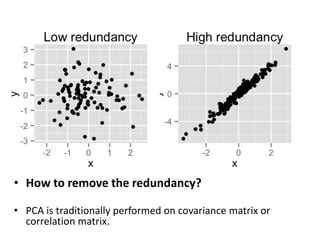
PCA is a dimensionality reduction technique that transforms a number of potentially correlated variables into a smaller number of uncorrelated variables called principal components. It works by geometrically projecting the data onto a lower dimensional space in a way that retains as much of the variation present in the original data as possible. PCA is widely used for applications like data visualization, feature extraction and dimensionality reduction. An example of using PCA in genetics is shown, where the variability in human DNA data can be strongly linked to geographical patterns through principal component analysis.