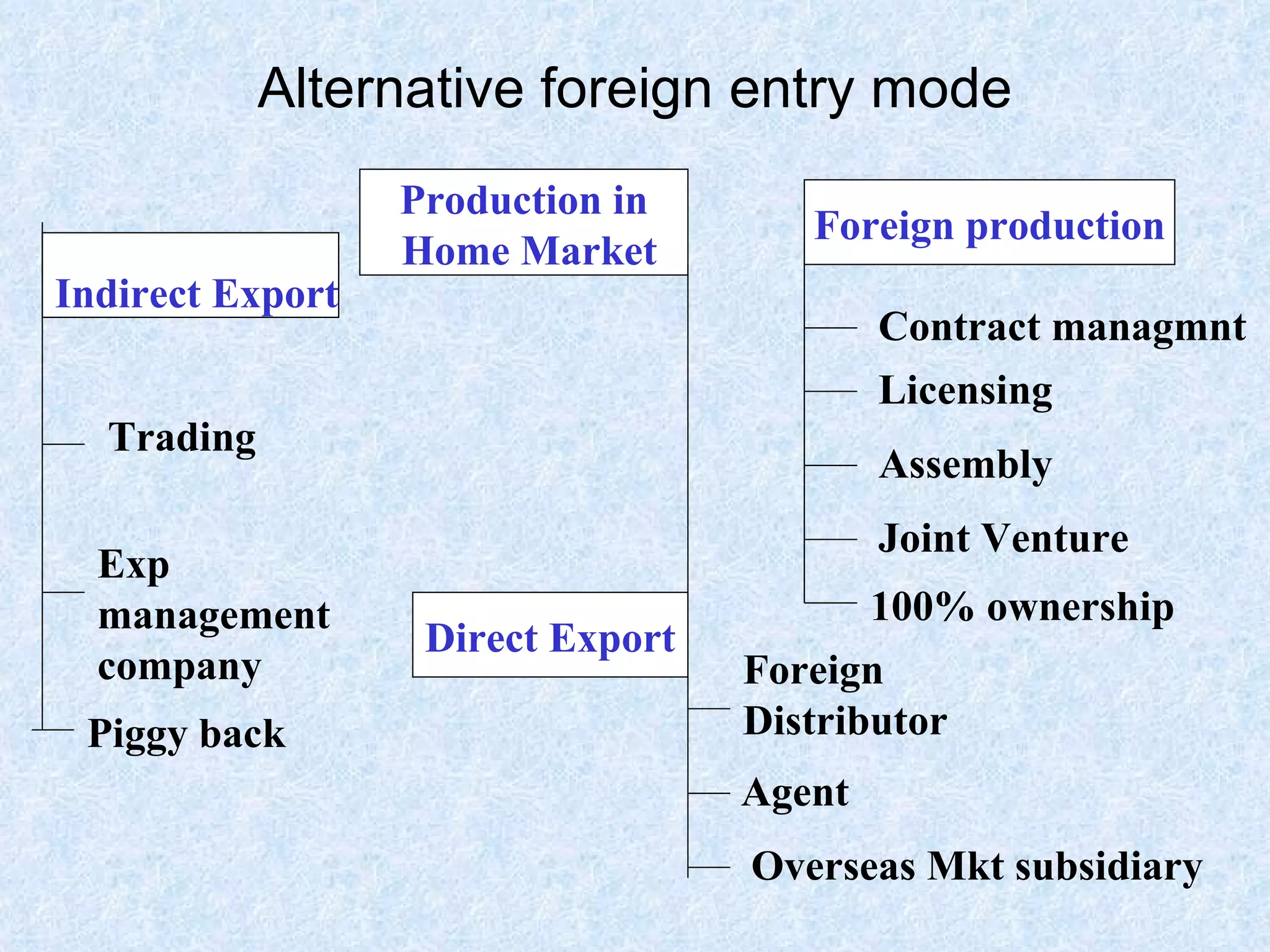
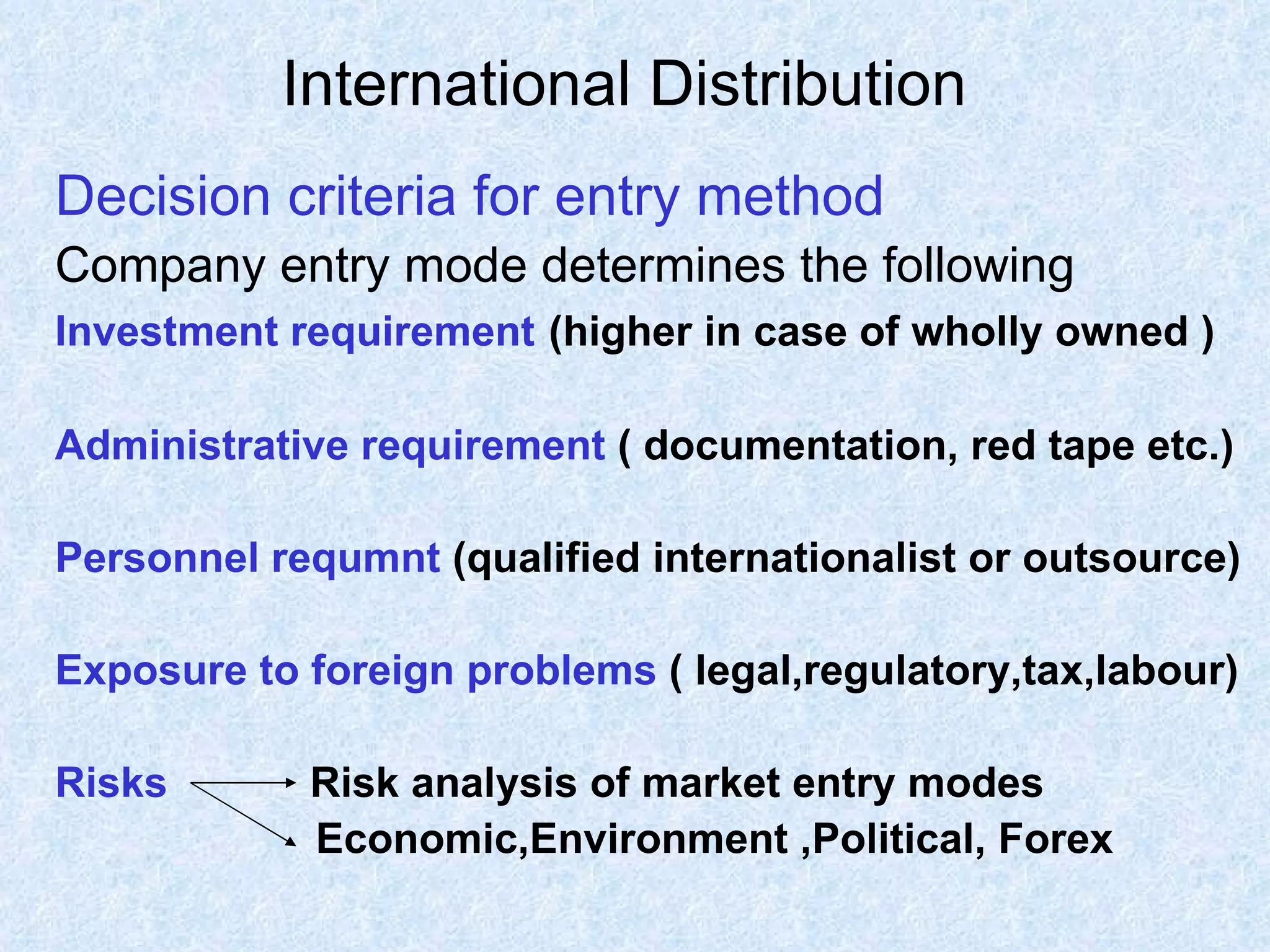
There are various methods for distributing products internationally once they reach a foreign market. These include using trading companies, export management companies, foreign distributors, or establishing a direct foreign presence through subsidiaries or wholly owned operations. The optimal distribution channel depends on factors like a firm's goals, resources, products, and the regulations and infrastructure of the target foreign market. Managing international logistics grows more complex with requirements for documentation, transportation, and navigating differences between multiple national markets. Facilities like freight forwarders and free trade zones can help address some challenges of cross-border physical distribution.