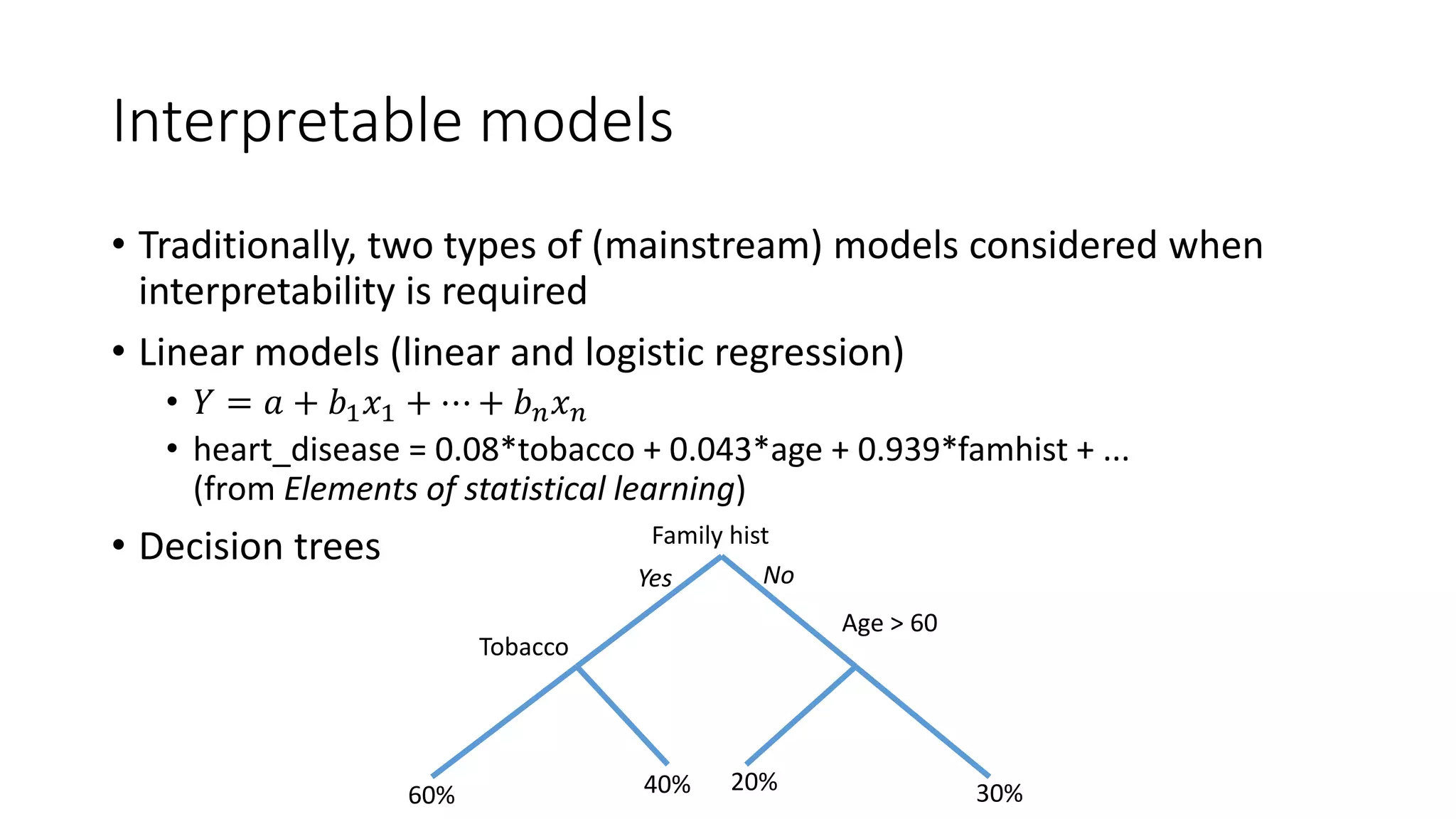
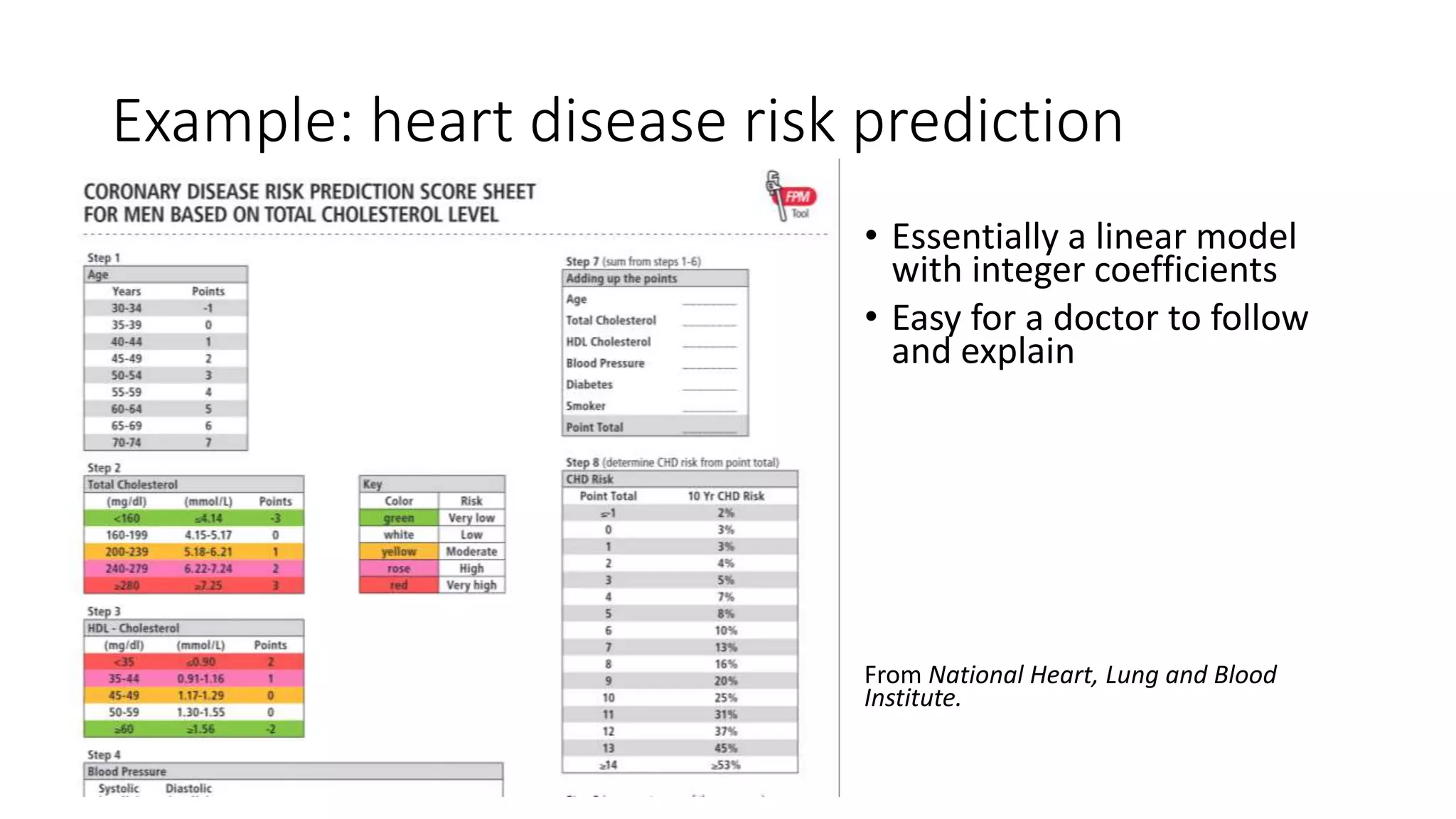
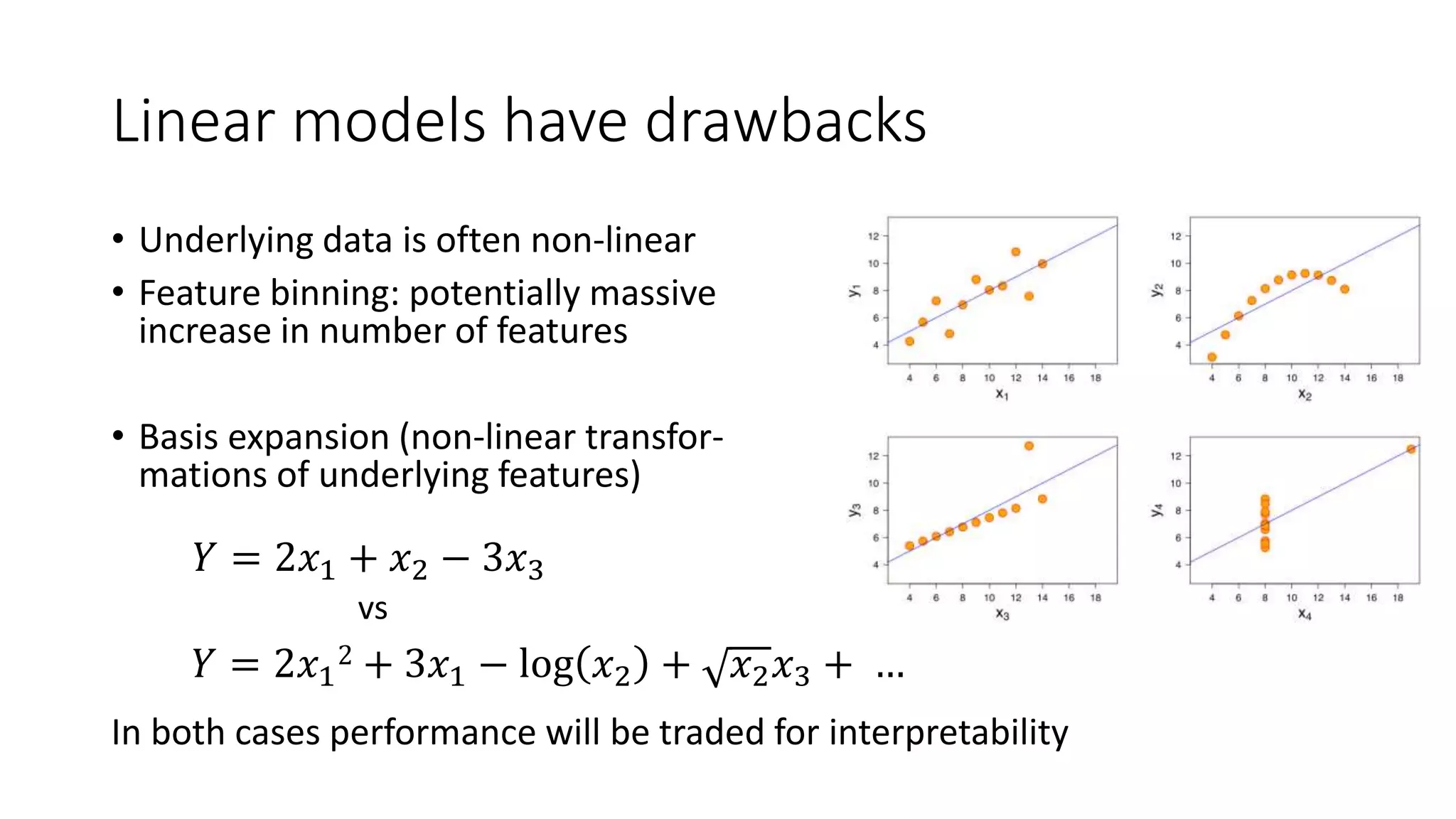
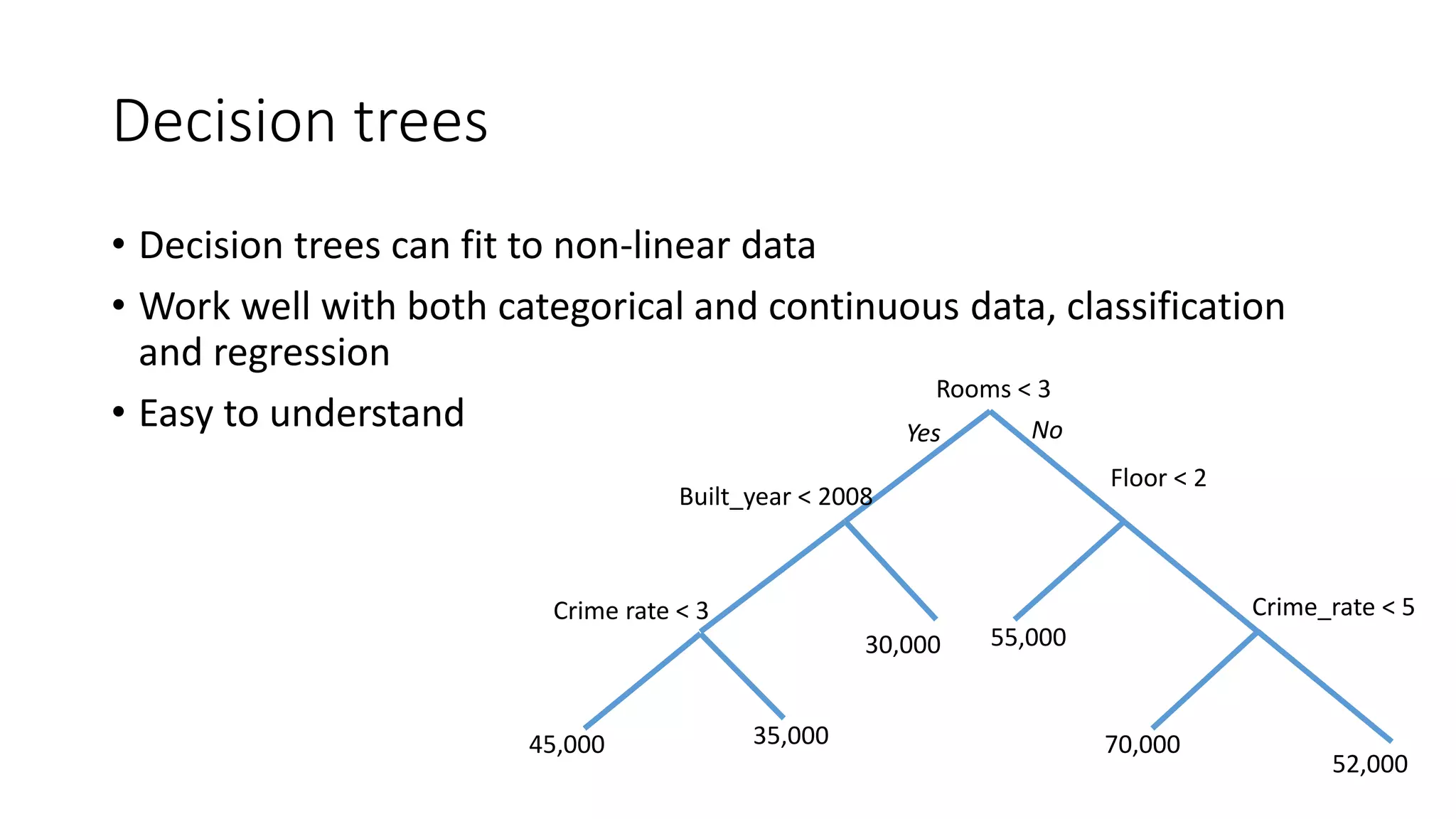
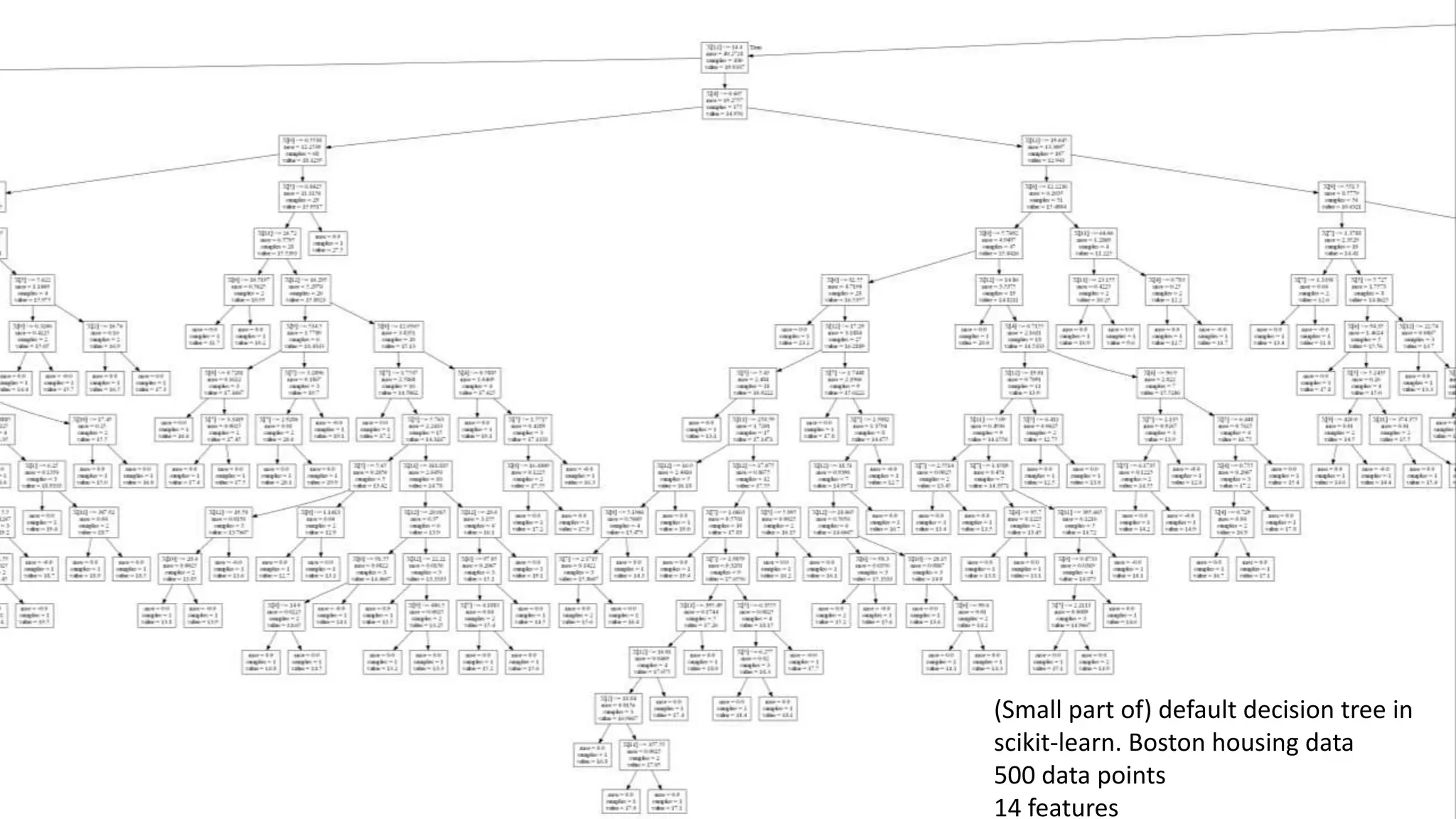
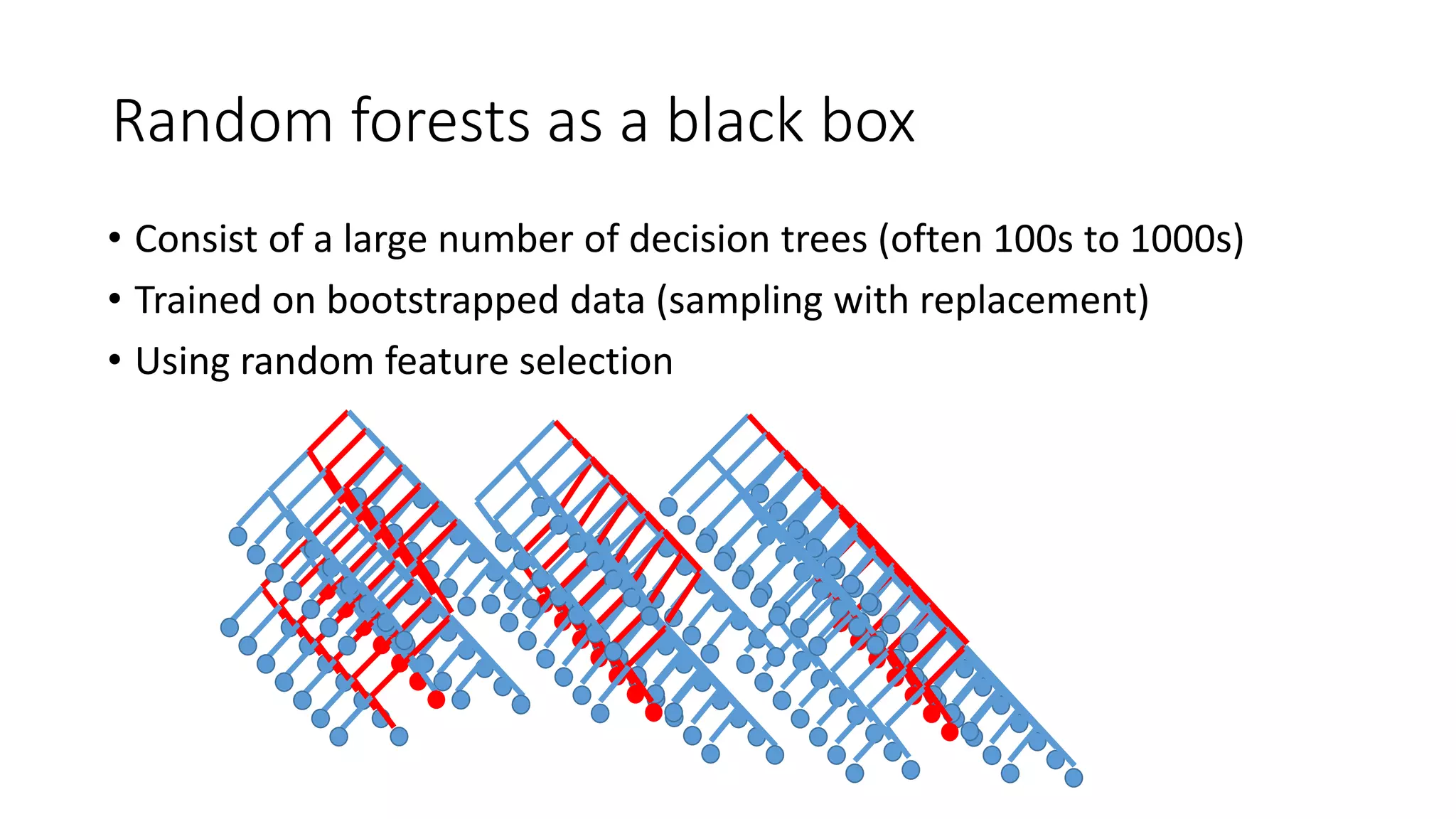
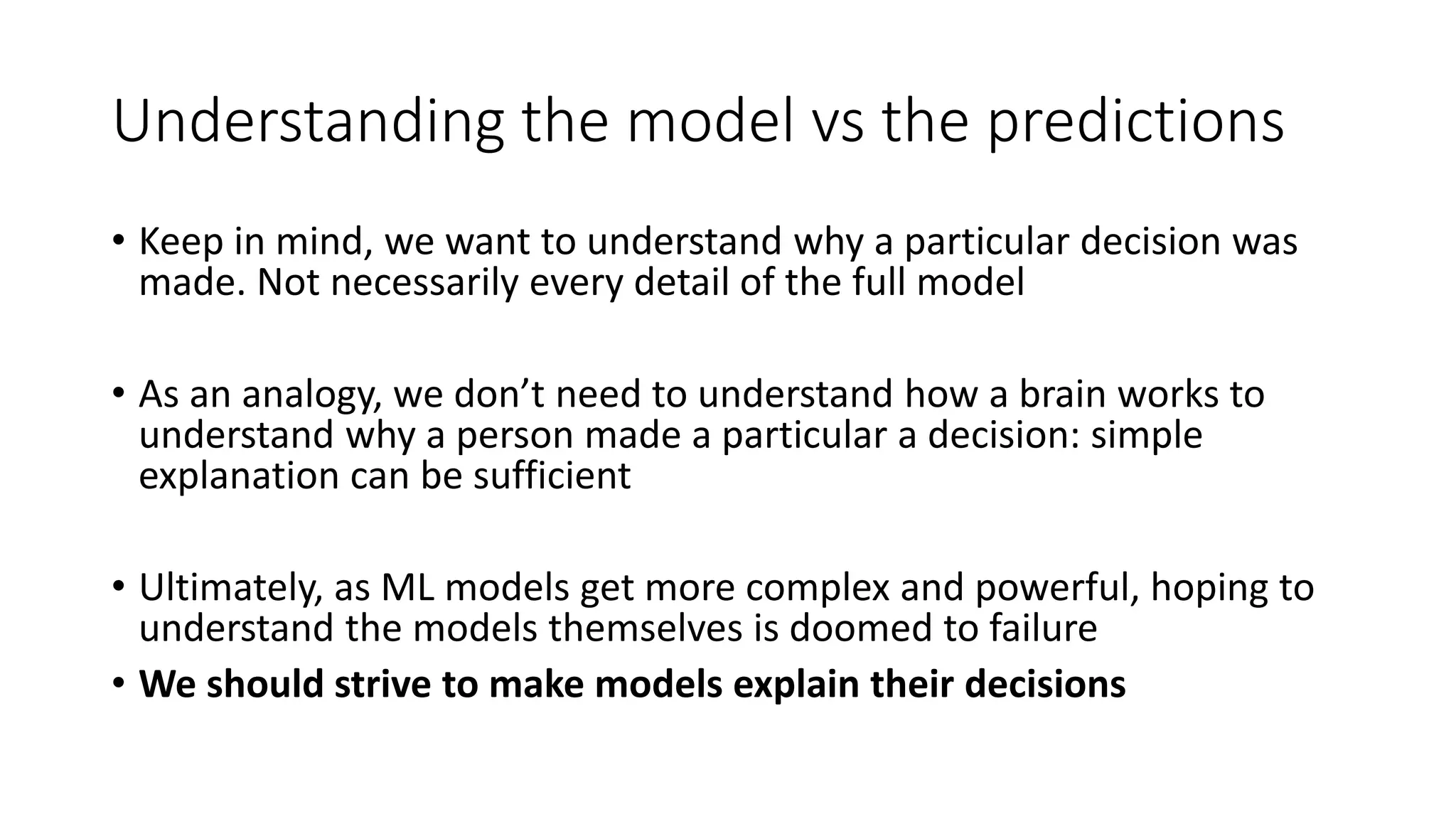
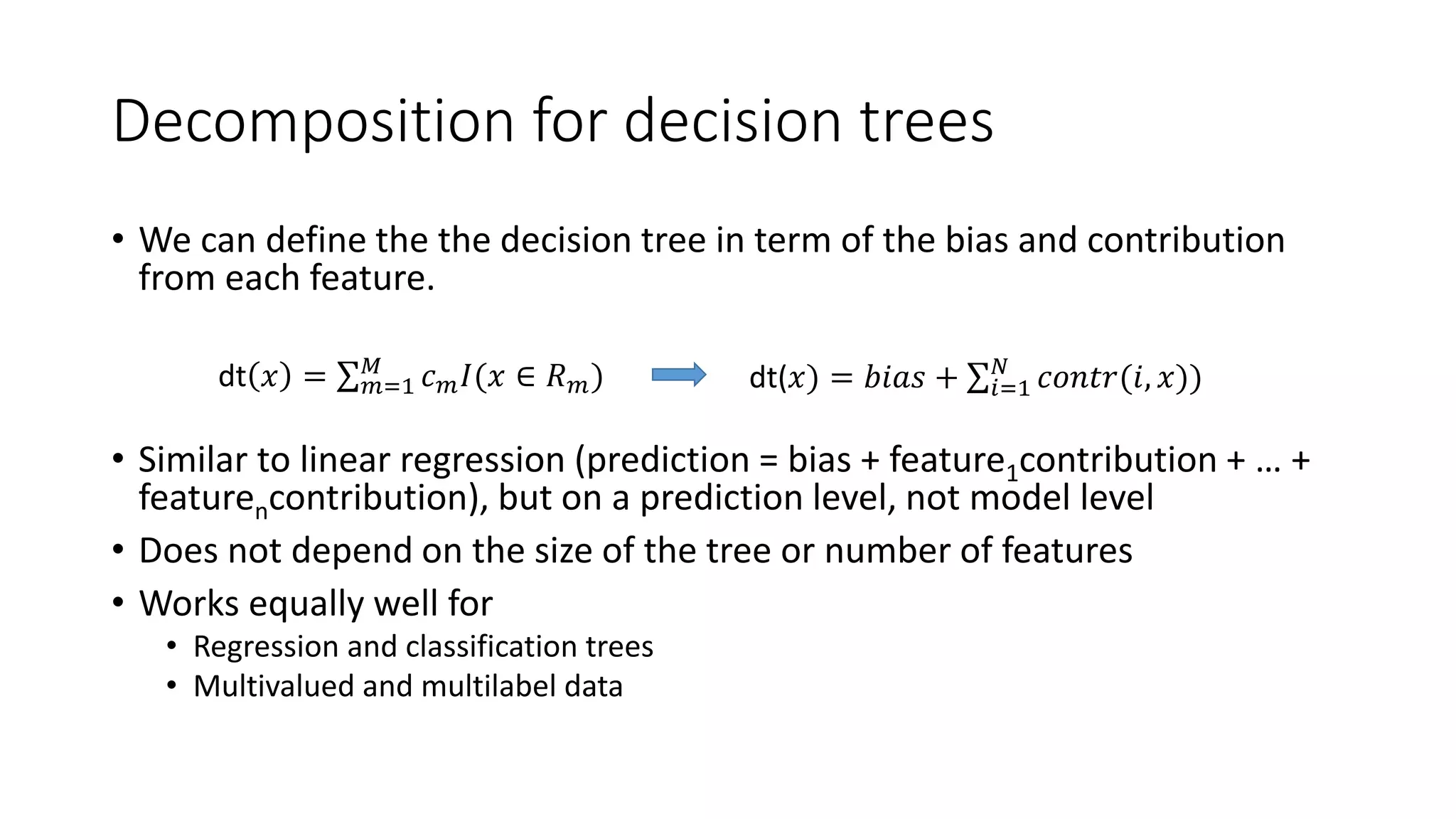
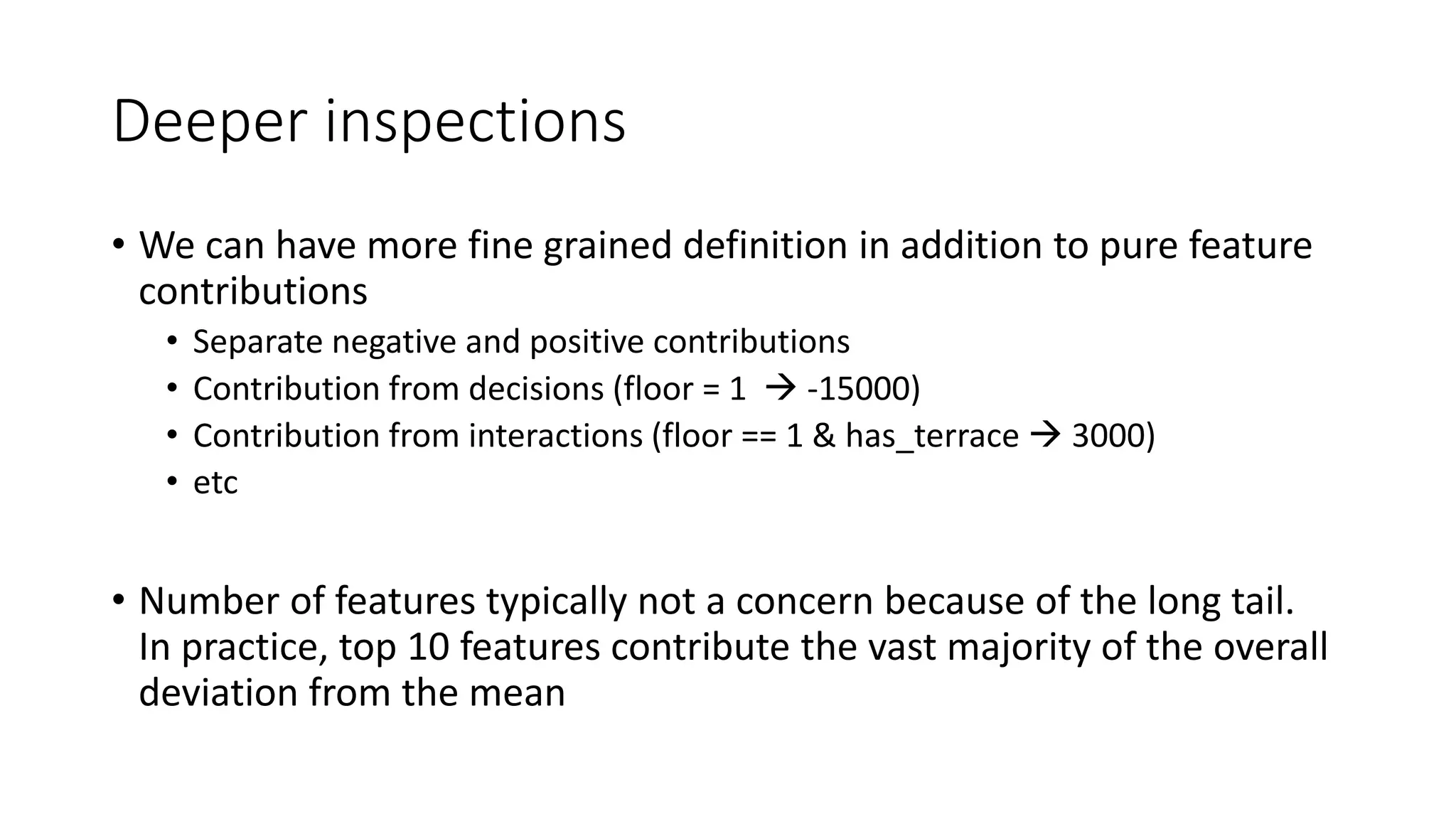
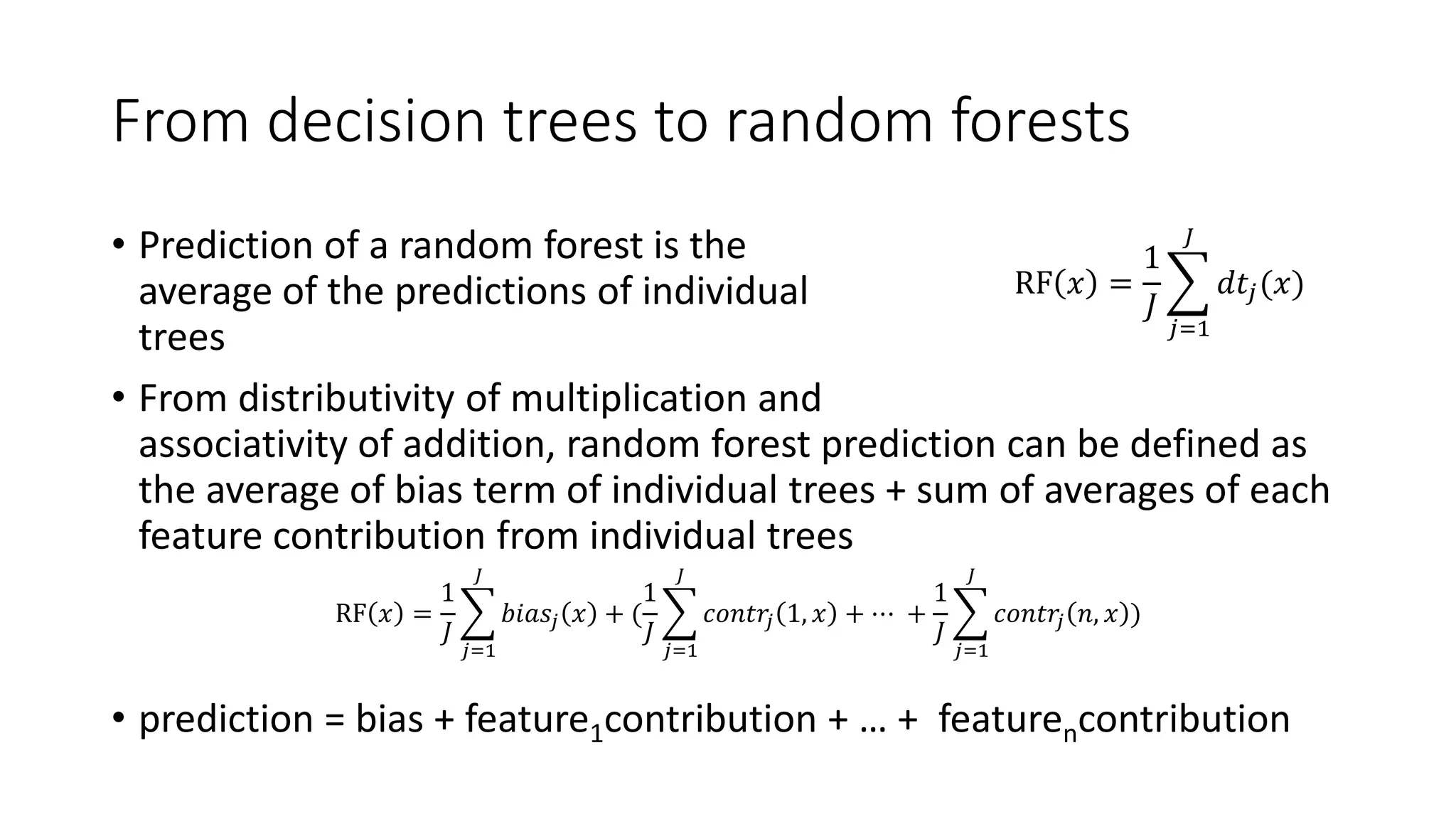
This document discusses interpreting machine learning models and summarizes techniques for interpreting random forests. Random forests are considered "black boxes" due to their complexity but their predictions can be explained by decomposing them into mathematically exact feature contributions. Decision trees can also be interpreted by defining the prediction as a bias plus the contributions from each feature along the decision path. This operational view of decision trees can be extended to interpret random forest predictions despite their complexity.









![Estimating apartment prices
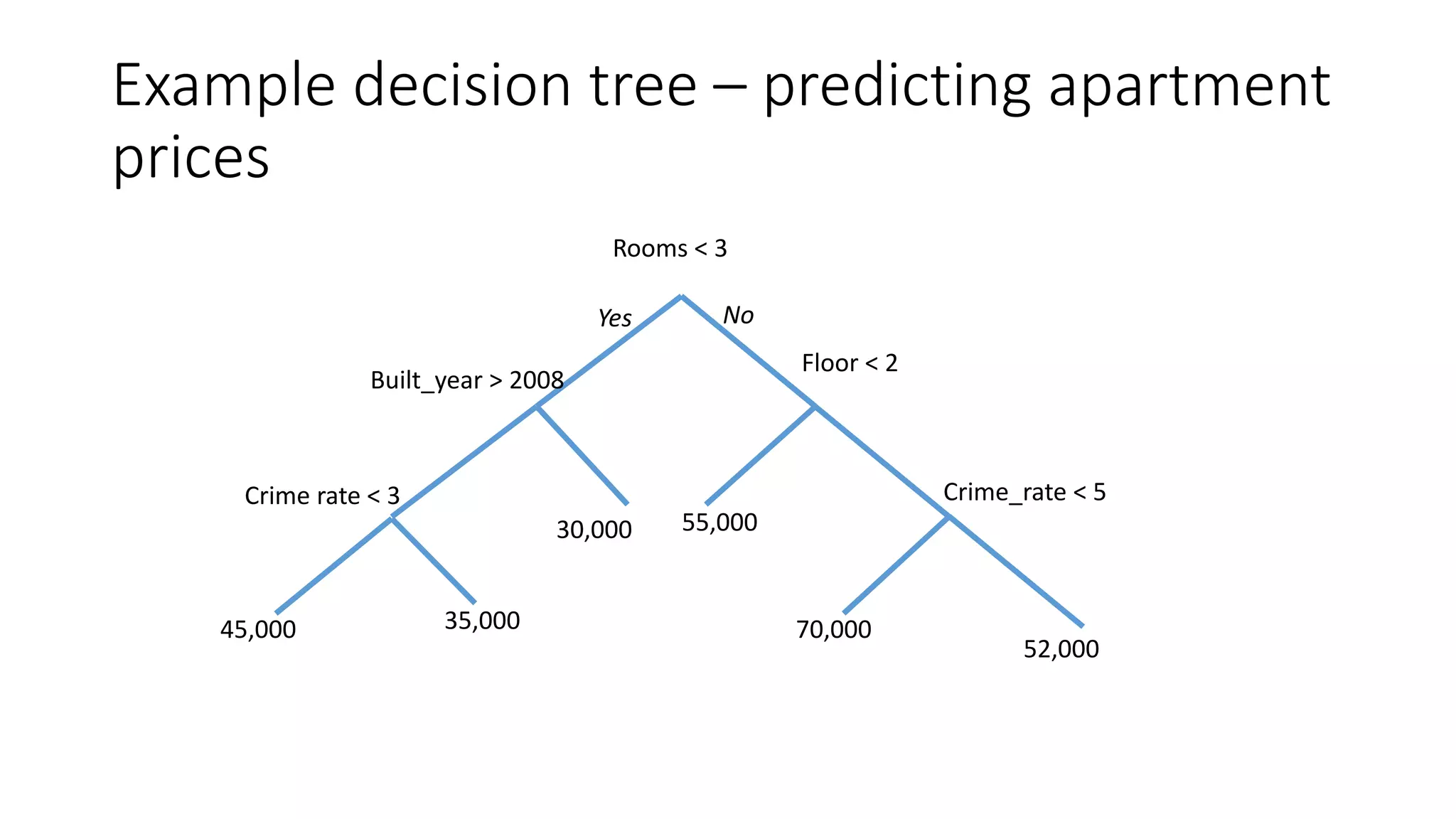
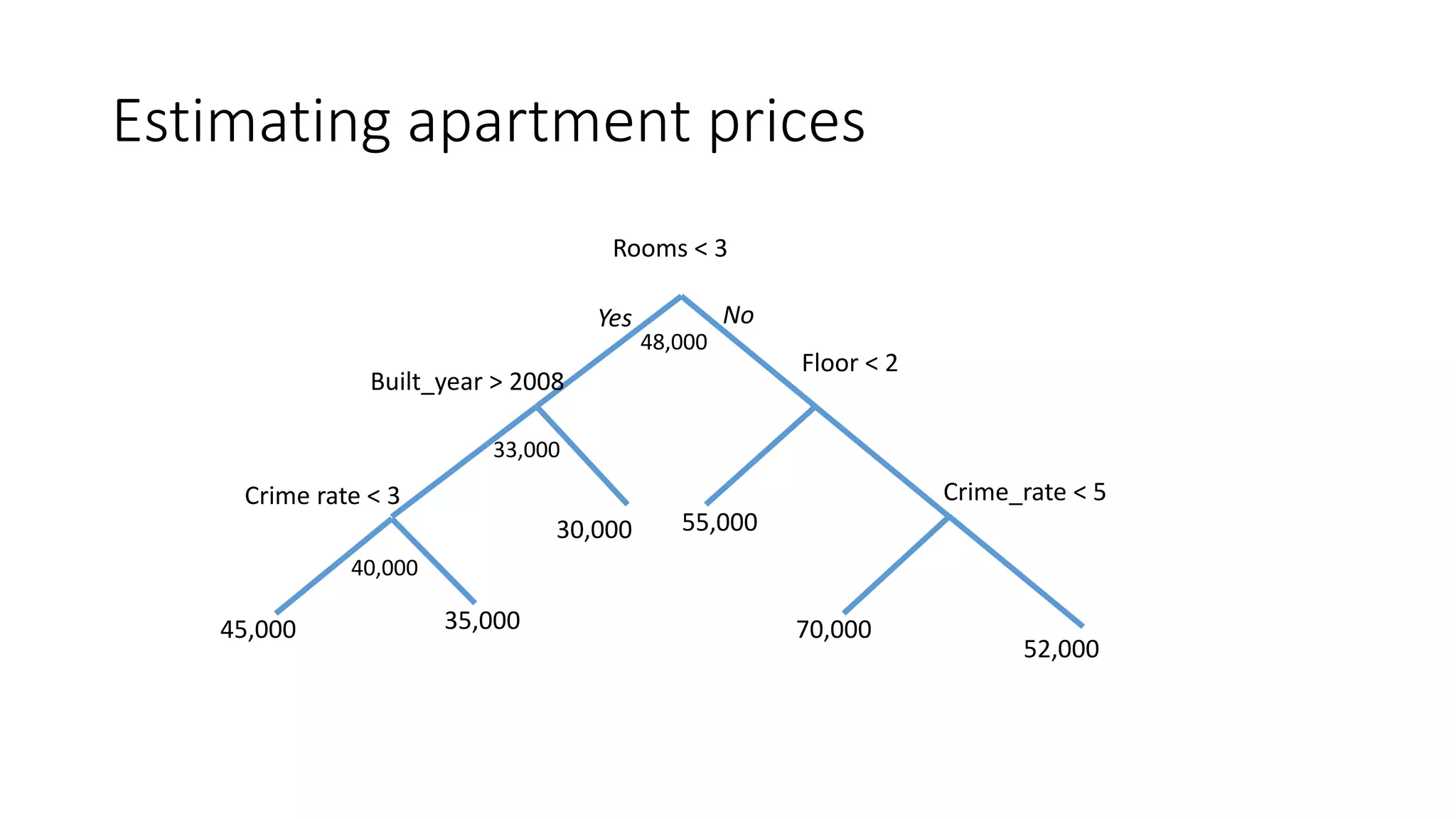
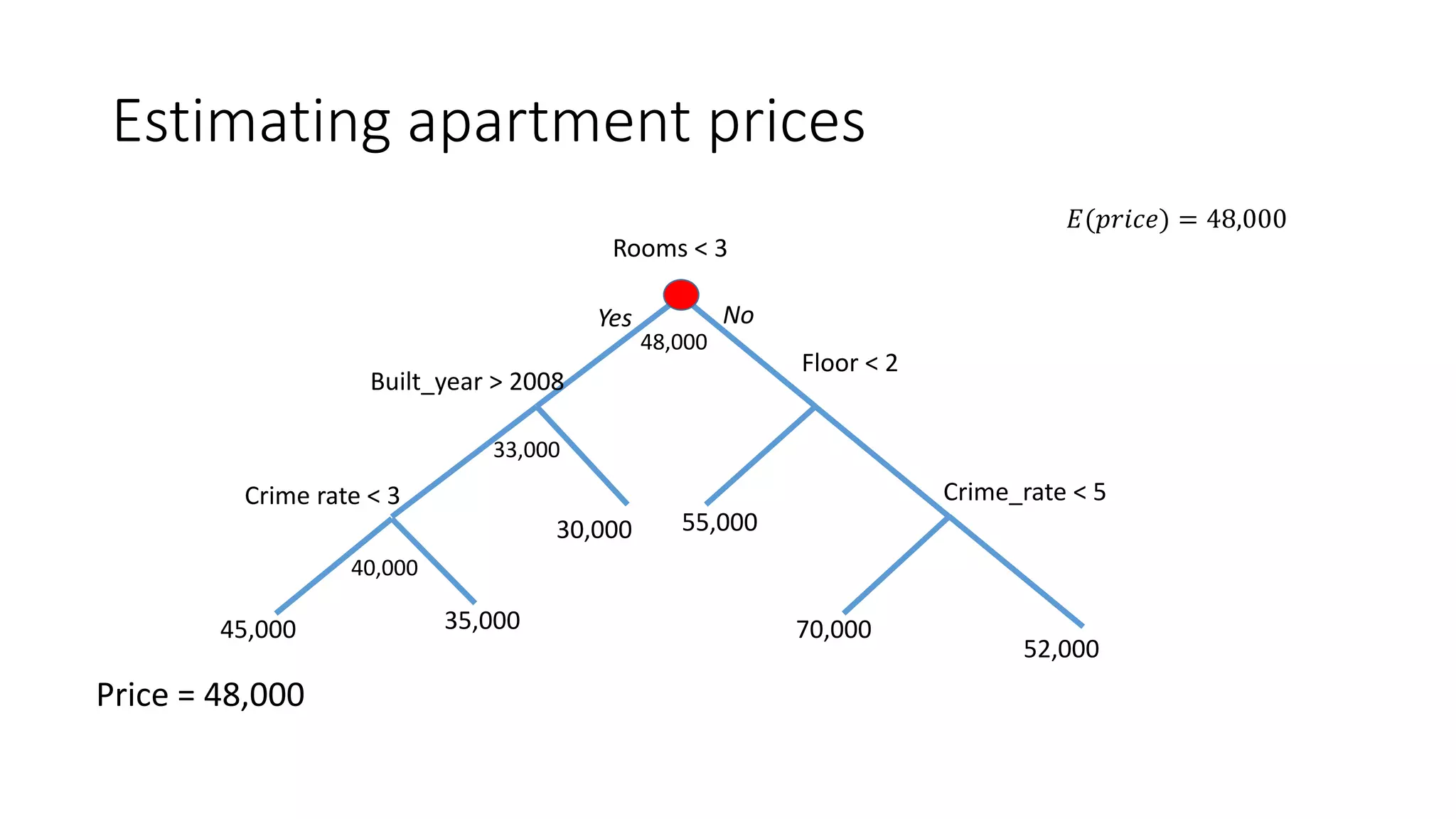
Assume an apartment [2 rooms; Built in 2010; Neighborhood crime rate: 5]
We walk the tree to obtain the price
Rooms < 3
Floor < 2
55,00030,000
70,000
52,000
Crime_rate < 5
Yes No
Crime rate < 3
35,00045,000
Built_year > 2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpretingmachinelearningmodels-151124213134-lva1-app6892/75/Interpreting-machine-learning-models-20-2048.jpg)
![Estimating apartment prices
[2 rooms; Built in 2010; Neighborhood crime rate: 5]
Rooms < 3
Floor < 2
55,00030,000
70,000
52,000
Crime_rate < 5
Yes No
Built_year > 2008
Crime rate < 3
35,00045,000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpretingmachinelearningmodels-151124213134-lva1-app6892/75/Interpreting-machine-learning-models-21-2048.jpg)
![Estimating apartment prices
[2 rooms; Built in 2010; Neighborhood crime rate: 5]
Rooms < 3
Floor < 2
55,00030,000
70,000
52,000
Crime_rate < 5
Yes No
Built_year > 2008
Crime rate < 3
35,00045,000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpretingmachinelearningmodels-151124213134-lva1-app6892/75/Interpreting-machine-learning-models-22-2048.jpg)
![Estimating apartment prices
Prediction: 35,000 Path taken: Rooms < 3, Built_year > 2008, Crime_rate < 3
[2 rooms; Built in 2010; Neighborhood crime rate: 5]
Rooms < 3
Floor < 2
55,00030,000
70,000
52,000
Crime_rate < 5Crime rate < 3
35,00045,000
Yes No
Built_year > 2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpretingmachinelearningmodels-151124213134-lva1-app6892/75/Interpreting-machine-learning-models-23-2048.jpg)

![Estimating apartment prices
[2 rooms]
Rooms < 3
Floor < 2
55,00030,000
70,000
52,000
Crime_rate < 5
Yes No
Built_year > 2008
Crime rate < 3
35,00045,000
48,000
33,000
40,000
Price = 48,000 – 15,000(Rooms)
𝐸(𝑝𝑟𝑖𝑐𝑒|𝑟𝑜𝑜𝑚𝑠 < 3) = 33,000](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpretingmachinelearningmodels-151124213134-lva1-app6892/75/Interpreting-machine-learning-models-27-2048.jpg)
![Estimating apartment prices
Rooms < 3
Floor < 2
55,00030,000
70,000
52,000
Crime_rate < 5
Yes No
Built_year > 2008
Crime rate < 3
35,00045,000
48,000
33,000
40,000
Price = 48,000 – 15,000(Rooms) + 7,000(Built_year)
[Built 2010]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpretingmachinelearningmodels-151124213134-lva1-app6892/75/Interpreting-machine-learning-models-28-2048.jpg)
![Estimating apartment prices
Rooms < 3
Floor < 2
55,00030,000
70,000
52,000
Crime_rate < 5
Built_year > 2008
Crime rate < 3
35,00045,000
48,000
33,000
40,000
Price = 48,000 – 15,000(Rooms) + 7,000(Built_year) – 5,000(Crime_rate)
[Crime rate 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpretingmachinelearningmodels-151124213134-lva1-app6892/75/Interpreting-machine-learning-models-29-2048.jpg)



![Decomposing a prediction – boston housing
data
prediction, bias, contributions = ti.predict(rf, boston.data)
>> prediction[0]
30.69
>> bias[0]
25.588
>> sorted(zip(contributions[0], boston.feature_names),
>> key=lambda x: -abs(x[0]))
[(4.3387165697195558, 'RM'),
(-1.0771391053864874, 'TAX'),
(1.0207116129073213, 'LSTAT'),
(0.38890774812797702, 'AGE'),
(0.38381481481481539, 'ZN'),
(-0.10397222222222205, 'CRIM'),
(-0.091520697167756987, 'NOX')
...](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/interpretingmachinelearningmodels-151124213134-lva1-app6892/75/Interpreting-machine-learning-models-36-2048.jpg)
