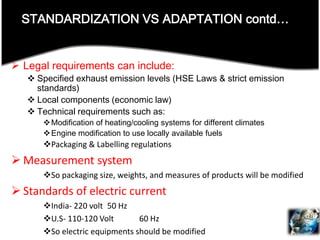
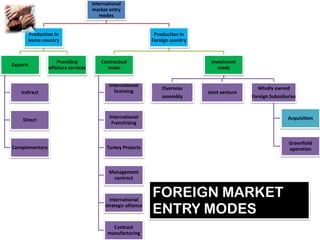
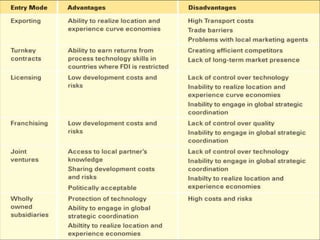
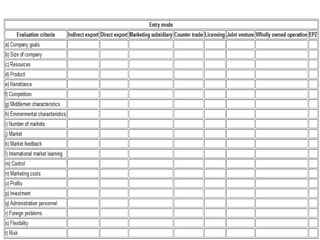
This document discusses international entry modes for businesses considering global expansion, detailing criteria for country selection and various strategies for entering foreign markets. It examines both proactive and reactive motivations for firms to venture abroad, explores product adaptation versus standardization, and outlines specific entry mechanisms such as exporting, licensing, and joint ventures. Additionally, it highlights the importance of understanding market conditions and cultural differences in successful international business approaches.