There are five main international entry modes: exporting, intermediate entry modes (contract manufacturing, licensing, franchising, strategic alliances), and hierarchical entry modes (sales subsidiaries, production subsidiaries, regional centers, transnational organizations).
Exporting can be direct or indirect through intermediaries like agents, distributors, trading companies. Intermediate entry modes involve partnerships and allow firms to gain resources without large investments. Licensing and franchising provide rights to use intellectual property. Strategic alliances share risks and costs.
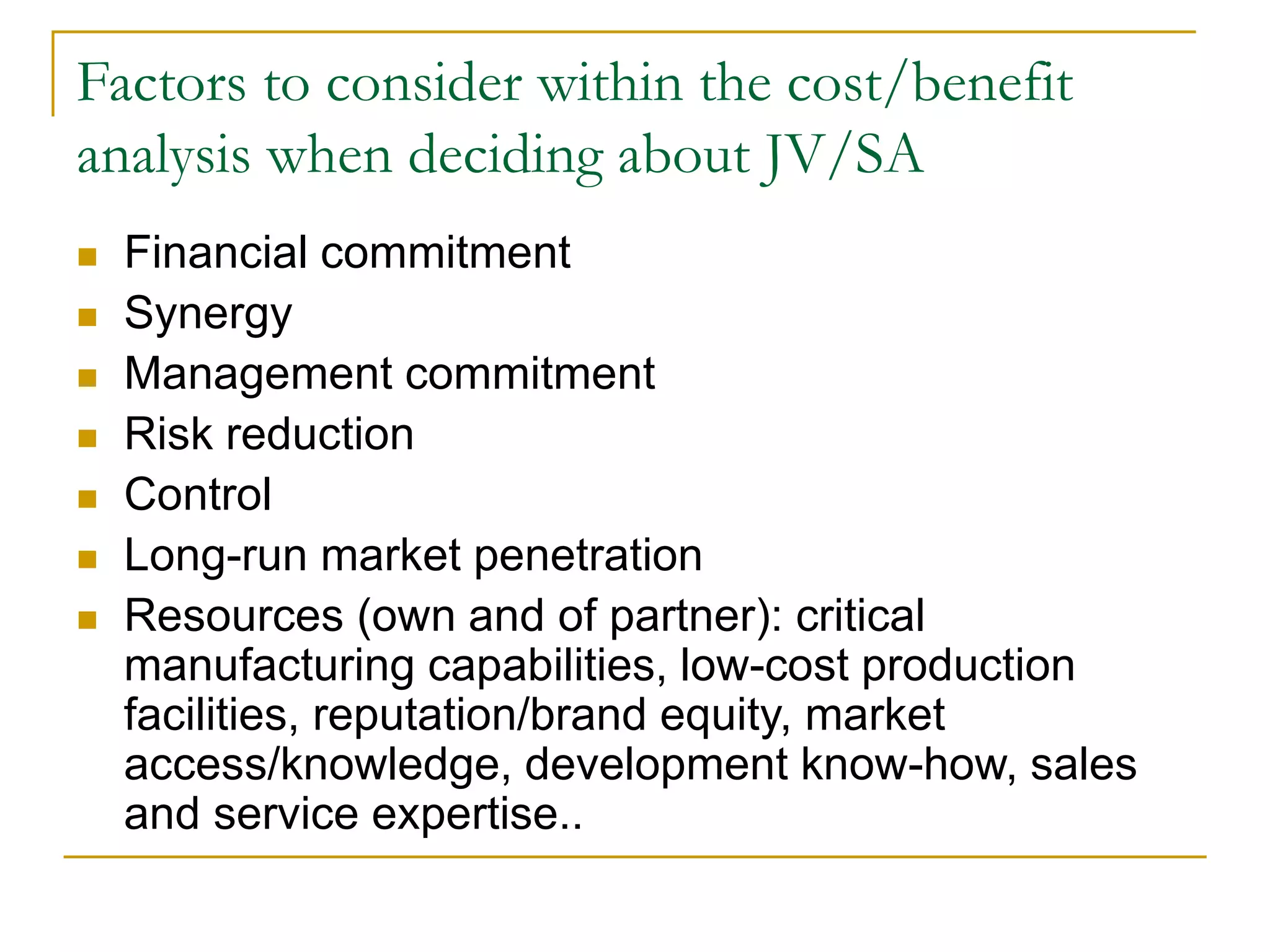
Hierarchical entry modes give more control through wholly owned subsidiaries operating locally. The choice of entry mode depends on factors like resources, risks, costs, market needs, and level of control required.