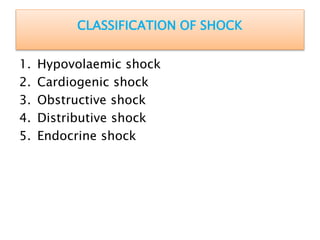
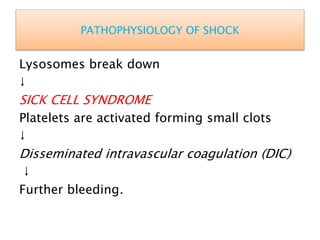
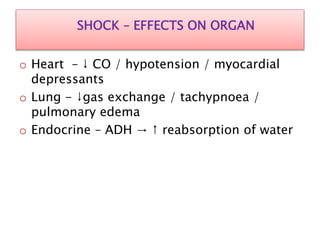
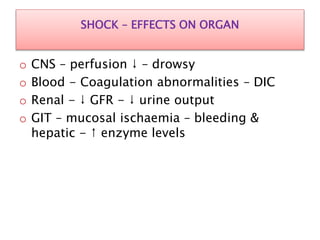
Shock is defined as inadequate tissue perfusion and oxygenation. There are five main types of shock: hypovolemic, cardiogenic, obstructive, distributive, and endocrine. Shock causes a decrease in cardiac output, vasoconstriction, and activation of stress responses in an attempt to maintain perfusion to vital organs. If shock persists, cellular damage occurs due to hypoxia, acidosis, and organ dysfunction. Treatment focuses on restoring circulating volume and oxygen delivery through fluid resuscitation, vasopressors, and inotropes while addressing the underlying cause. Septic shock involves an inflammatory response to infection that can lead to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome if not promptly treated with antibiotics and circulatory