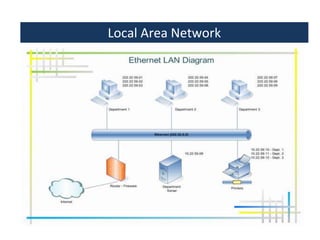
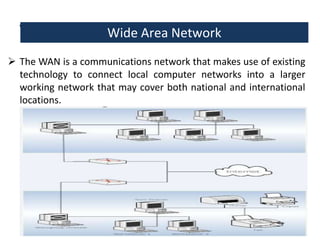
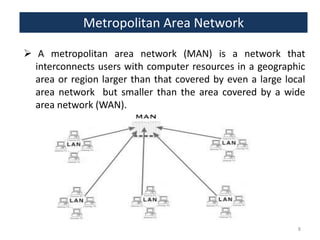
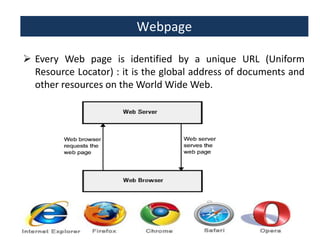
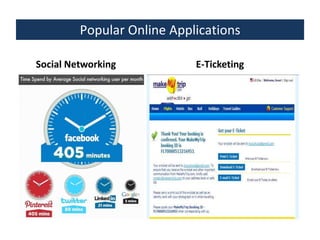
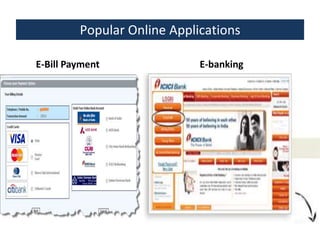
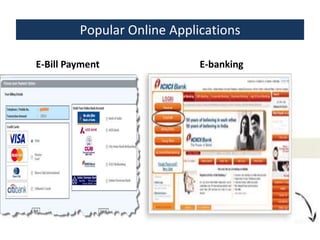
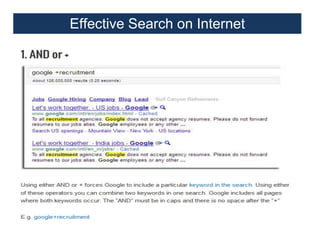
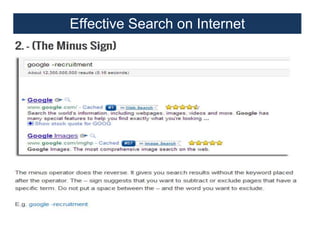
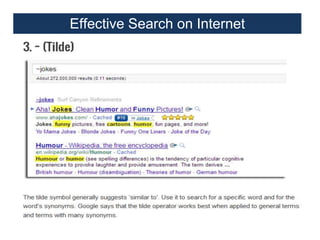
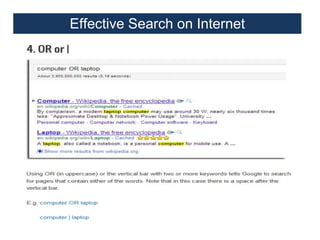
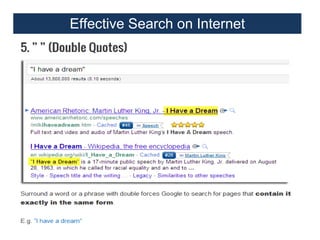
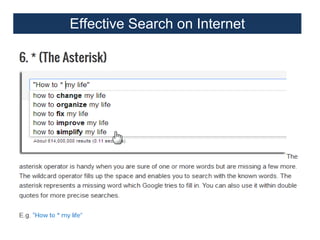
This document provides an overview of a foundation course on information technology. It covers topics such as networks, the internet, internet services, web pages, connecting to the internet, online applications, effects and threats of the internet, and ways to minimize ill effects. It also discusses information legal literacy, open source software, licenses, and popular open source programs.