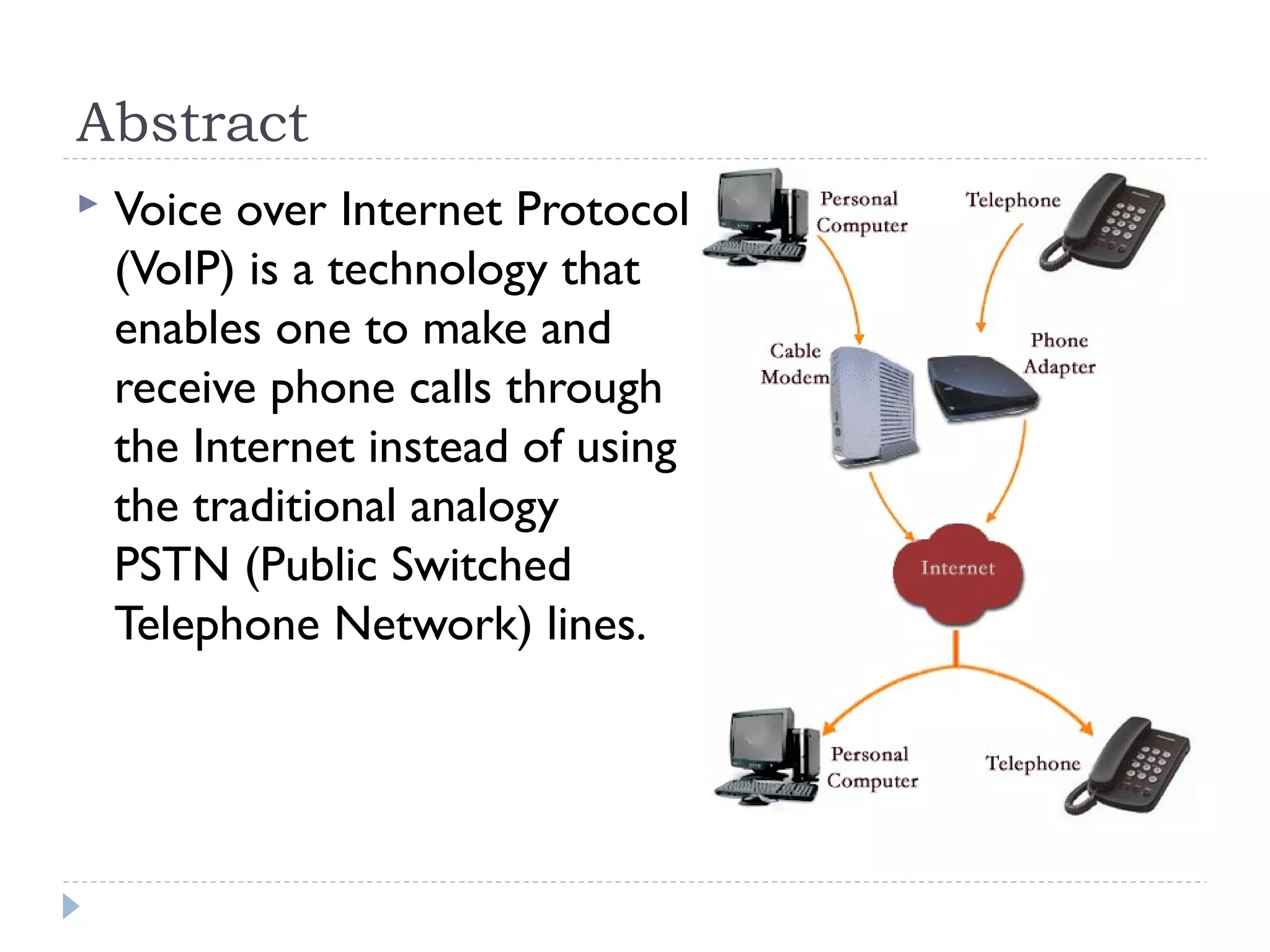
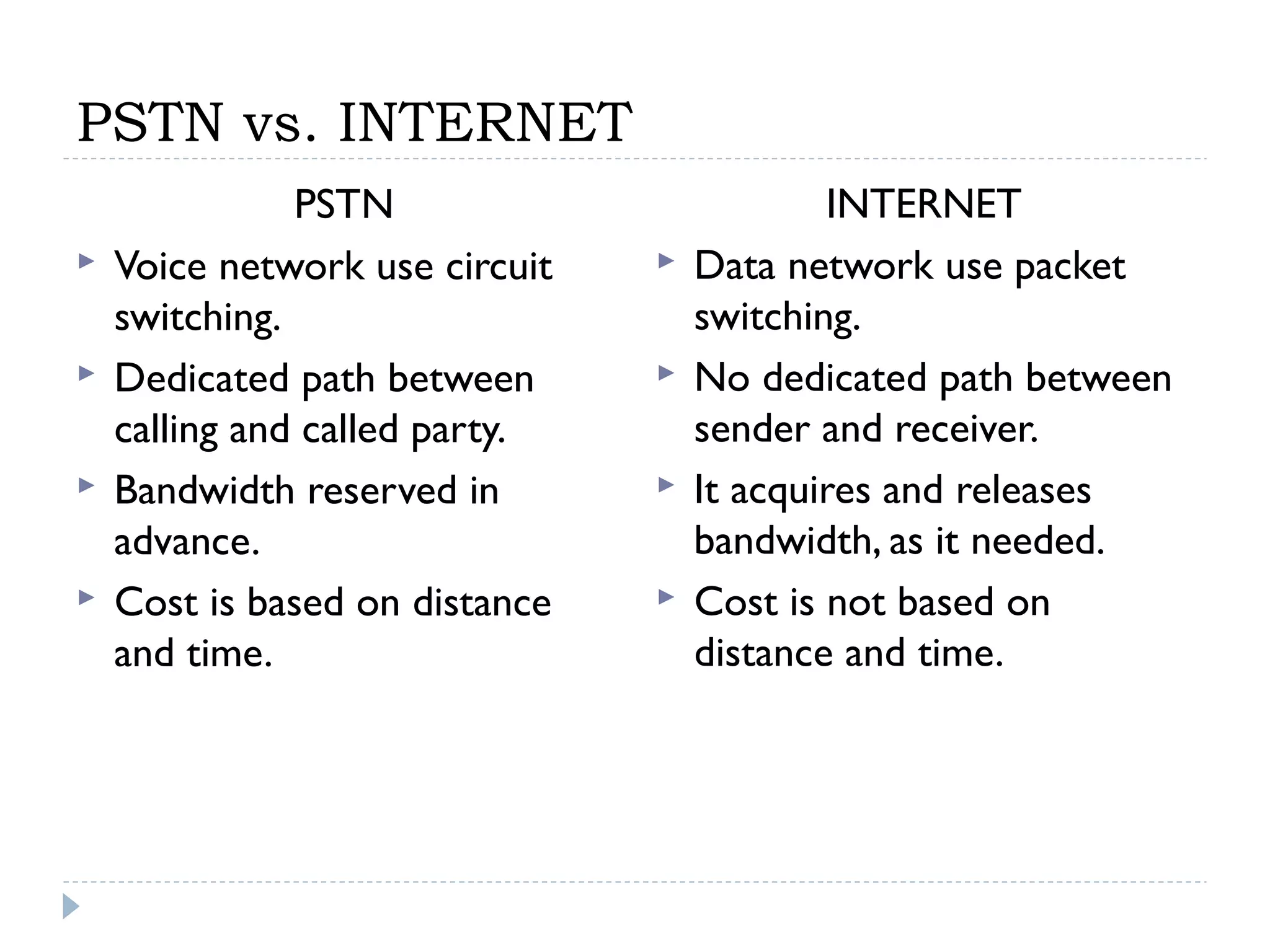
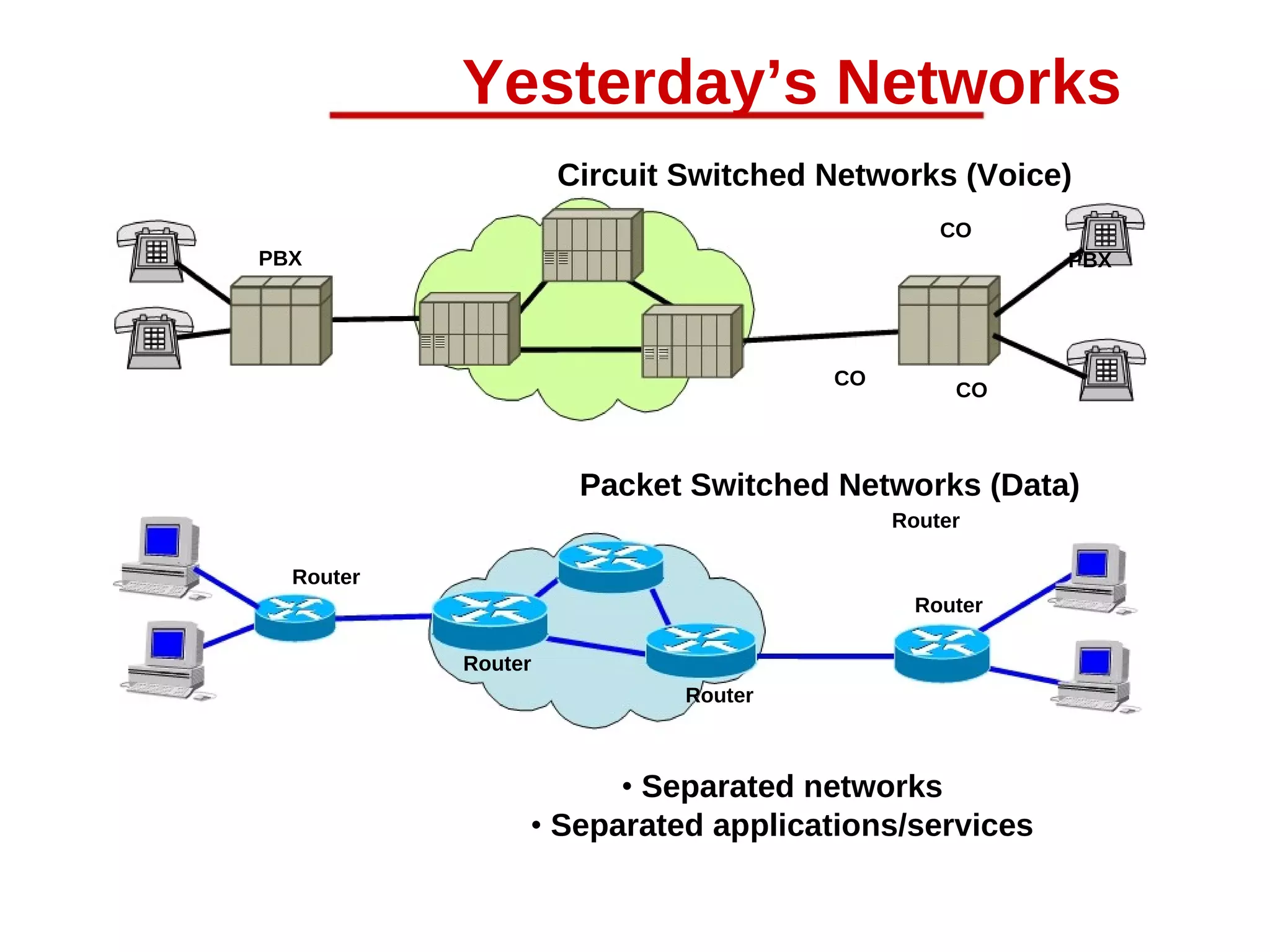
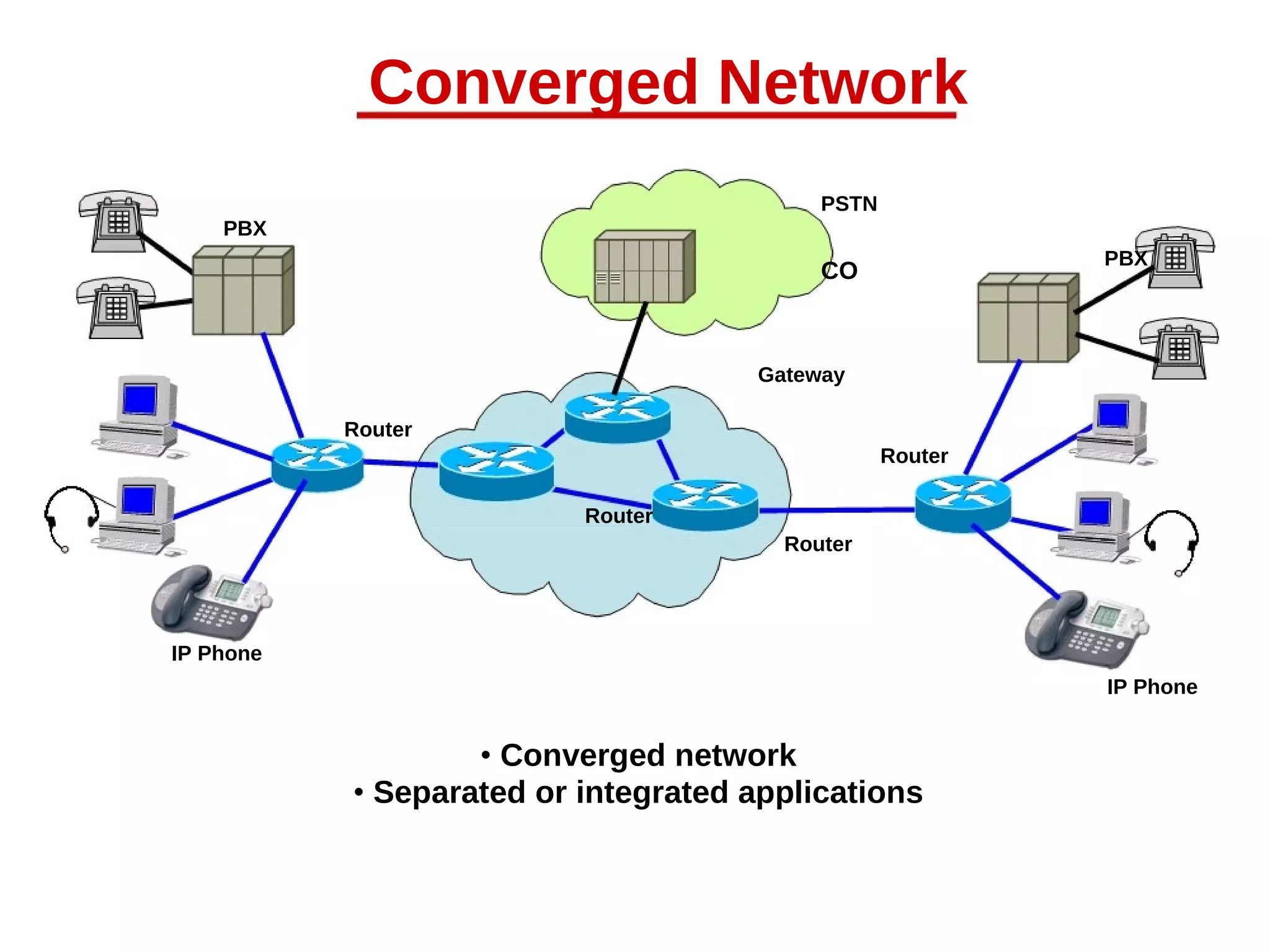
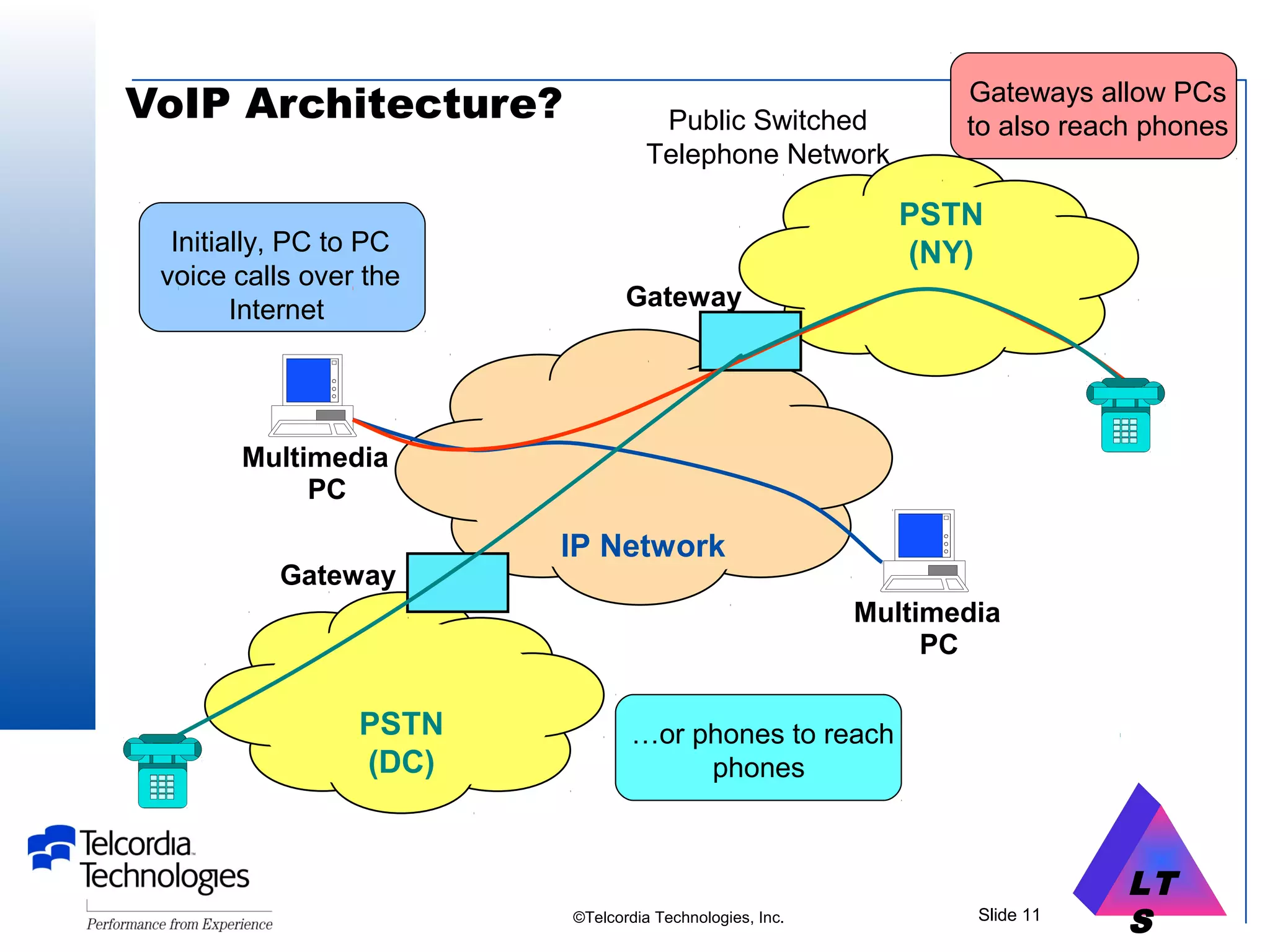
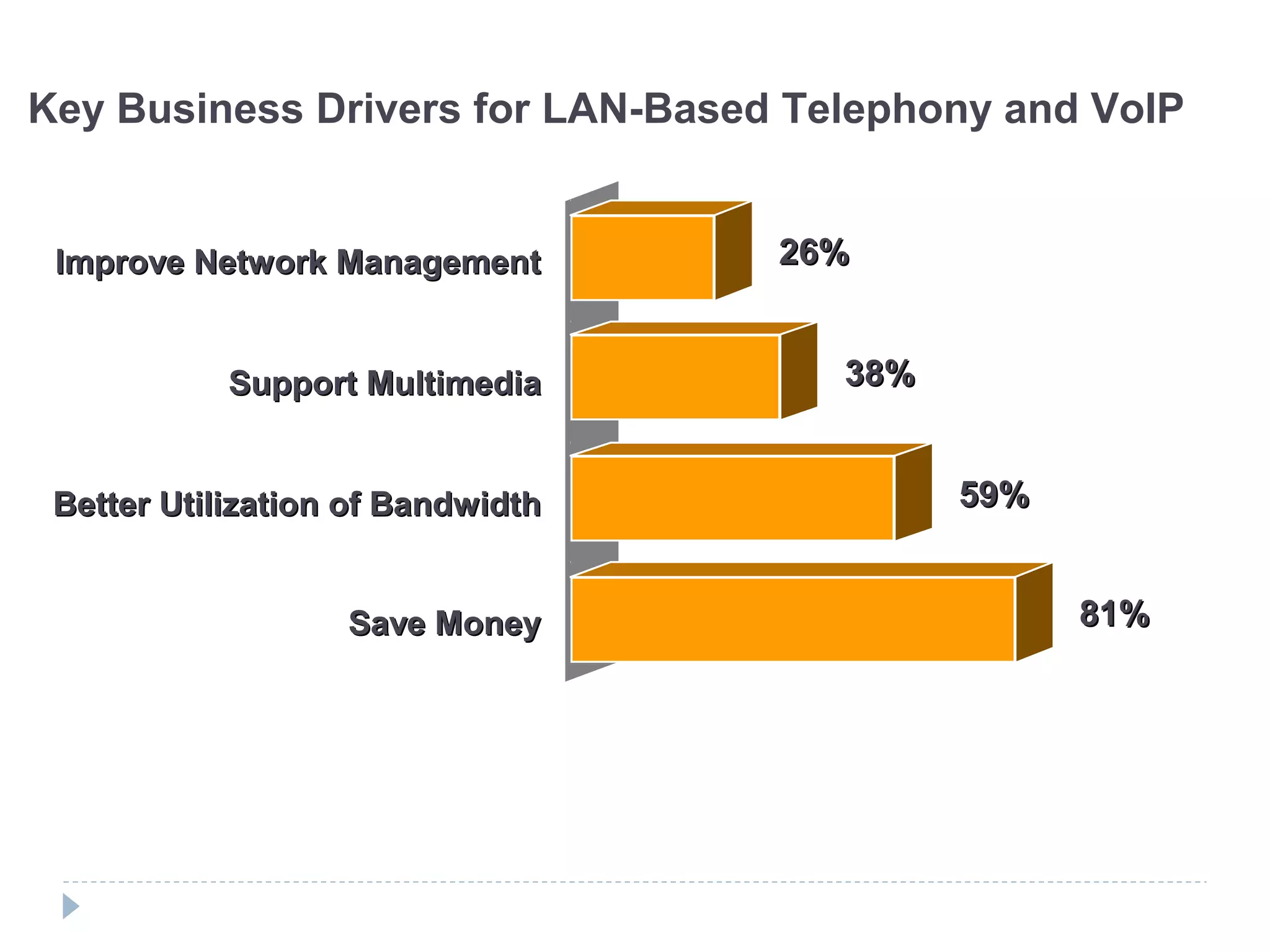
This document provides an overview of Voice over IP (VoIP) technology. It discusses how VoIP works by converting voice signals to digital packets and transmitting them over the Internet. The key components of a VoIP system include compression of the voice, encapsulation into IP packets, and routing through the network. Popular applications of VoIP include video chat programs and online gaming. The document also notes that many companies are interested in adopting VoIP to save costs and better utilize bandwidth. However, VoIP faces some security risks since it transmits voice over the public Internet.