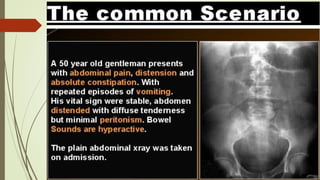
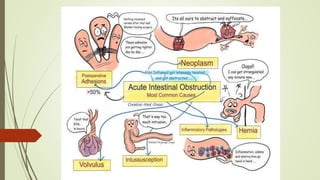
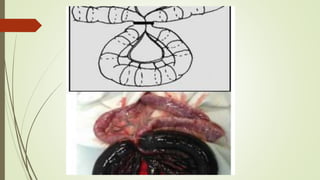
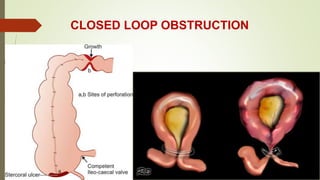
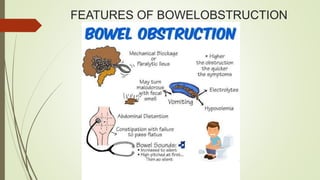
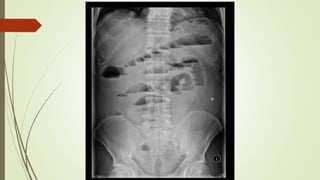
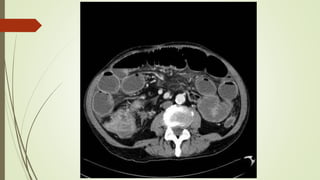
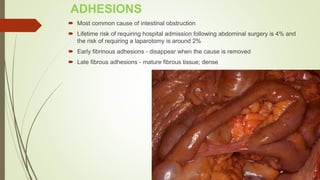
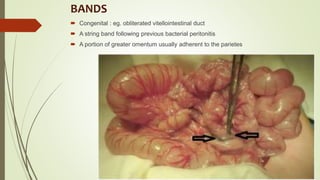
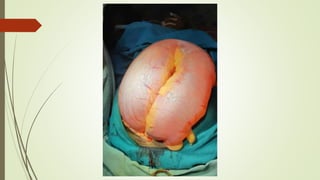
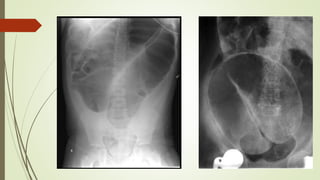
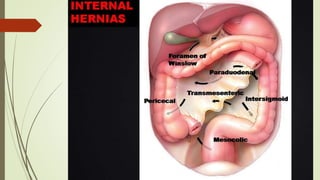
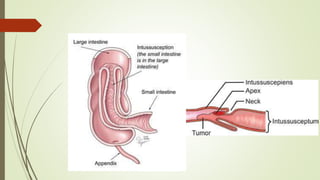
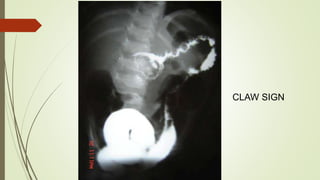
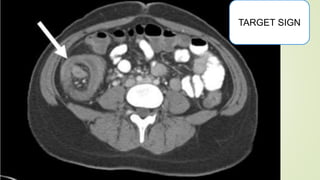
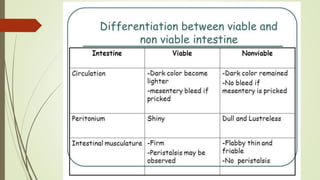
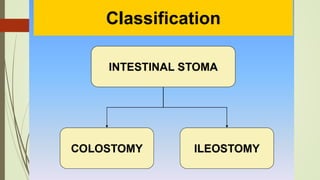
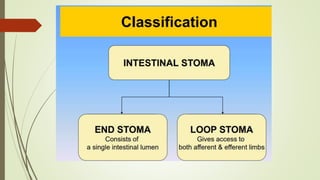
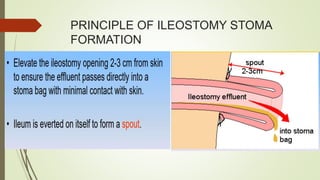
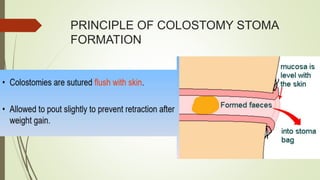
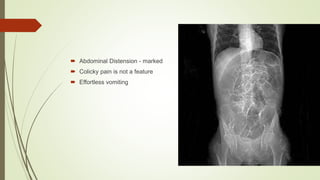
Intestinal obstruction occurs when there is a partial or complete blockage of the small or large intestine, interrupting the normal flow of intestinal contents. Causes include adhesions, bands, hernias, volvulus, tumors, and gallstones. Symptoms depend on the cause and location of the obstruction. Imaging studies like plain x-rays can show signs of obstruction like dilated bowel loops and air-fluid levels. Management involves treating the underlying cause, decompressing the bowel, providing IV fluids and electrolytes, and surgery if conservative measures fail or if the bowel is nonviable. Surgical options include resection of nonviable bowel and anastomoses.